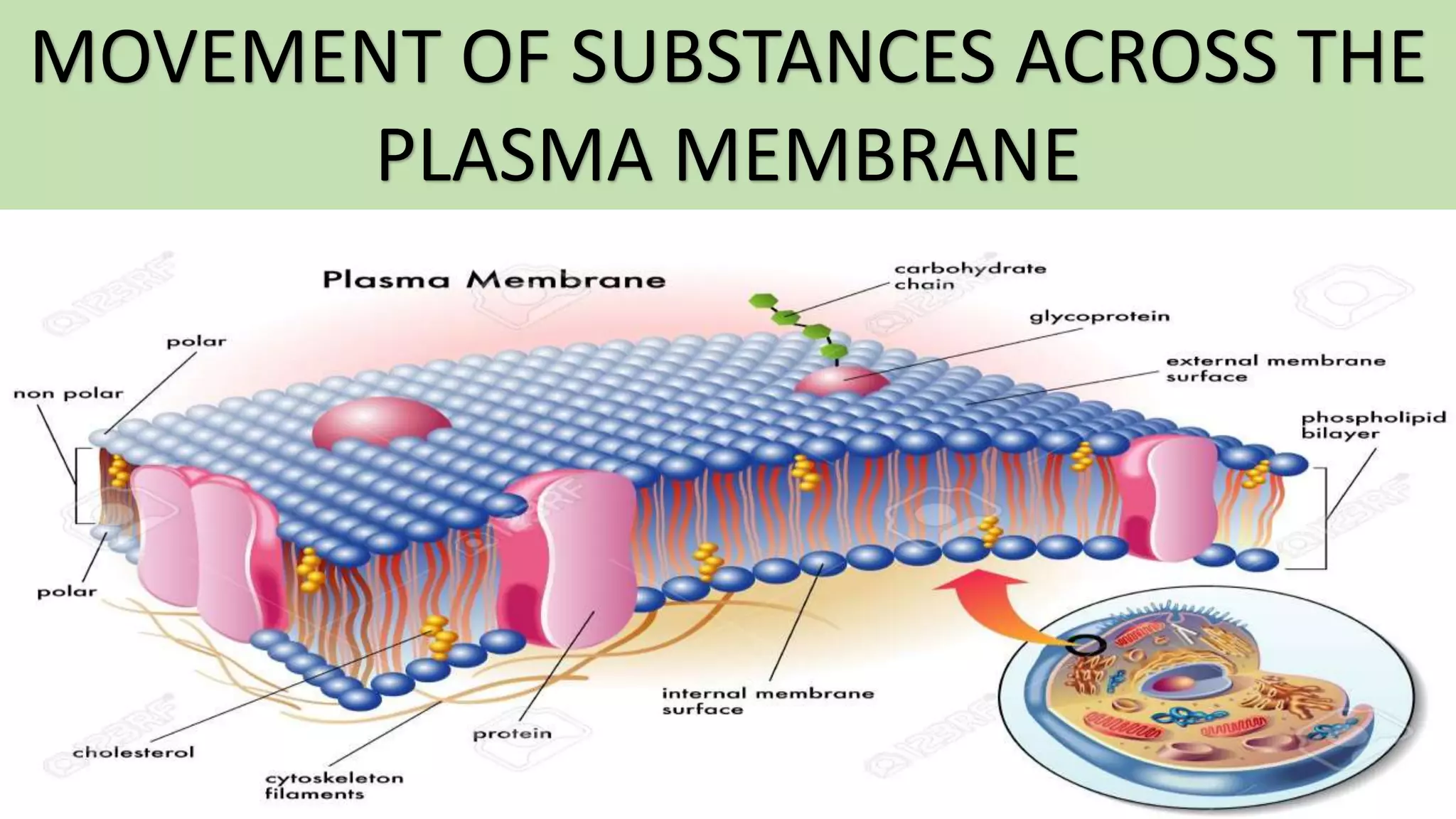
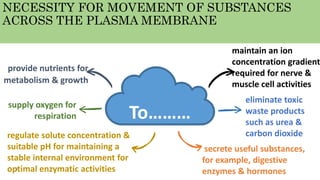
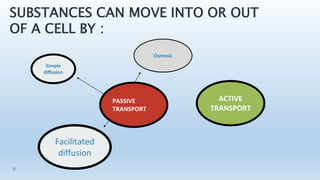
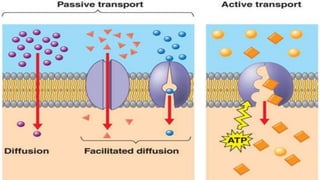
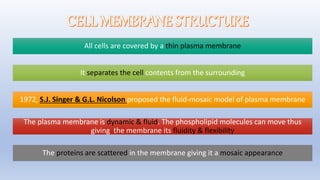
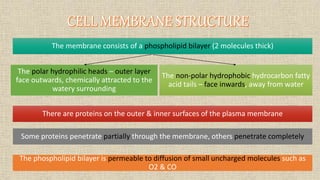
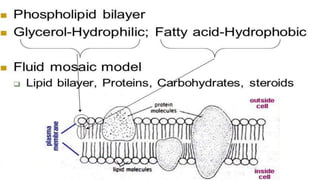
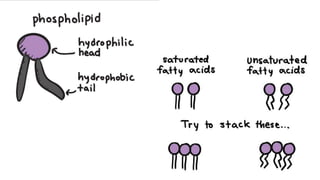
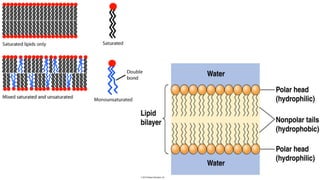
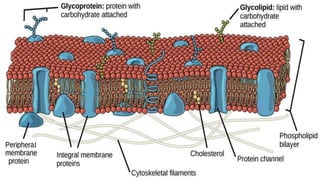
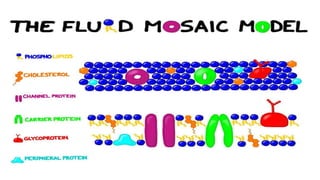
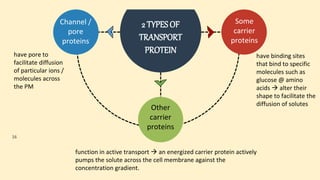
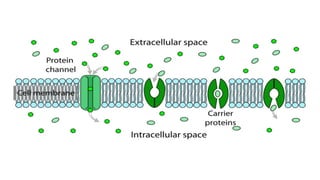
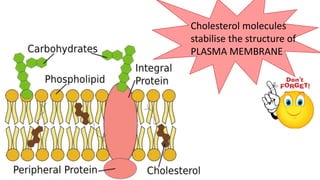
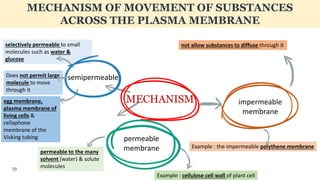
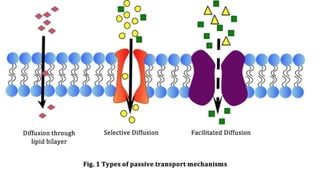
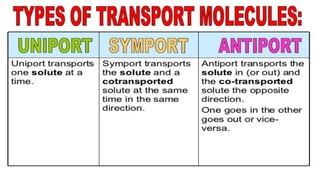
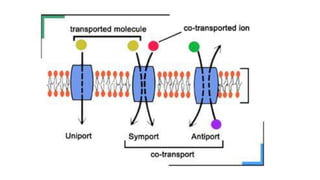
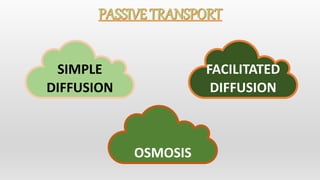
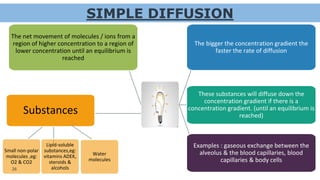
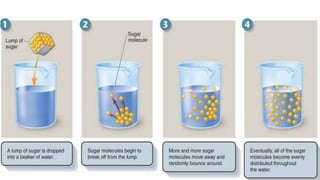
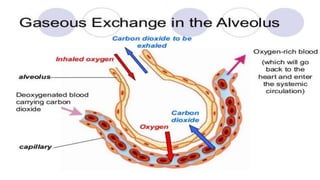
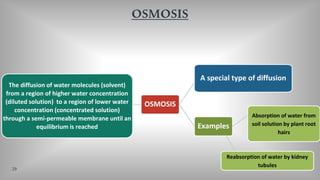
