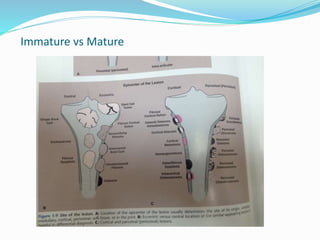
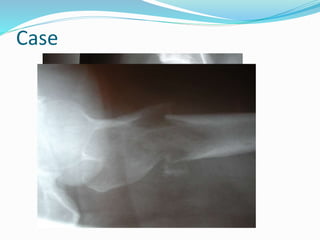
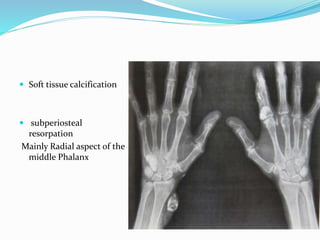
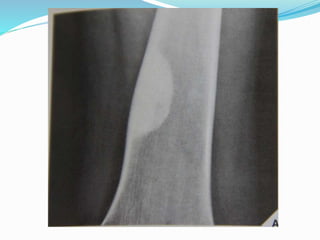
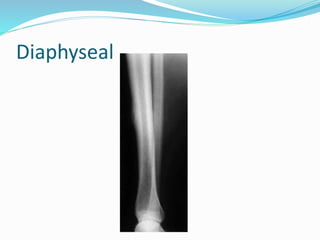
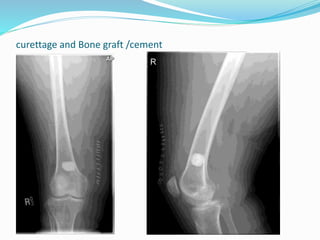
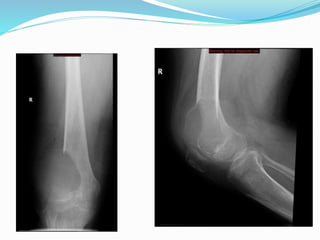
This document provides guidance on evaluating bone lesions based on patient age, lesion location and features on imaging. For patients under 40, benign lesions are more common and may include osteoid osteoma, aneurysmal bone cyst or fibrous dysplasia in the epiphysis or metaphysis. Between 20-40 skeletal mature lesions like giant cell tumor are possible. Over 40, metastases should be considered. Imaging should assess site, size, matrix and other features to characterize the lesion before determining if biopsy is needed. Treatment options depend on diagnosis and may include observation, ablation, curettage or resection.