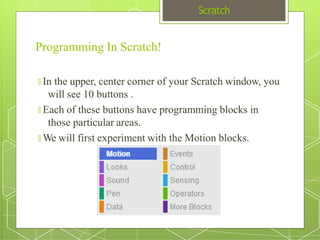
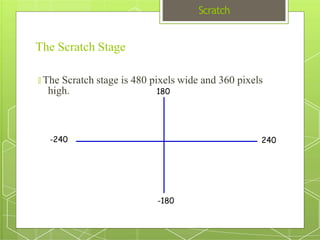
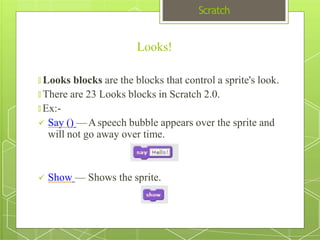
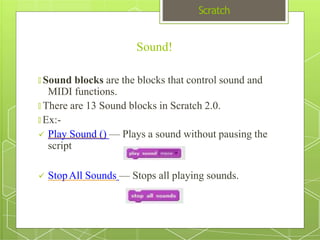
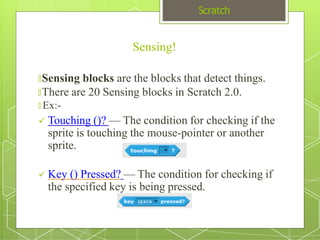
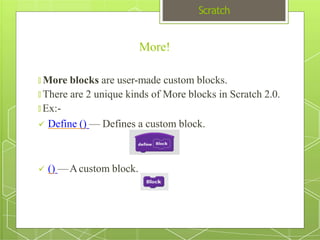
The document discusses the visual programming environment called Scratch. It provides an introduction to Scratch, describing its history starting in 2003 at MIT and objectives of making programming accessible and fun. It explains the major components of the Scratch interface and provides examples of the different types of blocks available for controlling things like motion, appearance, sound, pen, data, events, control structures and sensing. It concludes with proposing a simple program using Scratch that displays "hello world" when hovering over a sprite.







![Scratch
Major components
🞇 At left: the stage with sprite[s] or objects or actors
🞇 Center: operations and attributes for the sprites
🞇 At right: scripts or program[s] for the behavior[s] of the
sprites
🞇 A sprite is a small graphic that can be moved
independently around the screen, producing animated
effects .
🞇 Blocks are puzzle-piece shapes that are used to create
code in Scratch .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scratch-141107045720-conversion-gate02-221113122822-5f287397/85/scratch-141107045720-conversion-gate02-pptx-8-320.jpg)