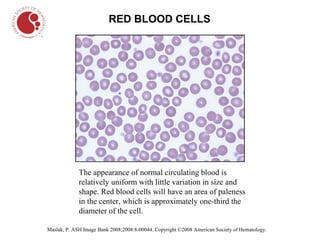
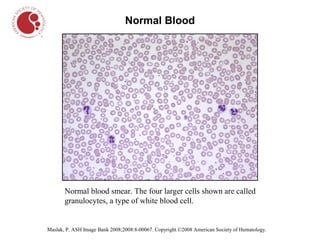
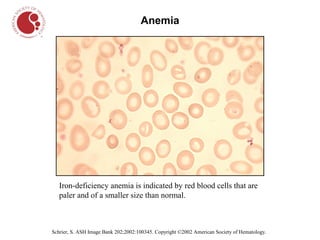
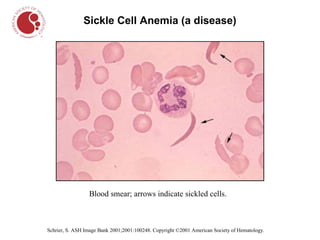
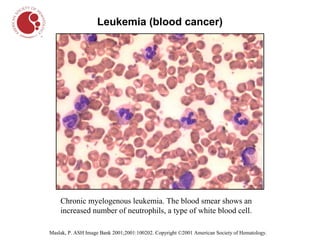
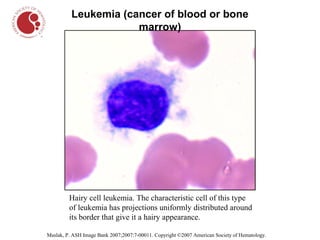
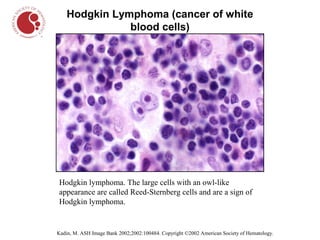
The document describes different types of blood cells and blood disorders through images from a blood smear. It shows normal red blood cells having a pale center, and normal white blood cells. Images then show the pale and smaller red blood cells of iron-deficiency anemia. Sickle cell anemia is indicated by sickled, crescent-shaped red blood cells. Chronic myelogenous leukemia shows increased white blood cells. Hairy cell leukemia features white blood cells with hair-like projections. Hodgkin lymphoma features large owl-like Reed-Sternberg cells.