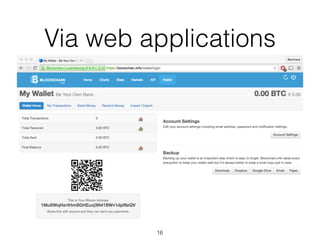
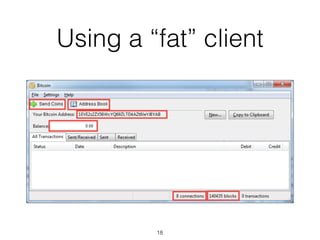
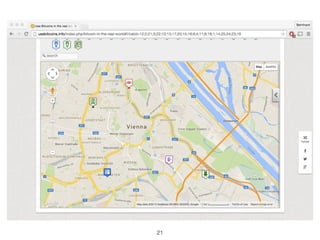
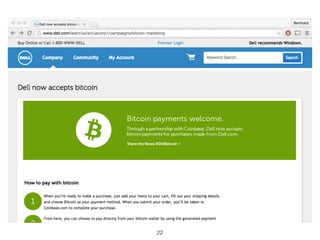
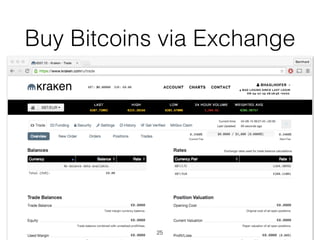
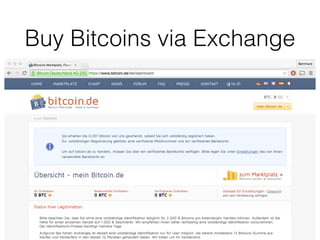
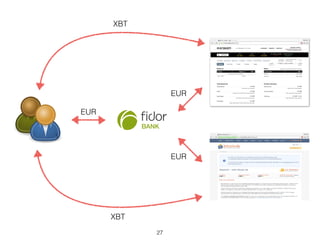
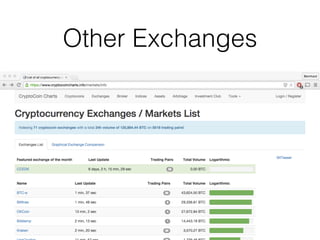
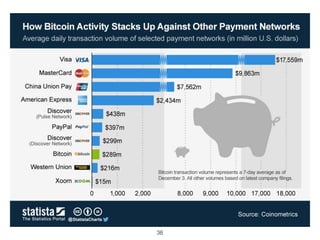
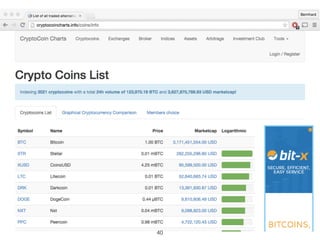
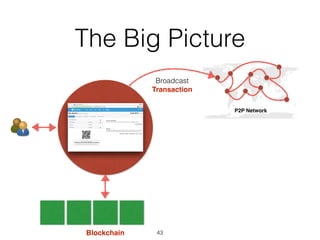
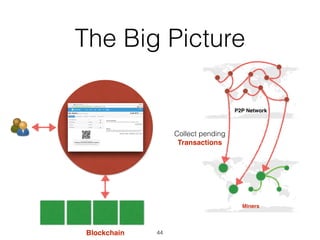
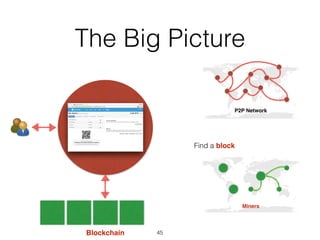
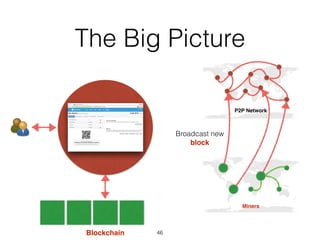
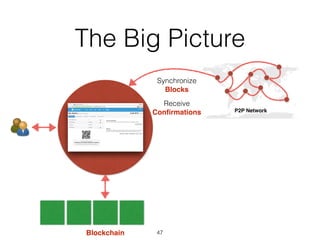
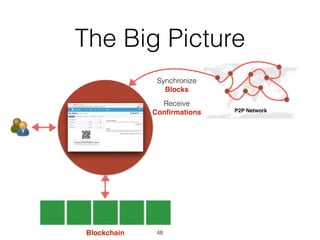
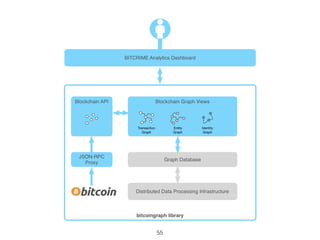
This document provides an introduction to Bitcoin, covering its technical aspects and ongoing developments. It begins with introductions from two presenters, Bernhard Haslhofer and Aljosha Judmayer. The agenda then outlines an overview of Bitcoin, including its introduction, technical aspects such as how the blockchain works, and ongoing developments like alternative applications and recent initiatives from MIT. It also briefly discusses Bitcoin's history with crime and potential applications beyond digital currency.