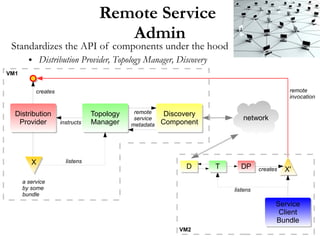
The document summarizes the OSGi 4.2 Enterprise Specification, which includes specifications for component models, distributed services, database access, web applications, and other supporting technologies. Key aspects include Blueprint for easier OSGi development, Remote Services for exposing and consuming services over the network, JPA and JDBC for database access, and integration with Java EE technologies like JNDI, JTA, and JMX. Examples of using these specifications include the Apache Aries Trader application and isolated examples from implementing projects. Future work may include specifications for subsystems, applications, package management, and asynchronous messaging.