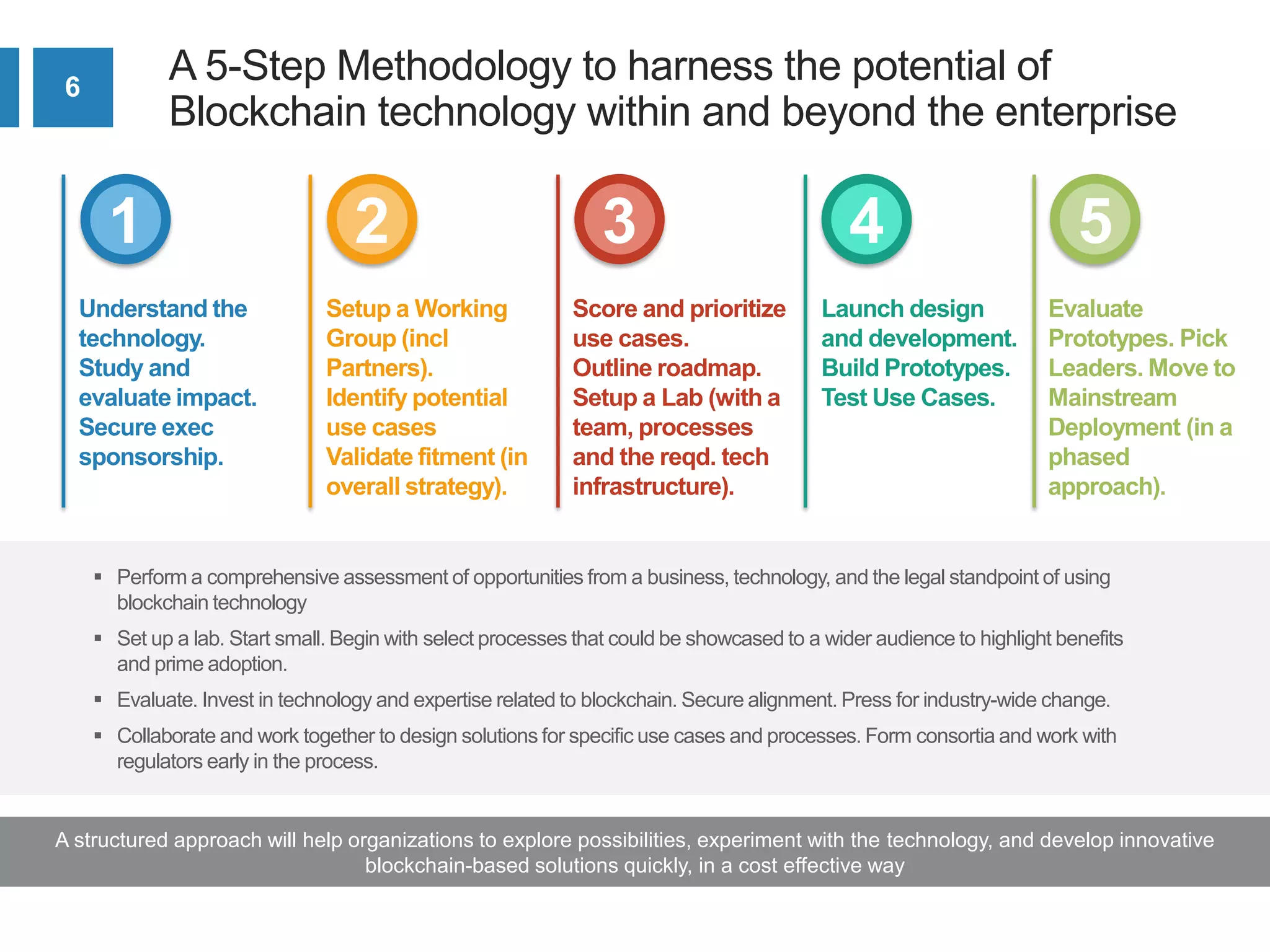
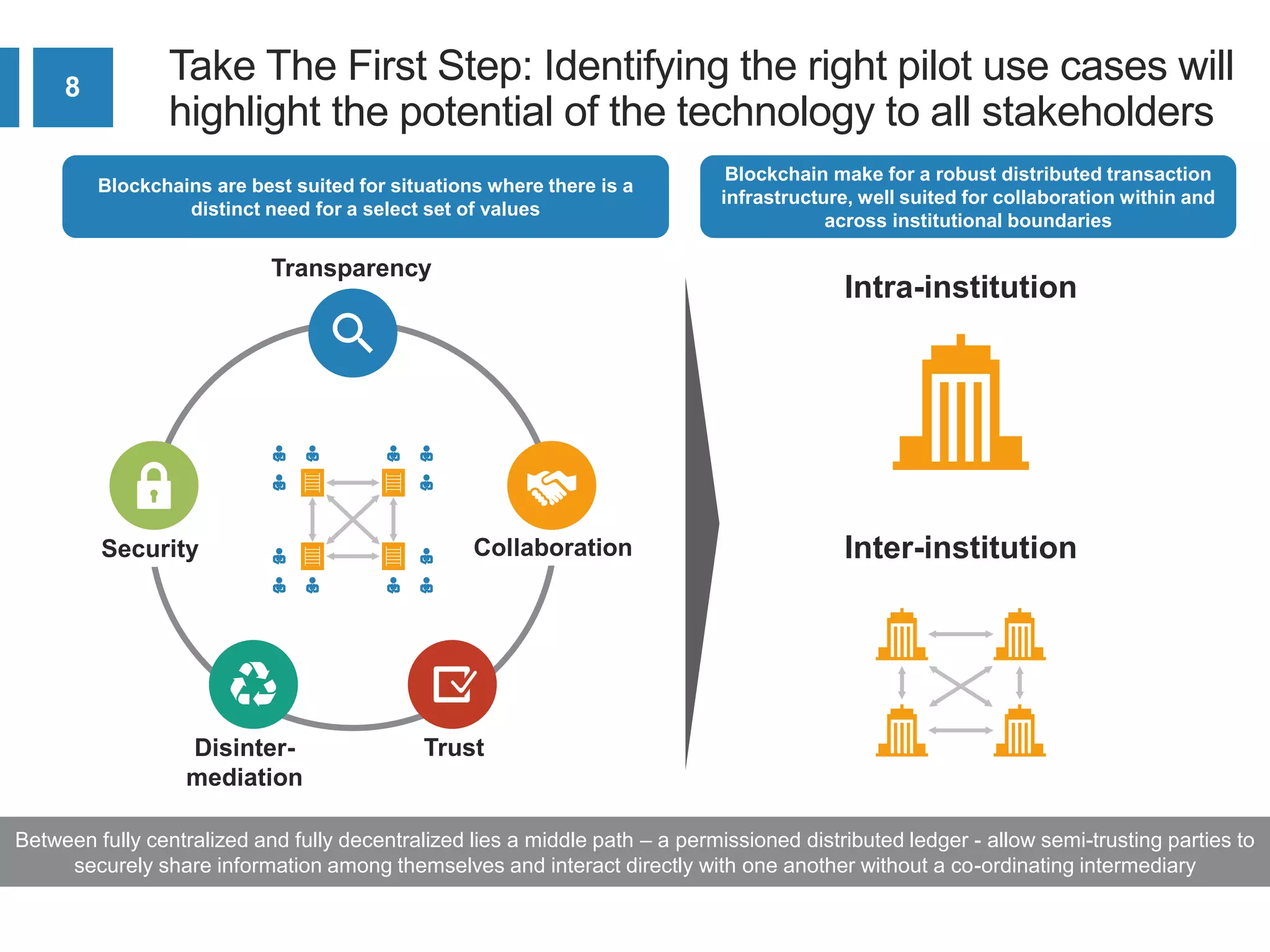
The document discusses the transformative potential of blockchain technology as a key enabler for digital transformation across various industries. It outlines a framework for organizations to explore and implement blockchain solutions, including assessing technology, securing executive sponsorship, and prioritizing use cases. Additionally, it emphasizes the need for integration with existing systems and collaboration within industry consortia to effectively deploy blockchain initiatives.