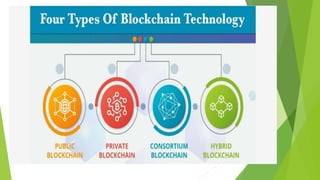
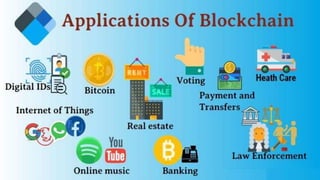
Blockchain technology is a distributed database or digital ledger that records transactions in a verifiable way without the need for a central authority. It works by sharing a constantly growing list of records called blocks that are linked together using cryptography. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. This design makes blockchains resistant to modification, ensuring data integrity. The document discusses the history and fundamentals of blockchain technology, how it works, applications like cryptocurrencies and smart contracts, and advantages like decentralization, security, and cost reduction as well as disadvantages like scalability issues.