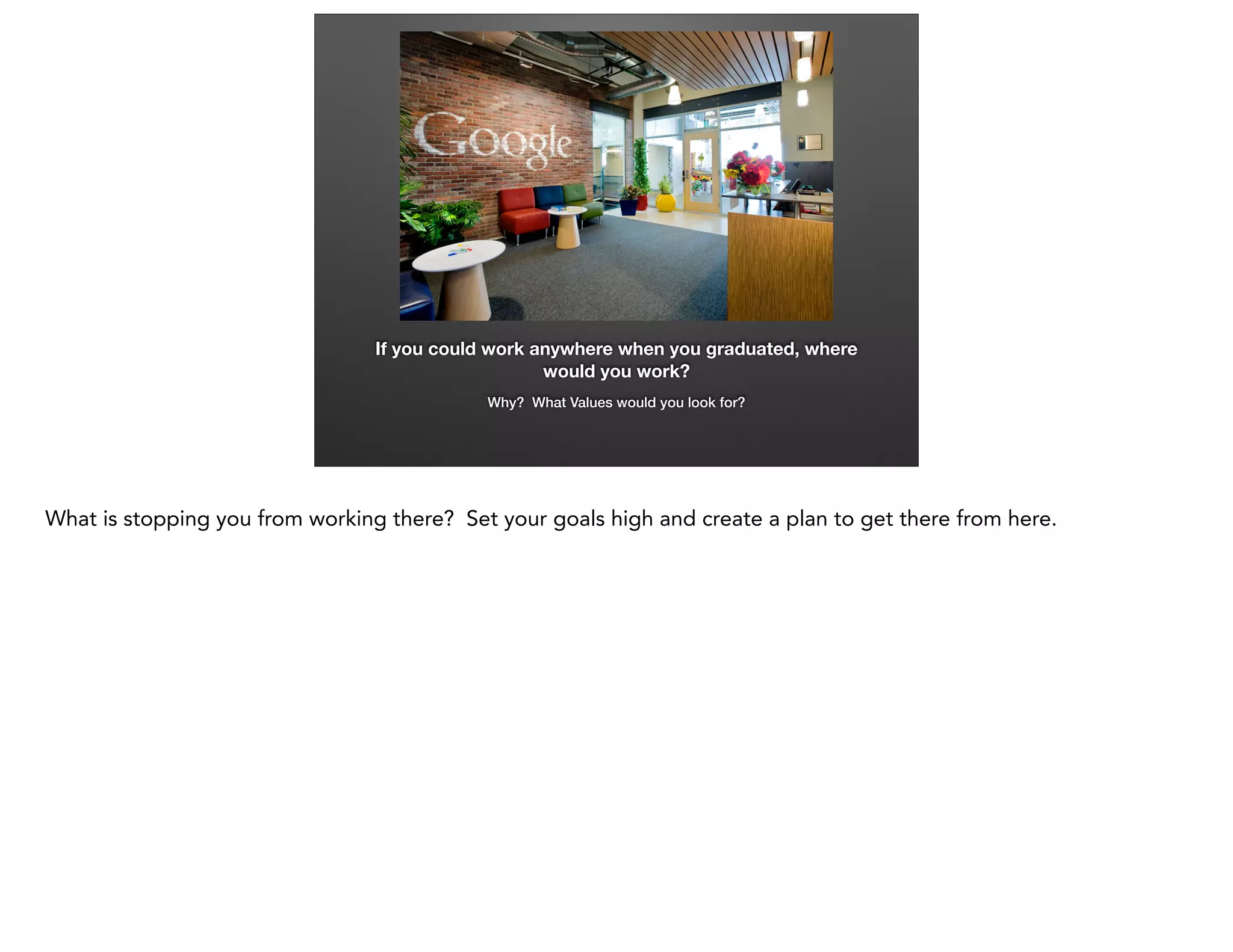
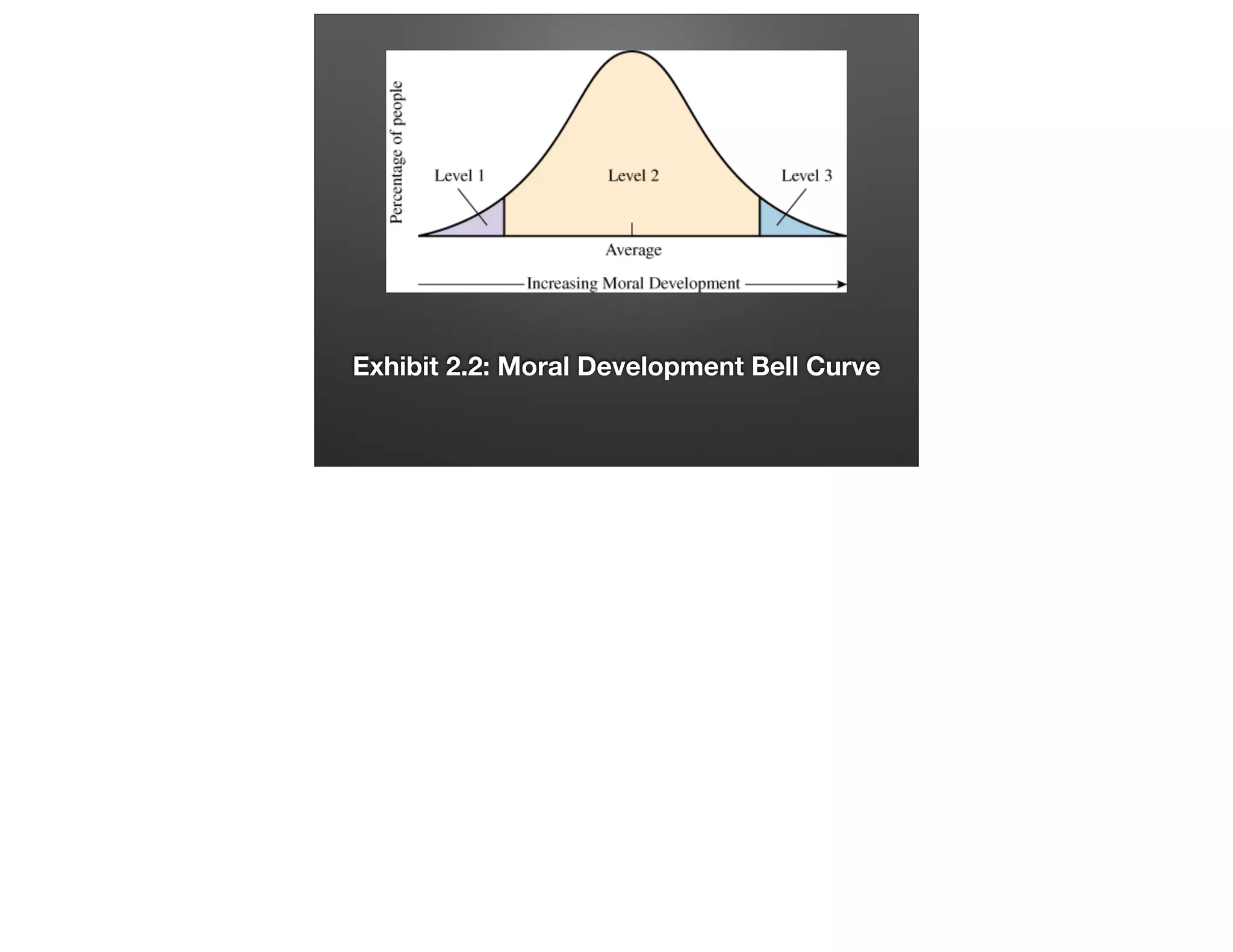
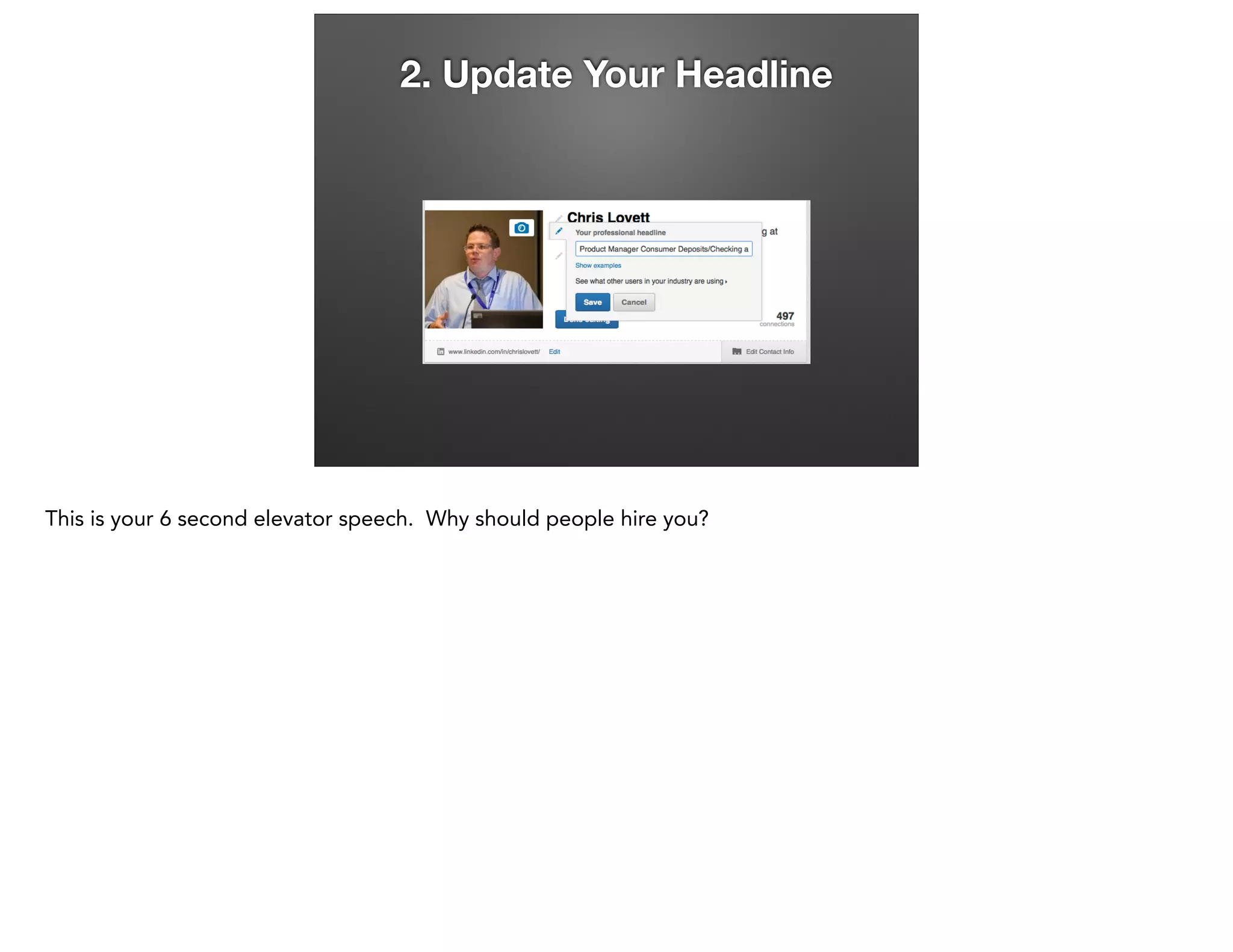
This document provides an overview of ethics in sales and career strategies. It discusses finding employment at companies with strong ethical values and avoiding scam jobs. The role of ethics at the individual, organizational, and societal levels is examined. Unethical practices like misrepresentation and bribery that can harm customers are identified. The importance of leadership setting a moral example within a company is emphasized. The financial crisis of 2008 is used as a case study of how an ethics breakdown in the mortgage industry can have widespread negative impacts. Students are assigned to create a professional LinkedIn profile to help market themselves for career opportunities.