Embed presentation
Download to read offline


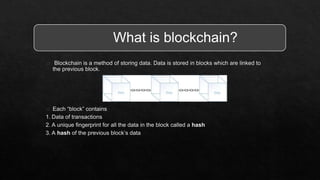





The document outlines the history and evolution of blockchain technology, beginning with its conceptualization in 1991 and leading to the implementation of Bitcoin's blockchain in 2009. It highlights key features such as immutability, decentralization, and transparency, while also discussing challenges like high energy consumption and scalability issues. Overall, it captures the transformative potential of blockchain beyond cryptocurrency applications.