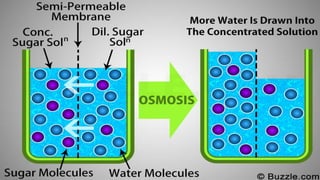
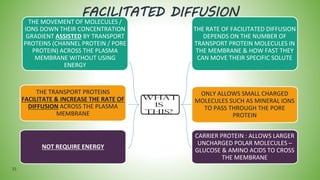
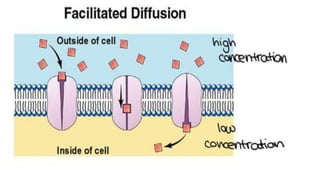
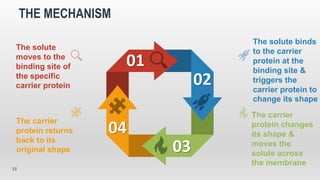
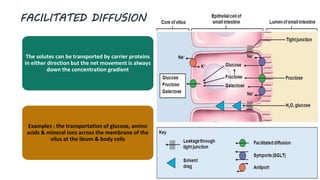
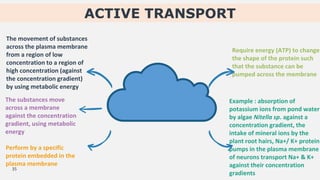
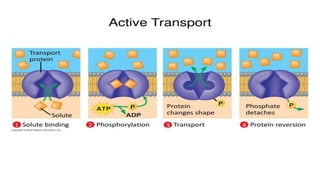
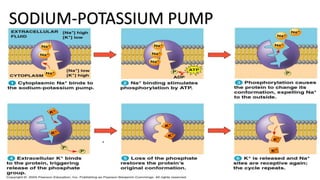
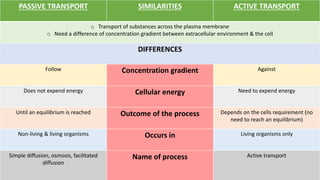
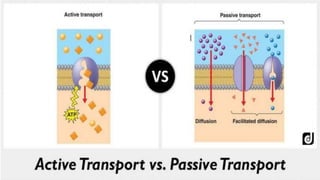
The document discusses the movement of substances across the plasma membrane in living cells. There are two main types of movement: passive transport, which moves substances down their concentration gradient without requiring energy, and active transport, which moves substances against their concentration gradient using energy from ATP. Passive transport includes simple diffusion, osmosis, and facilitated diffusion. Active transport is required to uptake nutrients from areas of lower concentration and pump out waste products against gradients.