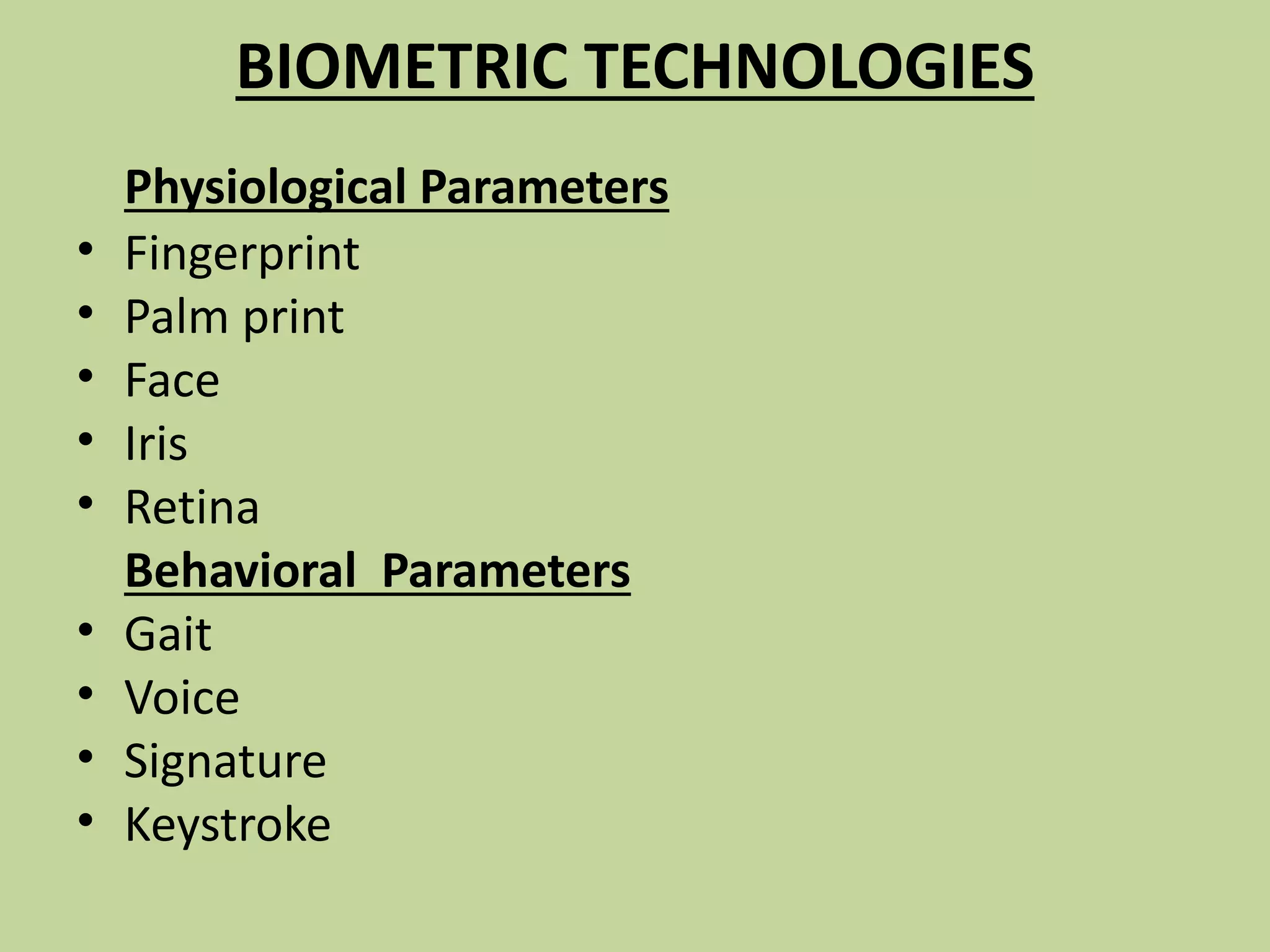
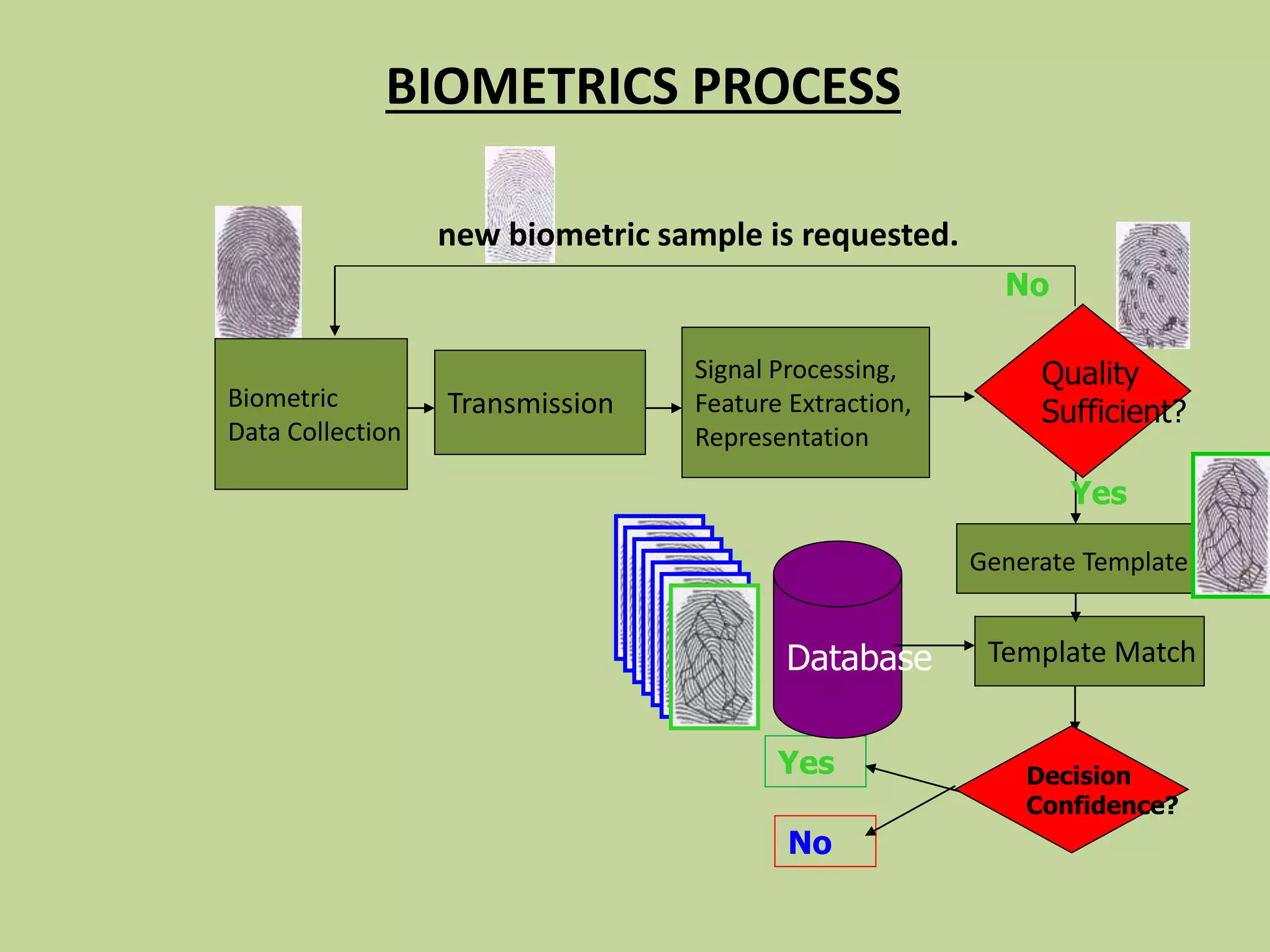
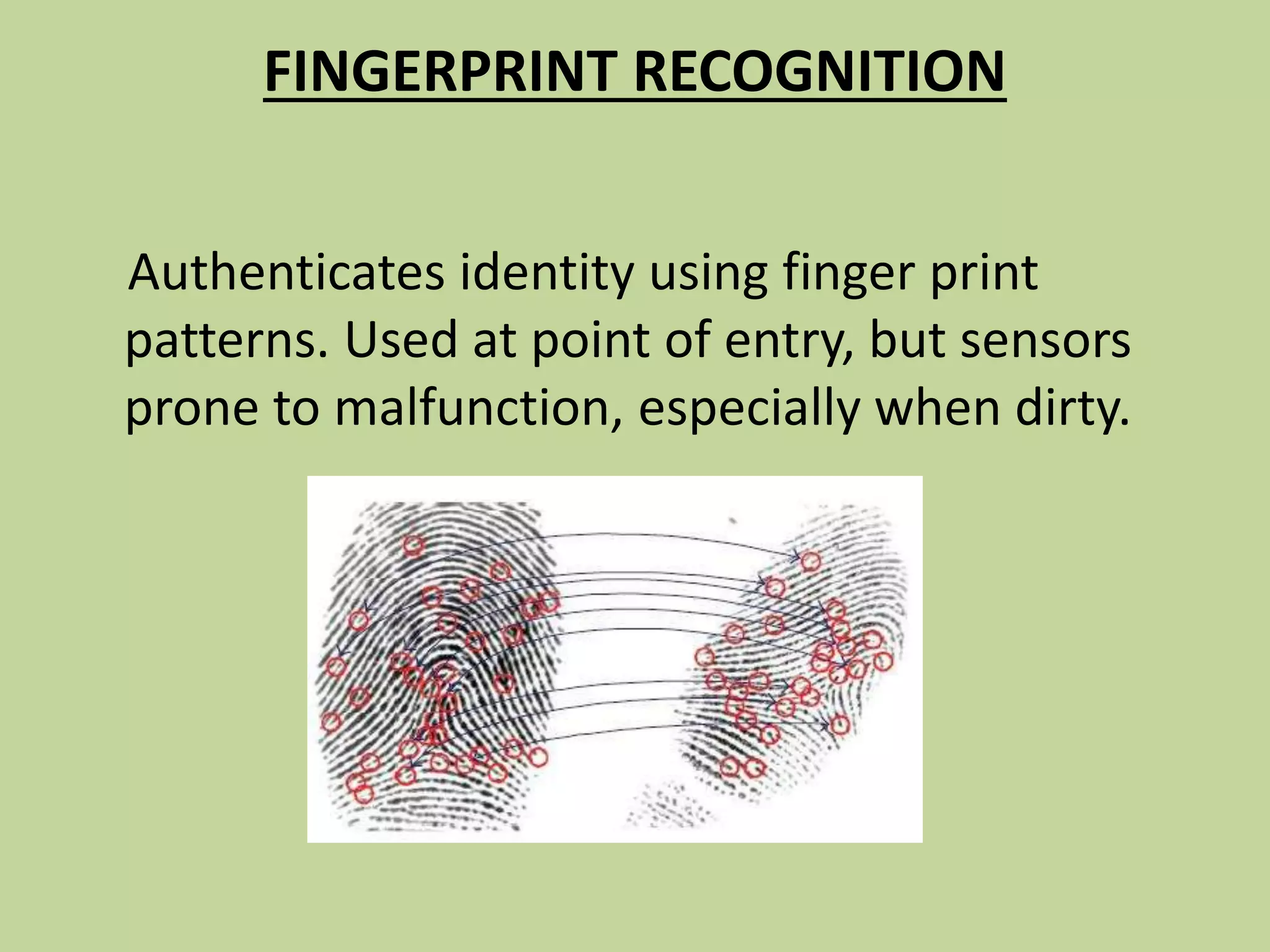
