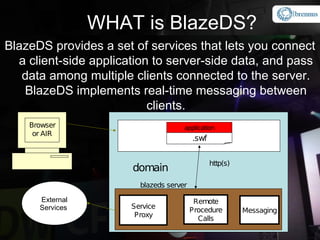
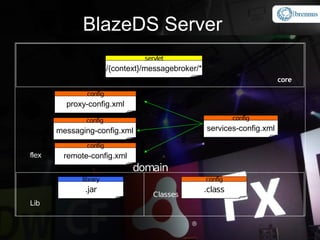
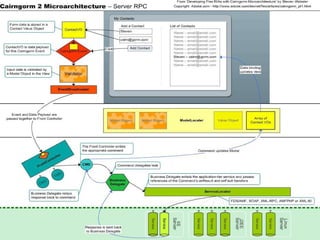
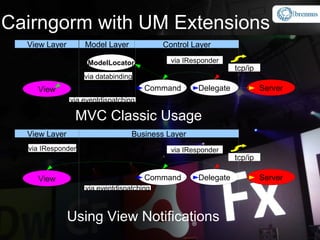
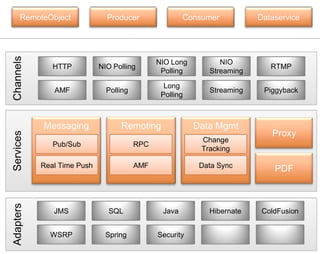
The document provides an overview and agenda for integrating Spring with Blaze DS and Cairngorm UM. It discusses what Spring and Blaze DS are, why they need to be integrated with Flex, how to integrate them through configuration files and code examples, and what Cairngorm UM and CairnSpring are and why they are useful frameworks. The key topics covered are Spring IoC container, exposing Spring beans for remoting via Blaze DS, configuring the MessageBroker as a Spring bean, using Spring DAOs, and how Cairngorm UM and CairnSpring simplify MVC usage and integration with Spring.





![WHY WE NEED FLEX ACCESS
SPRING?
The BlazeDS Remoting enables binding your
valueobjects with Java pojo Classes easily
by metadata
[RemoteClass(alias=”com.adobe.pojo.ob”]
By using the Spring Security 2.0 we can
make our application secured for
transactions.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/blazeds-100601004839-phpapp02/85/BlazeDS-7-320.jpg)