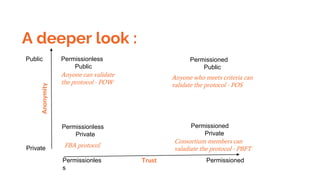
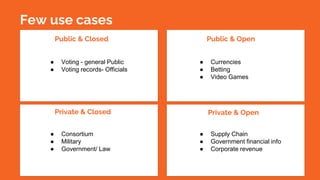
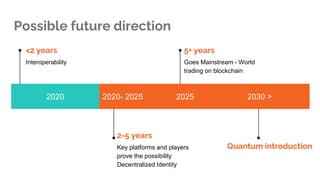
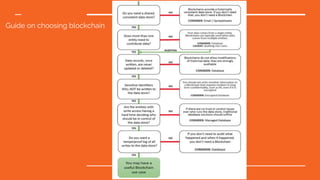
The document discusses blockchain technology, detailing the differences between permissioned and permissionless blockchains, including their features, use cases, and selection criteria. It highlights examples of projects in various sectors, such as government and banking, and outlines potential future directions for blockchain development. Key considerations for implementing blockchain include problem solving, participant governance, and ensuring immutability and provenance.