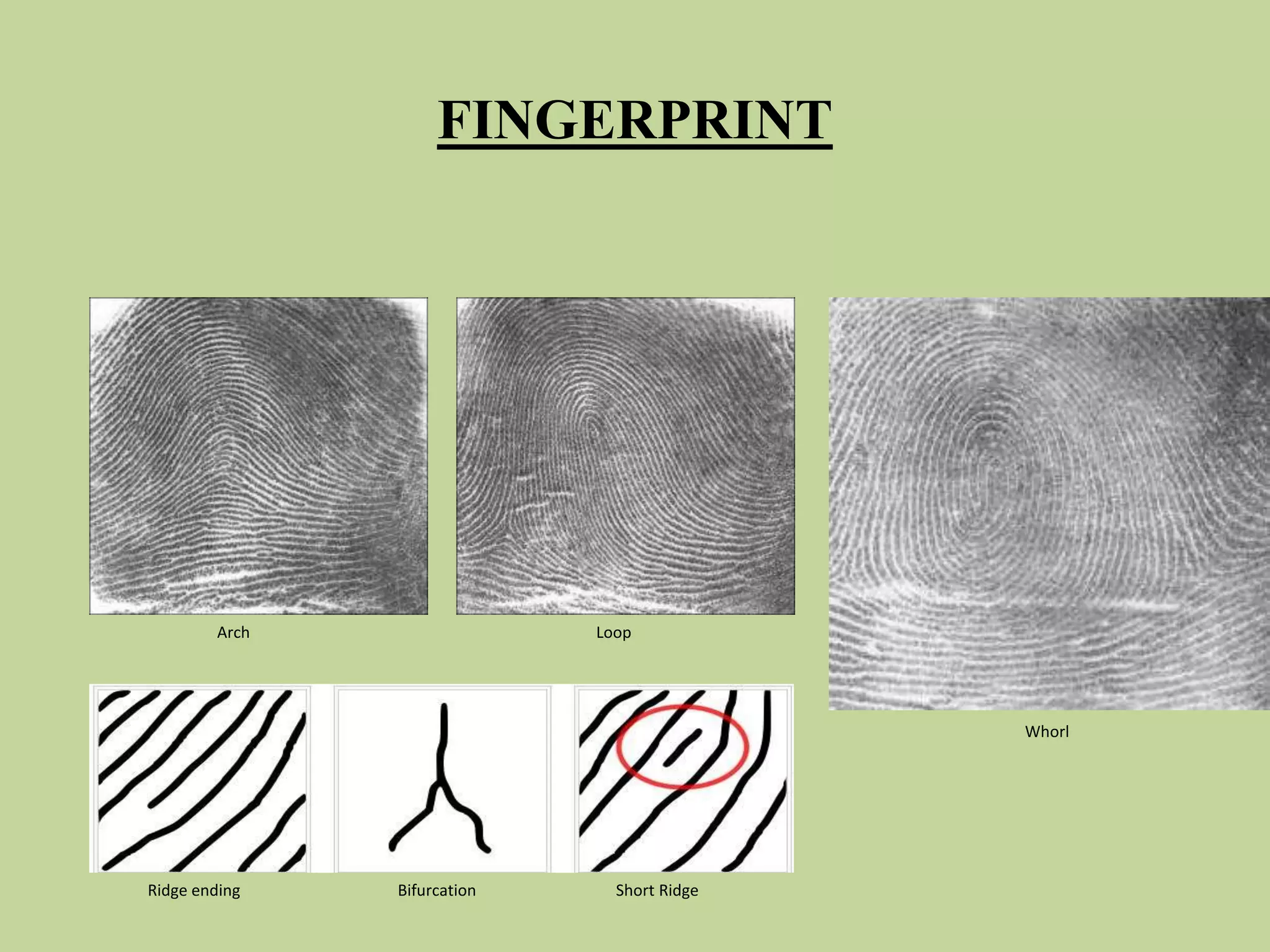
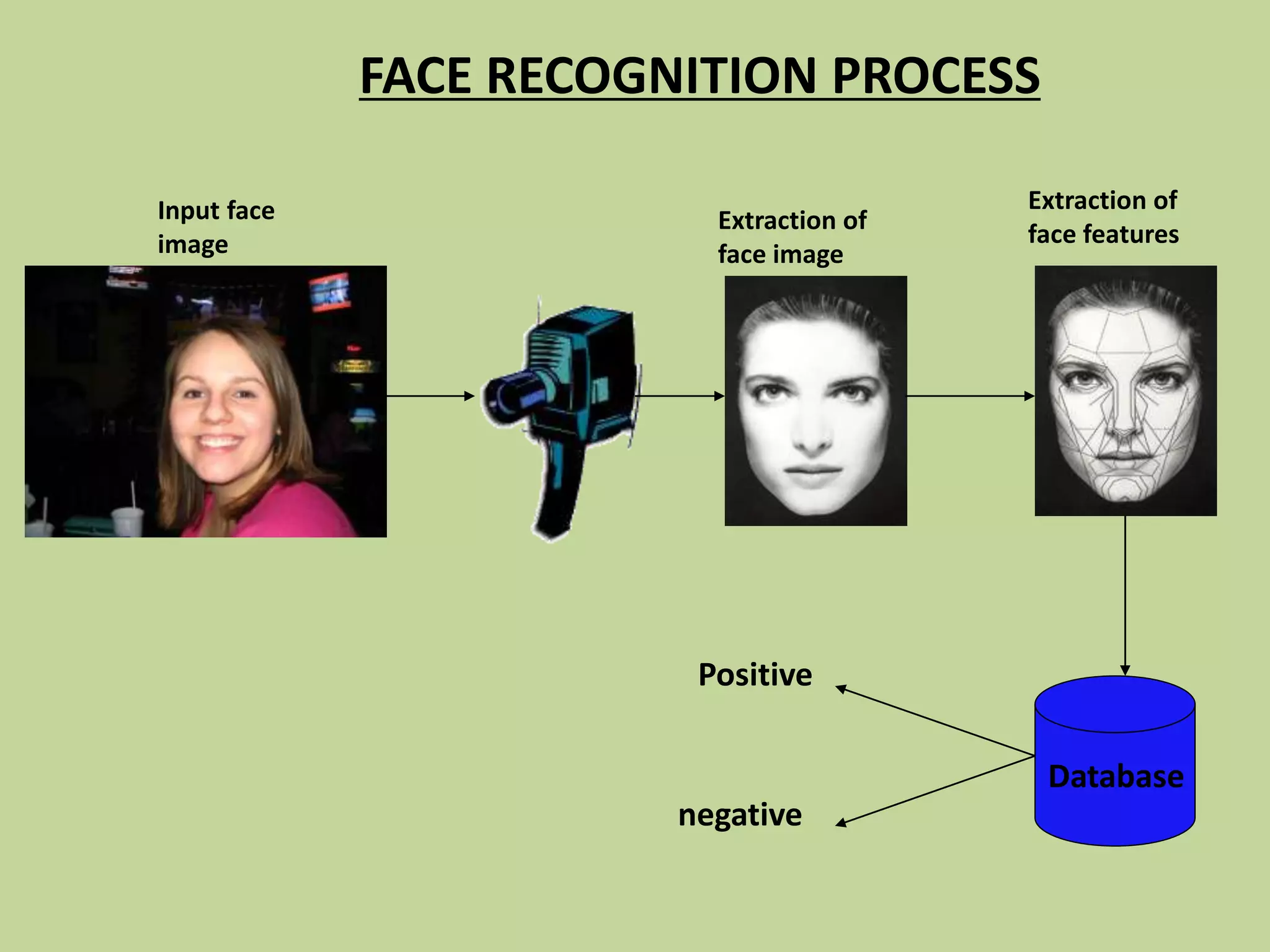
