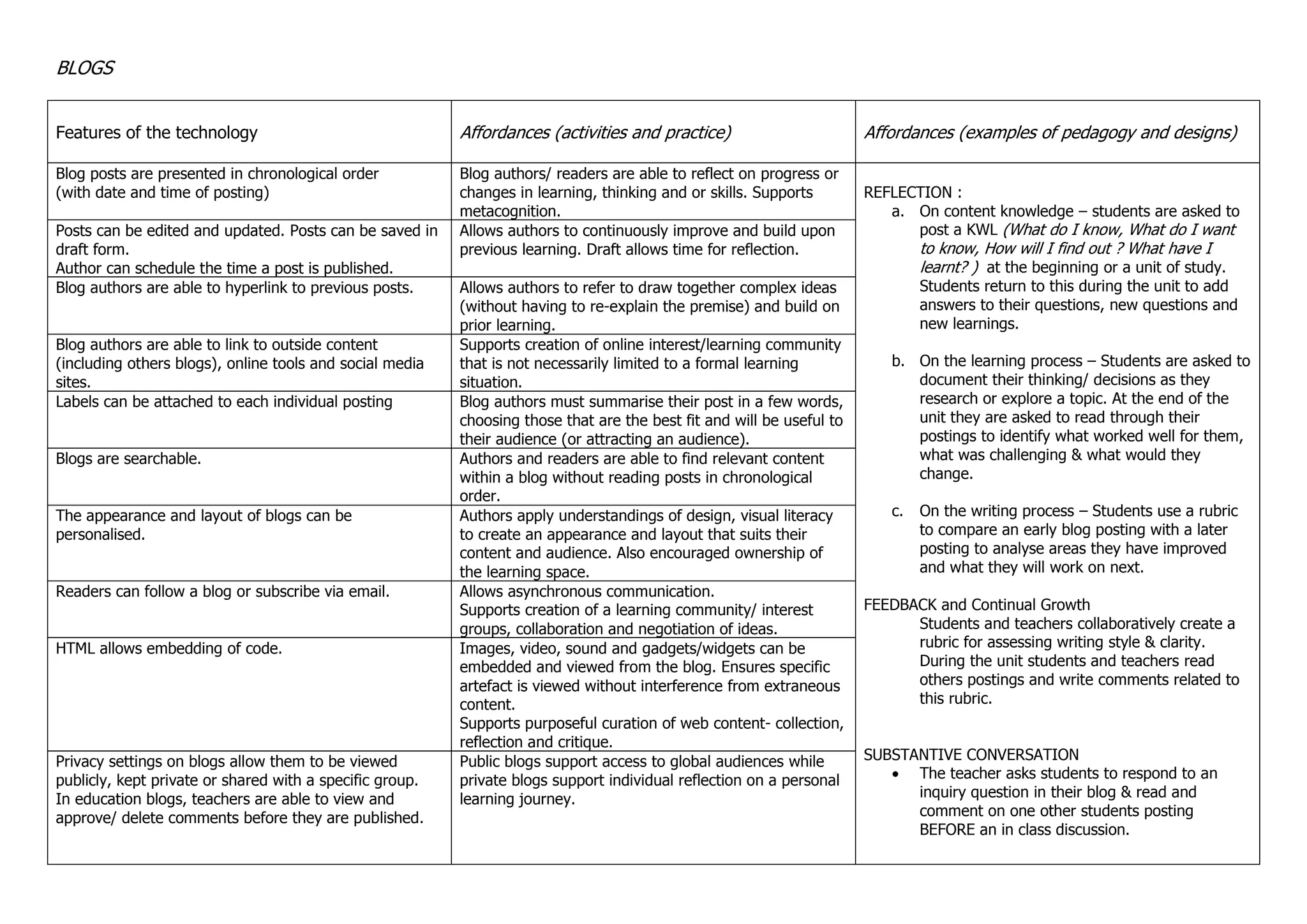
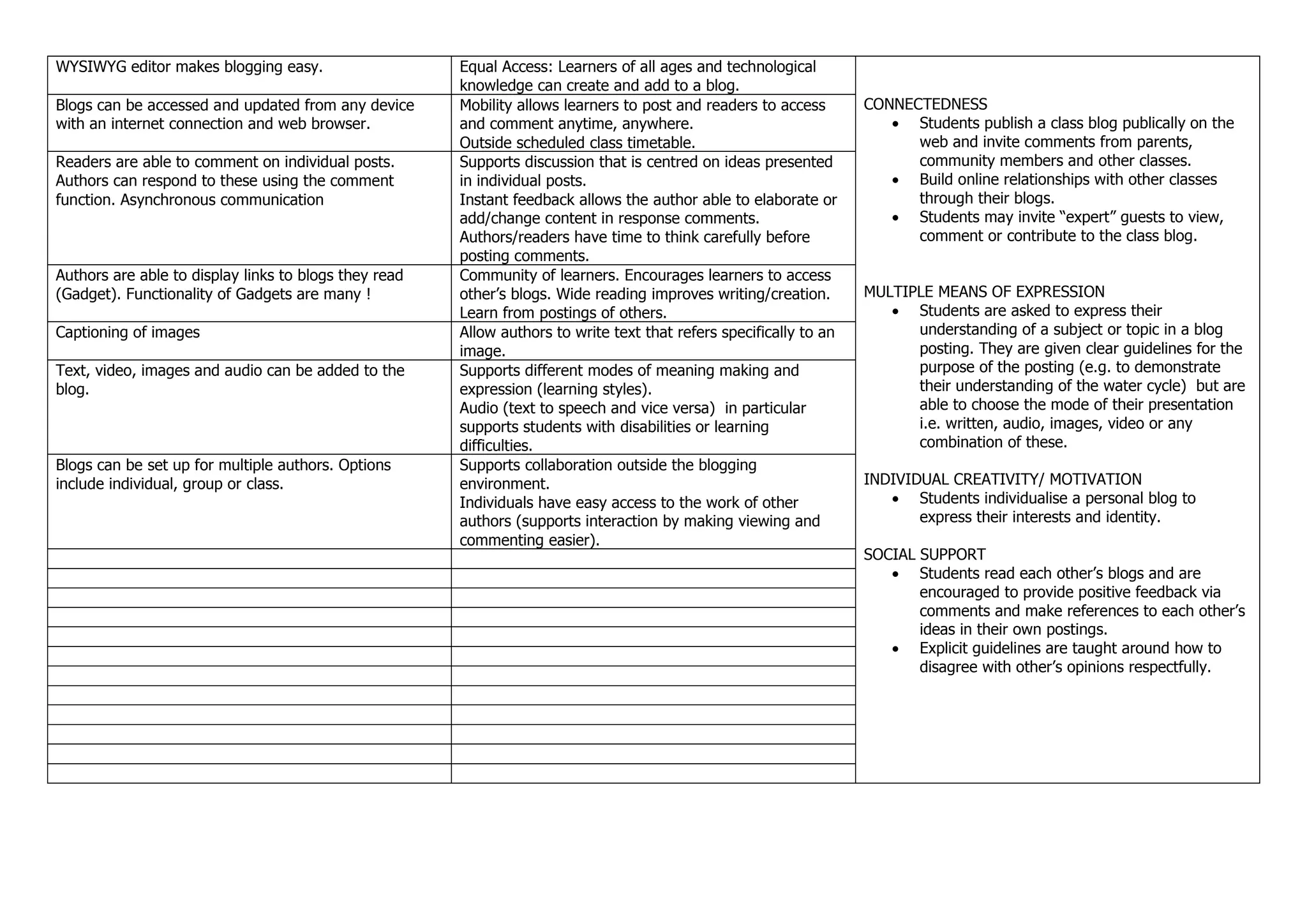
Blogs allow for reflection on learning, feedback and growth through comments, and building upon ideas over time. Key features include chronological posts, ability to edit and schedule posts, hyperlink to other sources, and comment on individual posts. This supports reflection on content and process, developing understanding through substantive conversation, and building an online learning community through sharing blogs publicly or within groups.