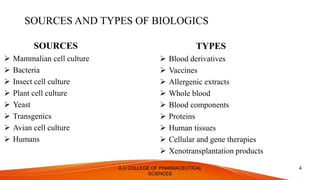
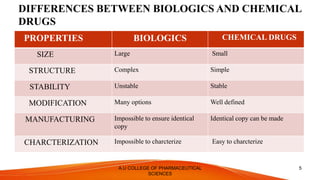
The document discusses the regulatory requirements for approval of biologics. It defines biologics as complex molecules produced through biotechnology from biological sources. The regulatory authority for biologics is the Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER) within the FDA. The approval process involves an Investigational New Drug Application, Biologics License Application, and approval or refusal. Key differences between biologics and chemical drugs are outlined regarding size, structure, stability and manufacturing. Regulatory guidelines in the US and EU are compared.