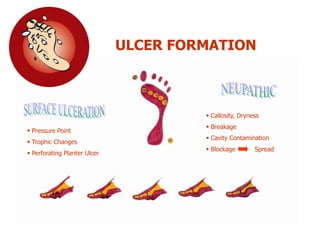
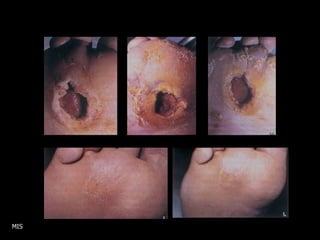
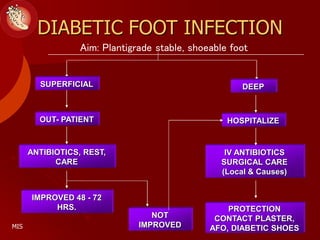
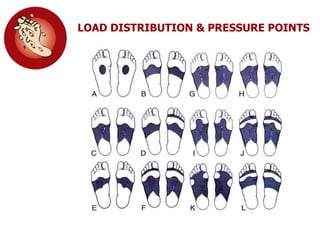
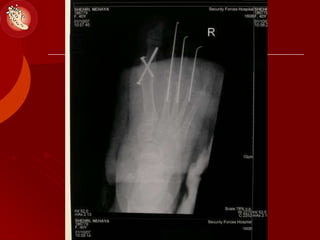
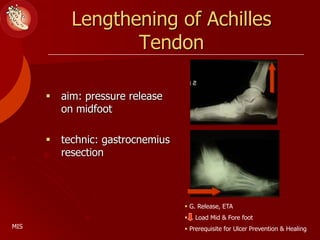
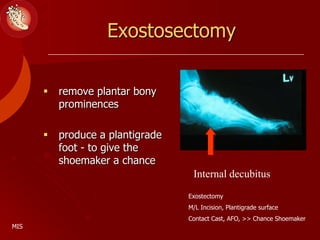
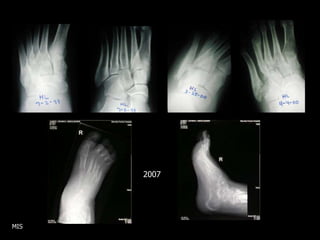
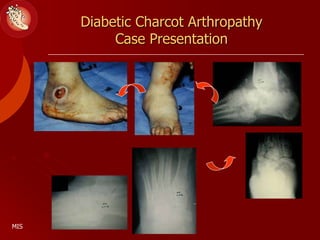
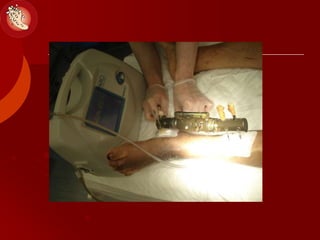
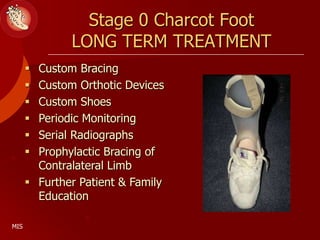
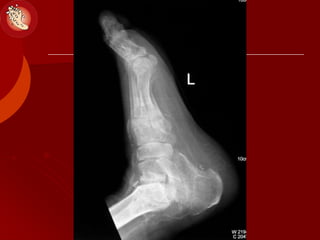
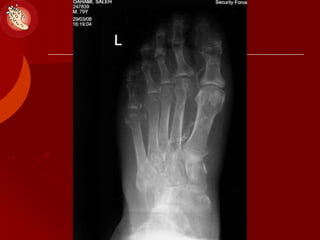
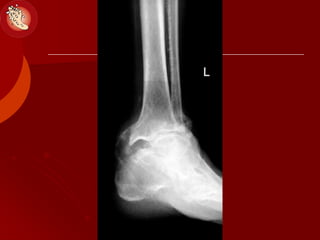
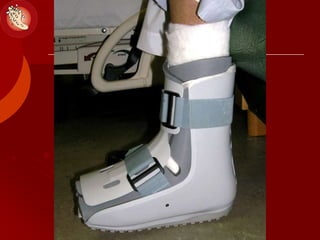
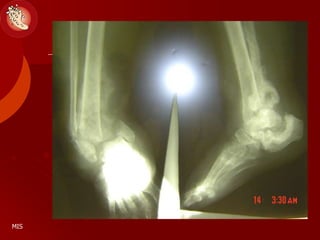
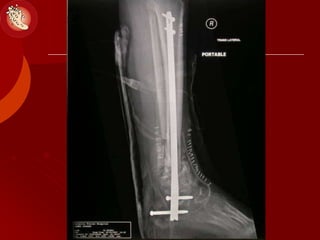
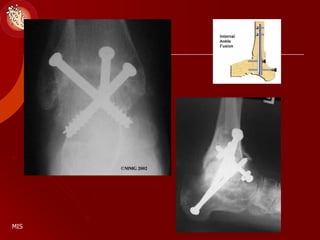
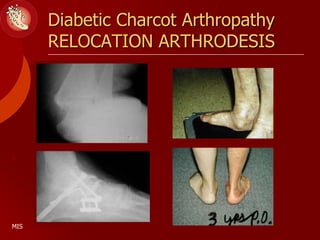
This document discusses the minimally invasive surgical management of the diabetic foot, specifically the Charcot foot. It provides statistics on the epidemiology of diabetes and its complications like foot ulcers and amputations. Diabetic foot complications represent a huge economic burden. The causes of foot ulcers and infections in diabetes are explored, including mechanical, vascular, immunological and more factors. Surgical management techniques for the diabetic foot are described, including soft tissue procedures and osteotomies to offload pressure and promote healing. The stages and natural history of Charcot arthropathy are outlined. Long term bracing and custom orthotics are recommended for Charcot foot management.