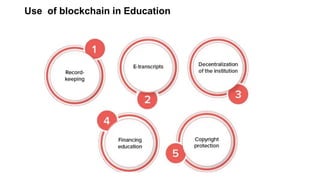
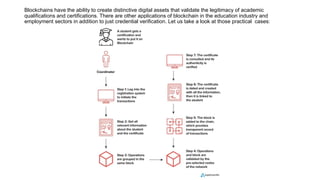
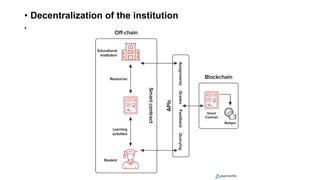
Blockchain technology is transforming education by providing decentralized and immutable records for academic credentials, which enhances data security and privacy. The global blockchain market in education is projected to grow significantly, offering solutions for efficiency in record-keeping and reducing administrative burdens. However, challenges such as security concerns, scalability issues, and low adoption rates need to be addressed for widespread implementation.