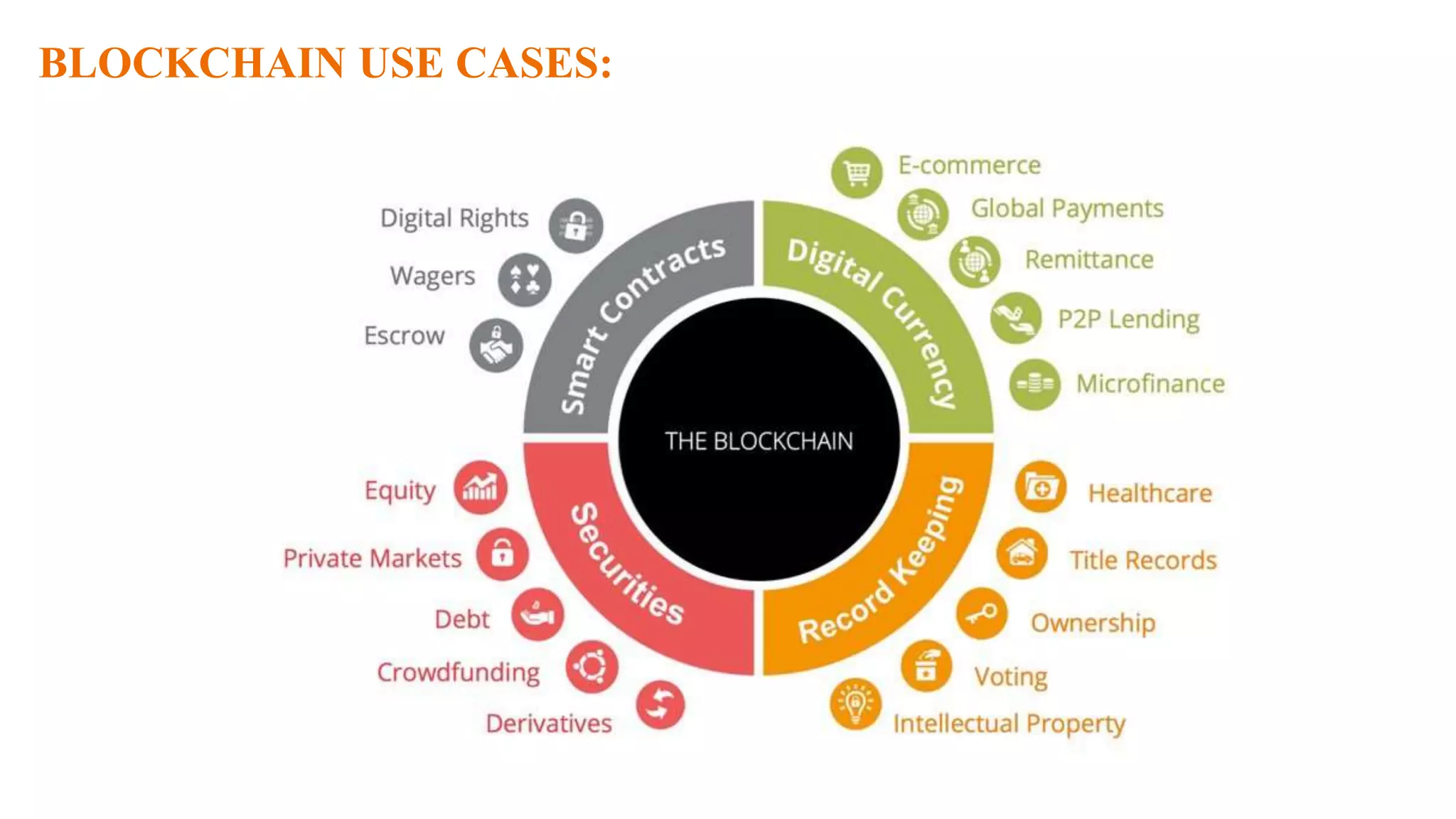
This document provides an overview of blockchain technology. It discusses how blockchain can provide an alternative to centralized ledgers for storing transaction records. Key points made include:
