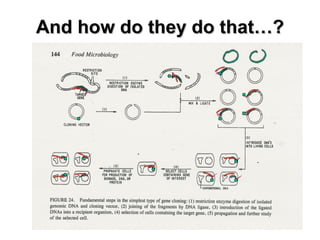
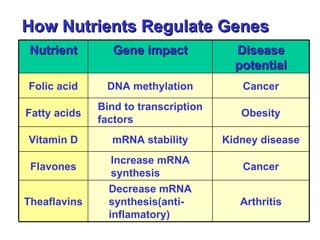
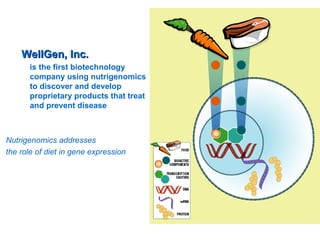
Food biotechnology employs modern genetic techniques to enhance beneficial traits in plants, animals, and microorganisms for food production. It allows adding or extracting select genes to achieve desired traits like increased yields, nutrition, and resistance to pests and disease. Studies show that properly regulated food biotechnology is safe and can help address issues like global hunger by producing more food on less land. However, some argue unintended effects need further review and consumers support labeling of biotech ingredients. Overall, experts agree food biotechnology has potential benefits but continuous research and oversight is important.