Embed presentation
Download to read offline


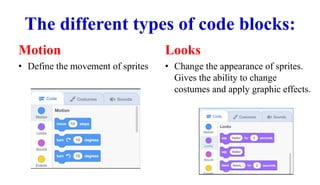

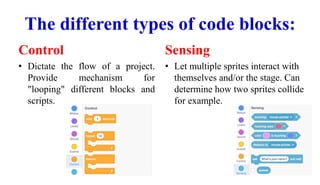

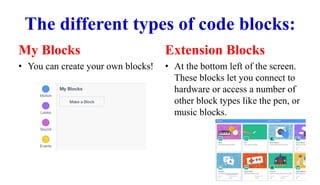
Scratch uses block-based programming where code blocks represent commands instead of text. There are different categories of blocks that tell sprites how to move, change appearance, play sounds, control flow, sense interactions, perform math operations, store variables, create custom blocks, and connect to hardware. Blocks control sprite motion, looks, sounds, events, control flow, sensing, operators, variables, custom blocks, and extensions. Code blocks determine the movement, appearance, audio, triggers, loops, interactions, math functions, stored data, user-defined blocks, and connections of sprites and the stage.