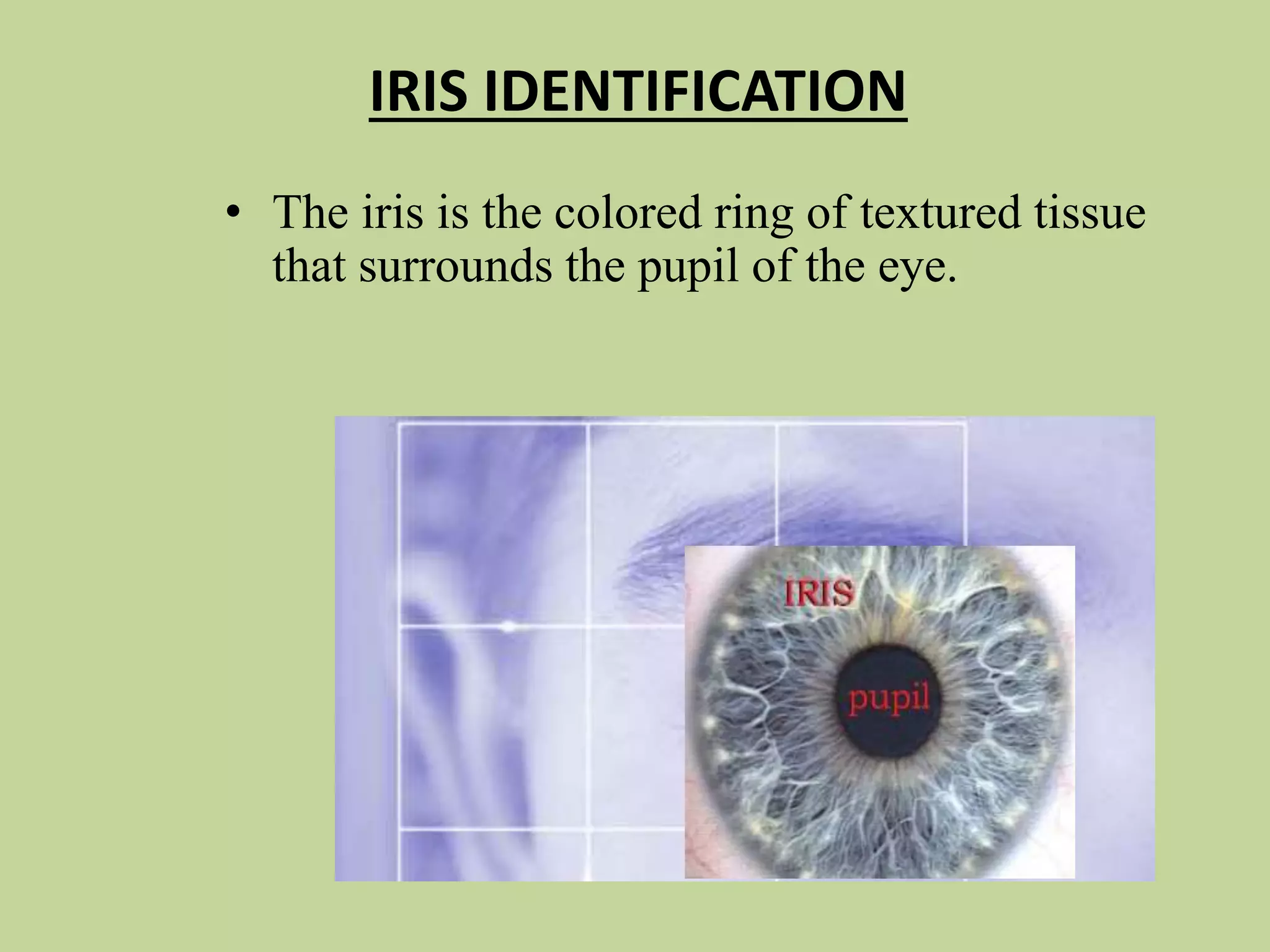
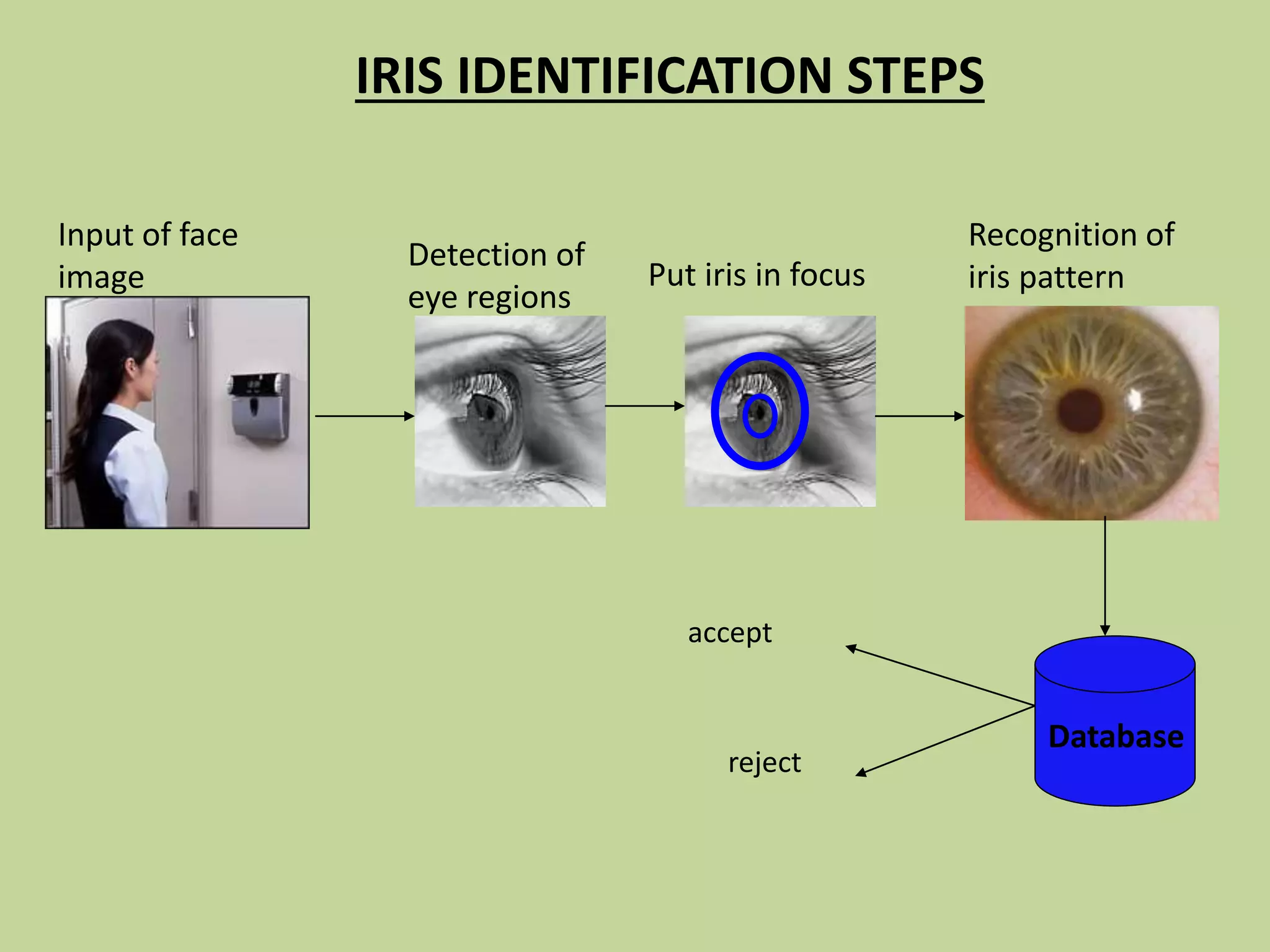
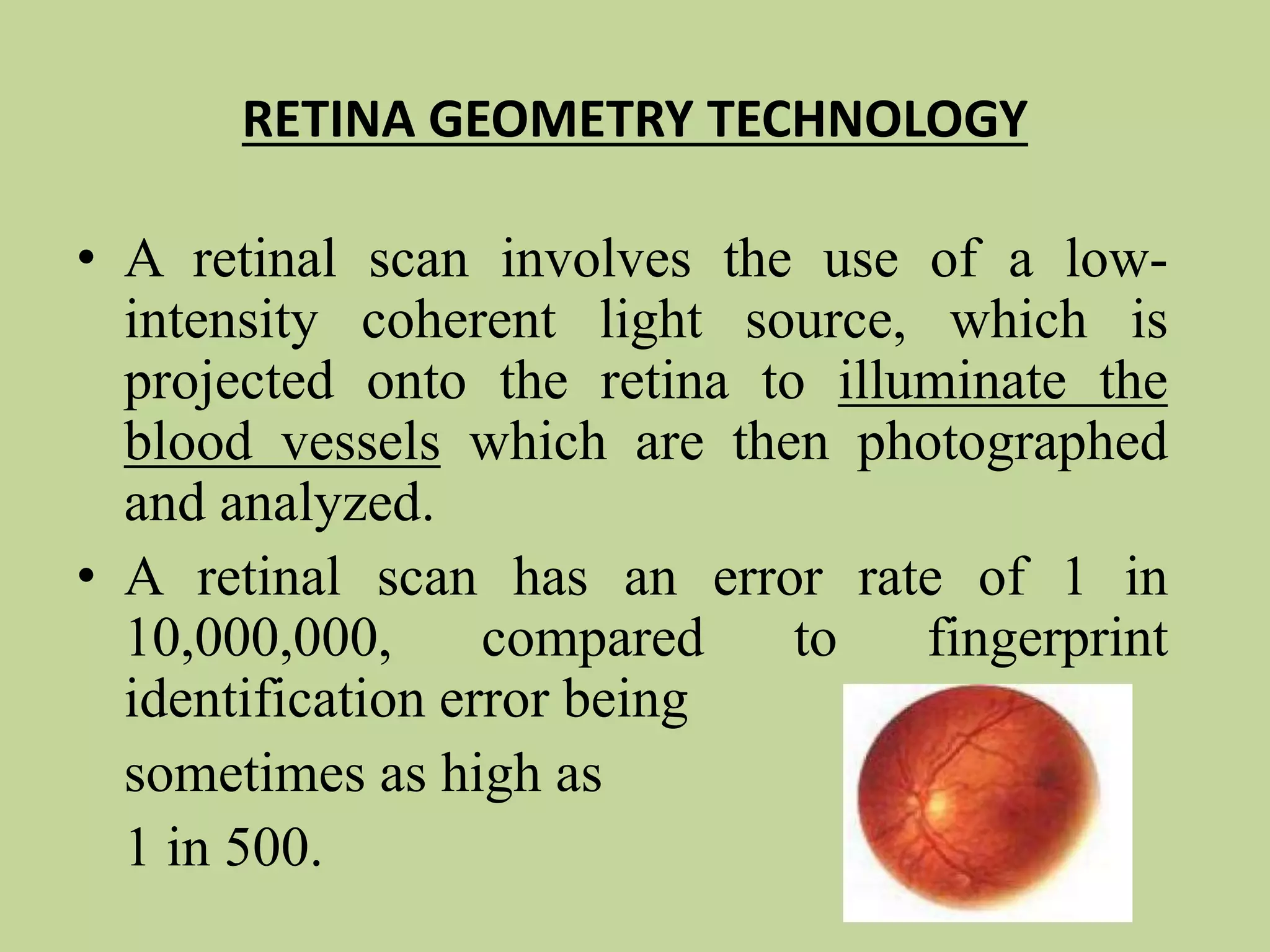
