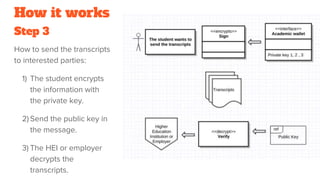
The document discusses the need for a blockchain-based system in higher education to mitigate issues of credential fraud and reduce the resources spent on validating transcripts. It outlines a process where higher education institutions create and encrypt transcripts, students manage their private keys, and employers verify transcripts easily through a public ledger. Potential benefits include reduced bureaucracy for students, lower administrative costs for institutions, and instant verification for employers.