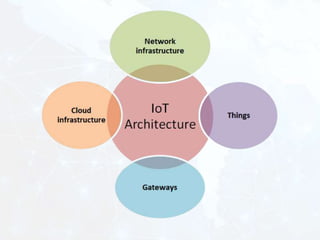
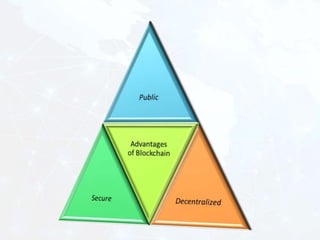
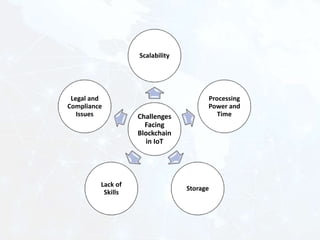
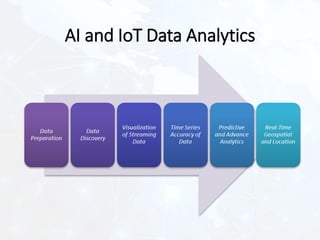
The document outlines the complexities and challenges of securing the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem, emphasizing the need for well-designed architectures and standards. It discusses the potential of blockchain technology to enhance security and privacy in IoT environments while also addressing scalability and compliance challenges. Additionally, it explores the role of artificial intelligence in enhancing IoT data analytics, highlighting various types of data analysis and the associated challenges.