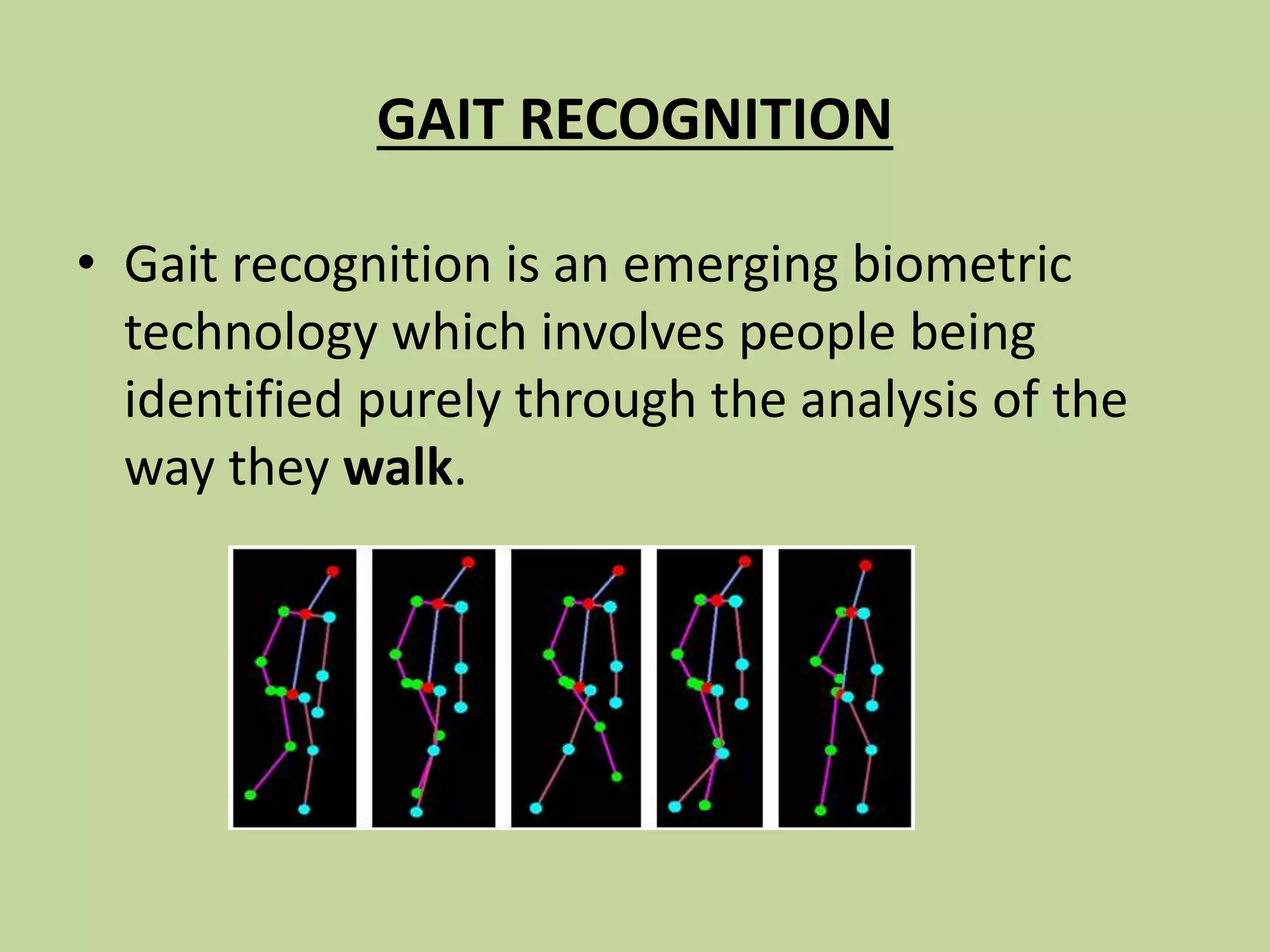
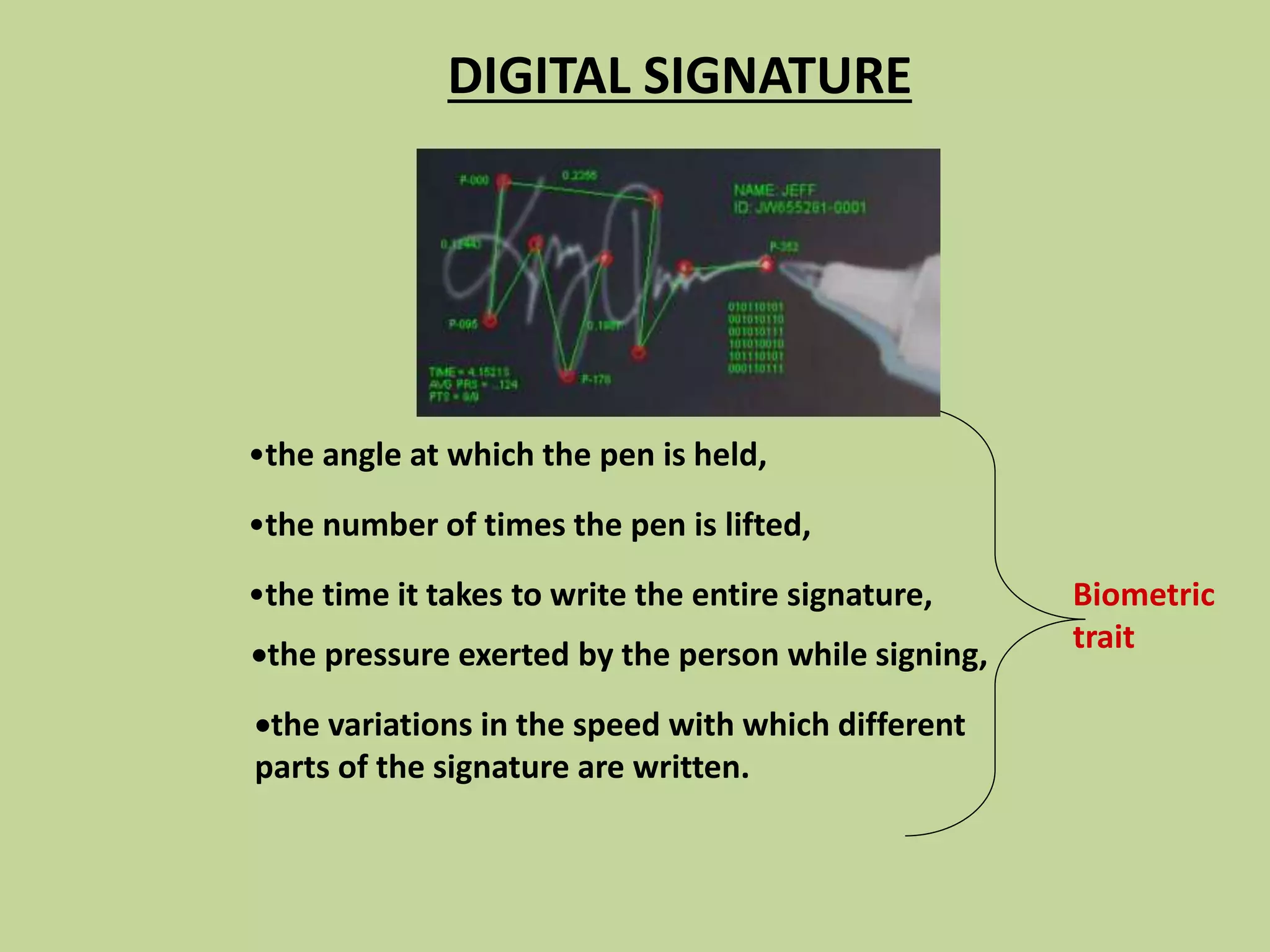
This document discusses biometrics, which uses physical and behavioral characteristics to identify individuals. It outlines various biometric technologies including fingerprints, palm prints, iris scans, retina scans, voice recognition, signatures, and keystrokes. The biometric process involves data collection, template generation, matching, and decision making. Benefits of biometrics include strong security, accountability, convenience, and reduced password administration costs.