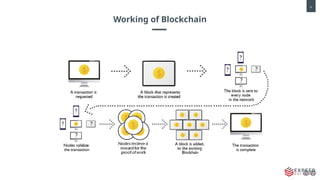
Blockchain is revolutionizing industries with its secure, transparent, and decentralized capabilities. From finance and healthcare to supply chain and beyond, businesses are leveraging blockchain to enhance security, streamline operations, and build trust.
In this presentation, explore:
✅ How blockchain works
✅ Key applications across industries
✅The future of blockchain technology
Discover how blockchain can drive innovation in your business!