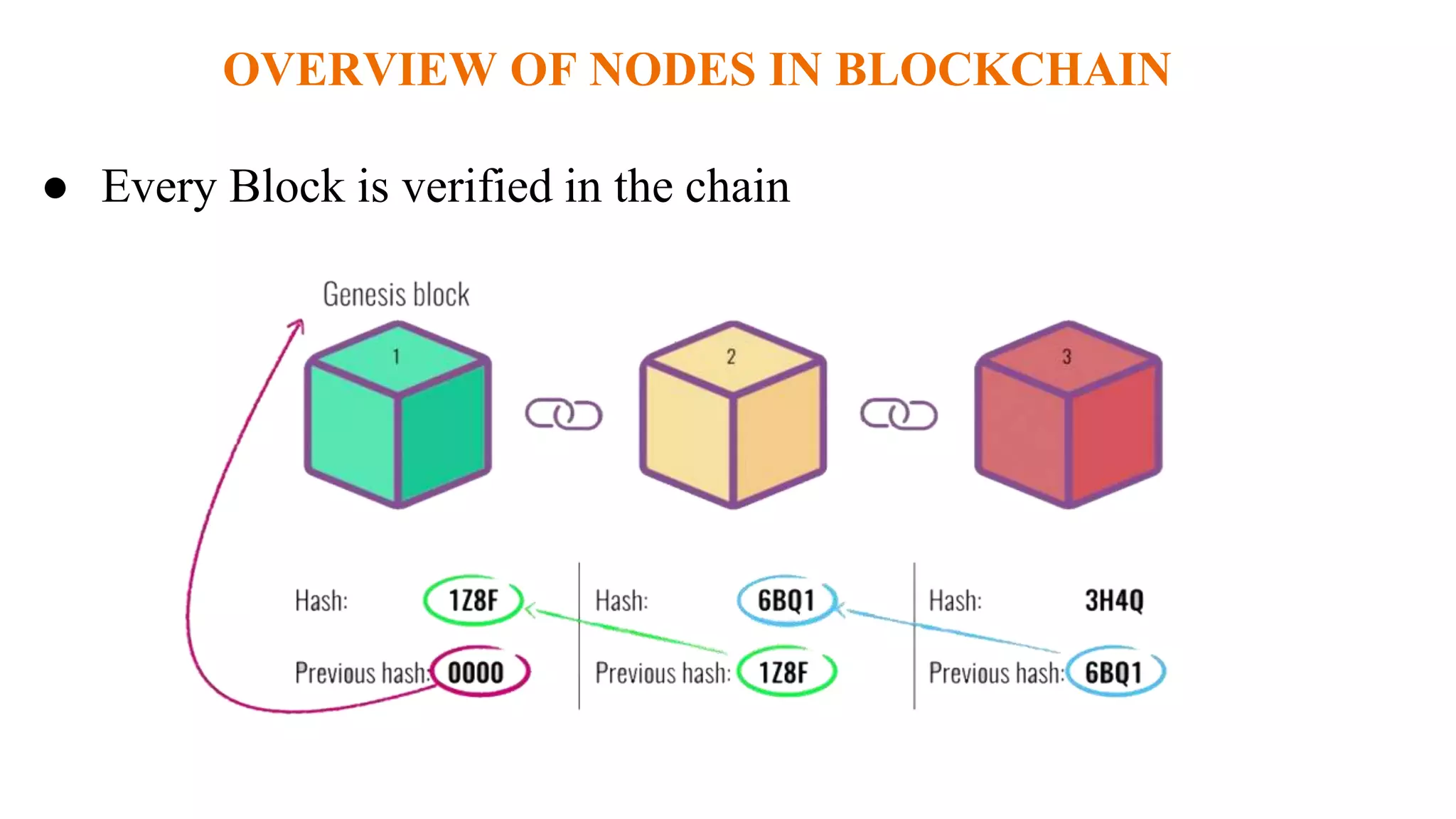
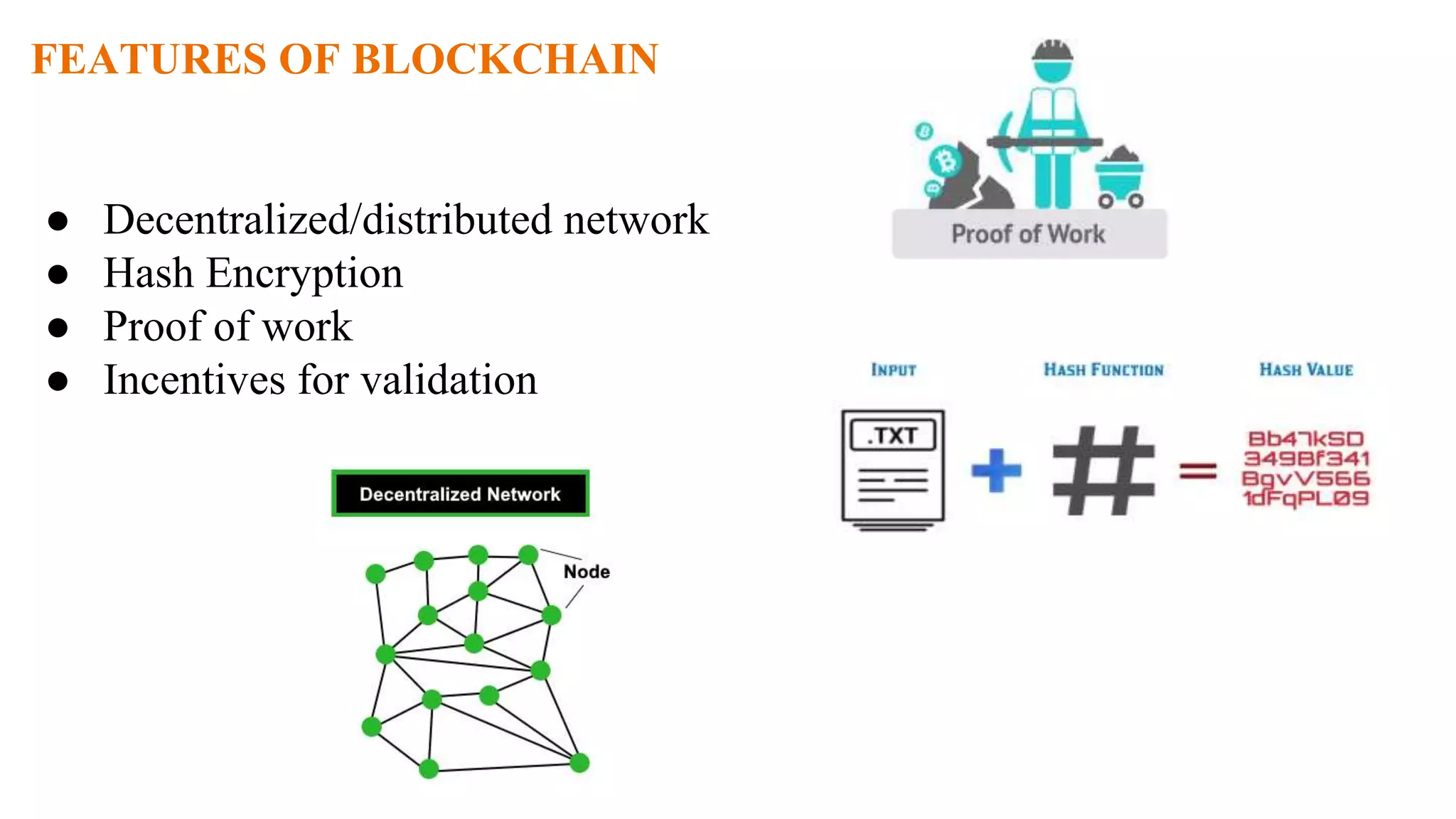
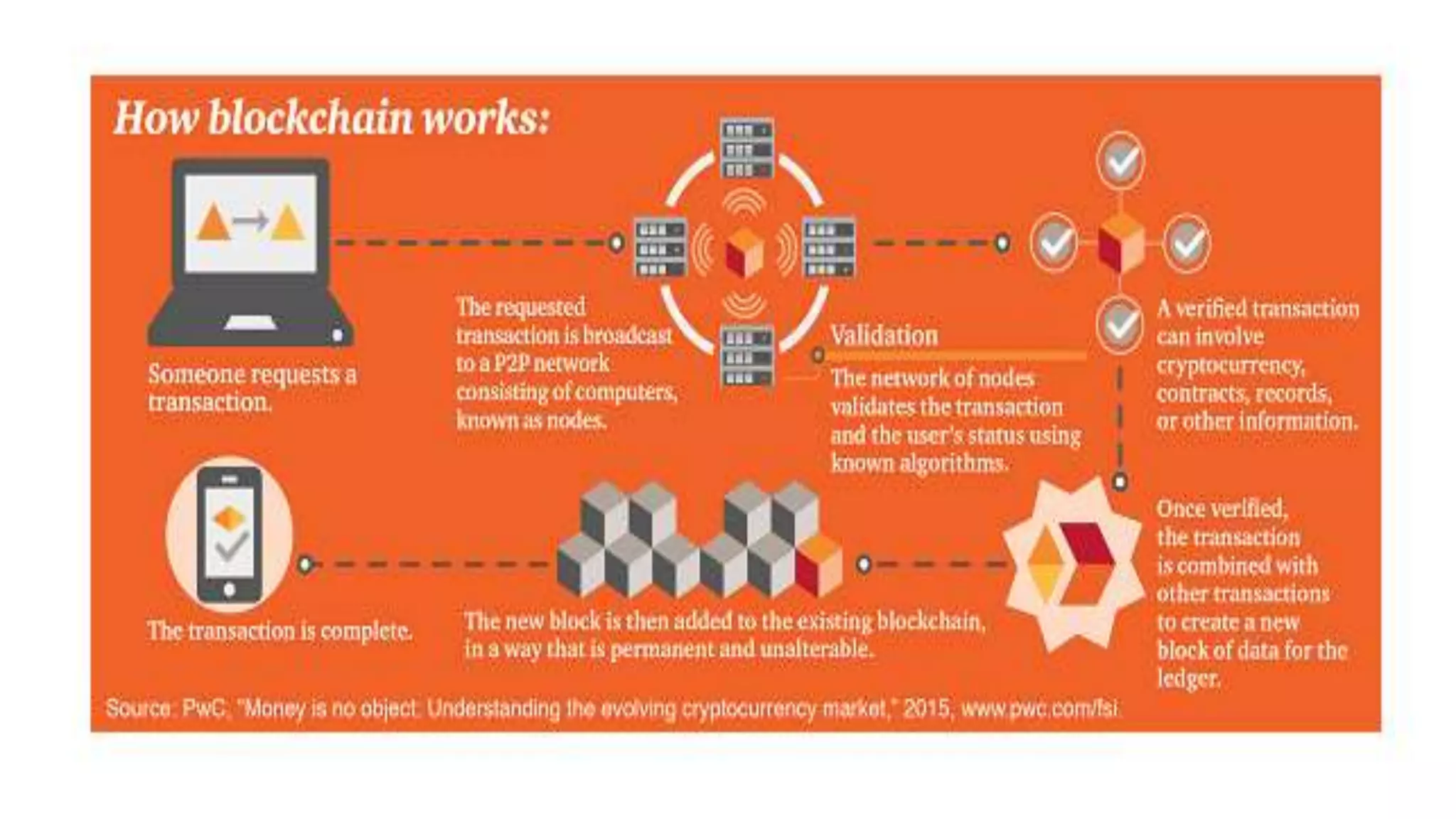
- Blockchain uses a distributed ledger that is shared across a network of nodes and updated through consensus, eliminating the need for a centralized authority.
- Information stored on the blockchain is hashed and encrypted, providing security. New blocks are added through proof-of-work mining which involves solving computationally difficult puzzles and is incentivized with cryptocurrency rewards.
- Ethereum is a popular platform for building decentralized applications on blockchain through the use of smart contracts, which allow for automated execution of agreements.
- Potential use cases of blockchain include banking,