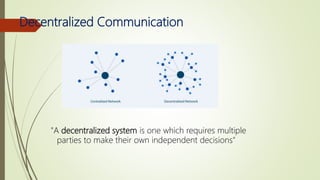
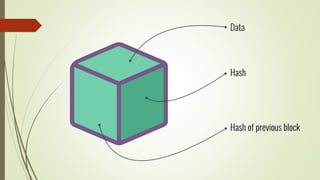
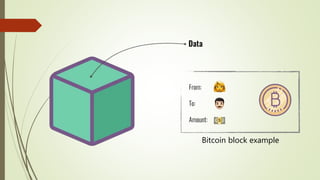
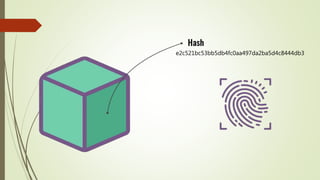
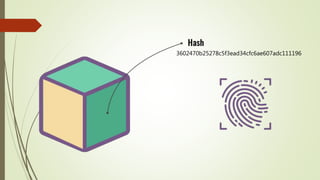
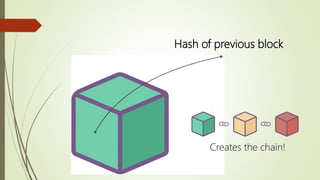
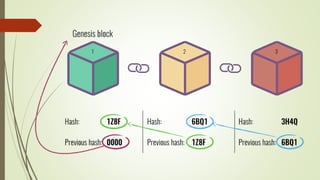
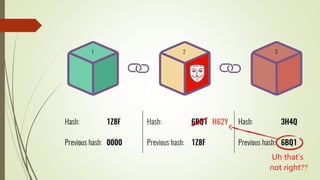
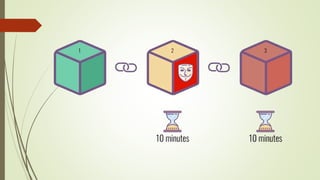
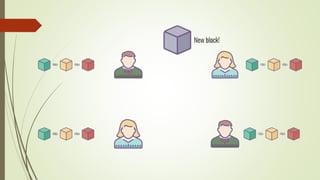
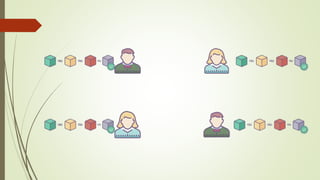
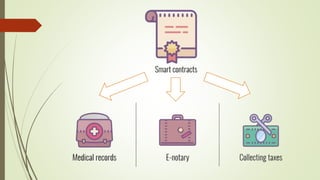
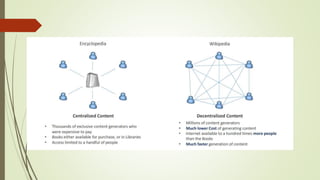
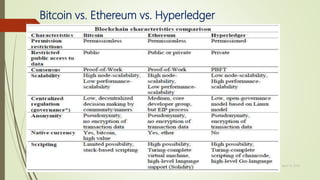
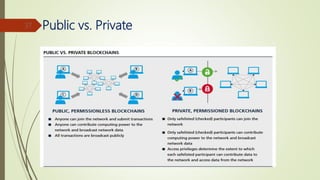
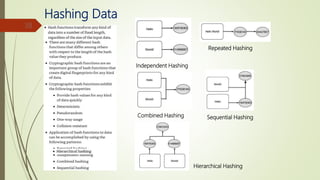
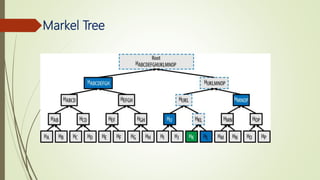
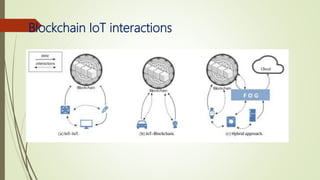
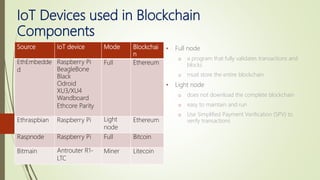
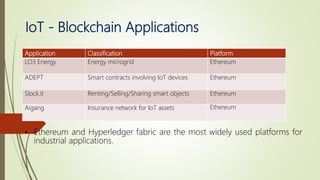
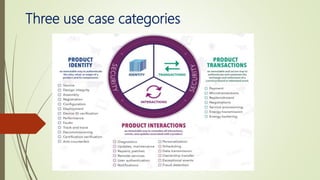
The document discusses using blockchain technology for IoT applications. It first defines IoT and describes problems with centralized IoT communication, such as lack of trust and higher costs. Decentralized communication methods are proposed as an alternative. The document then provides an overview of blockchain technology, describing its key characteristics like distributed ledgers and consensus mechanisms. Finally, the document discusses how blockchain can address issues like security, reliability and autonomy for IoT applications and provides examples of existing blockchain-IoT projects.