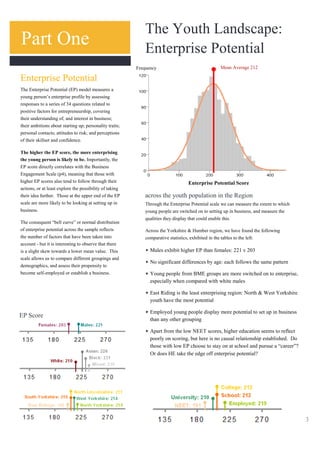
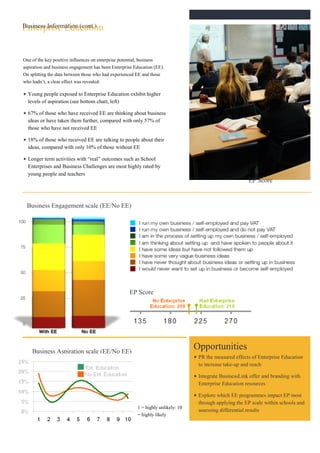
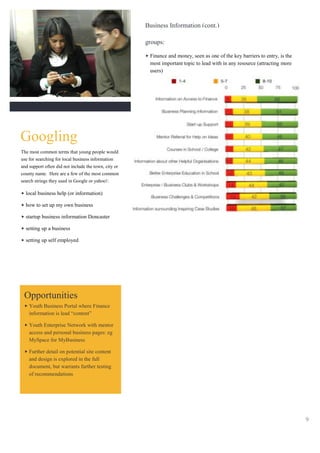
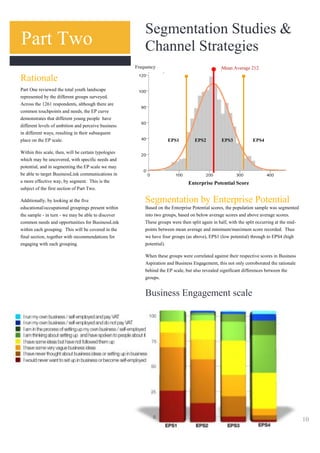
The document analyzes data from a survey of 1,261 young people aged 14-25 in Yorkshire & Humber to understand their attitudes towards entrepreneurship. Key findings include:
1) 6 out of 10 respondents have business ideas but only 3 out of 10 have sought information or support, showing untapped potential.
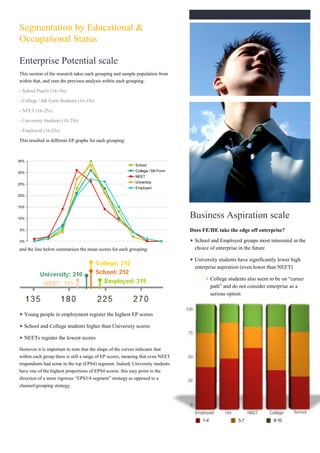
2) Segmentation based on an "Enterprise Potential" scale identified four groups with differing levels of entrepreneurial skills, aspirations, and engagement.
3) Exposure to enterprise education correlated with higher aspirations and business engagement among respondents.
4) Careers advisors and friends/family were most likely information sources for young people's business ideas, showing opportunities to better support advisors and leverage personal