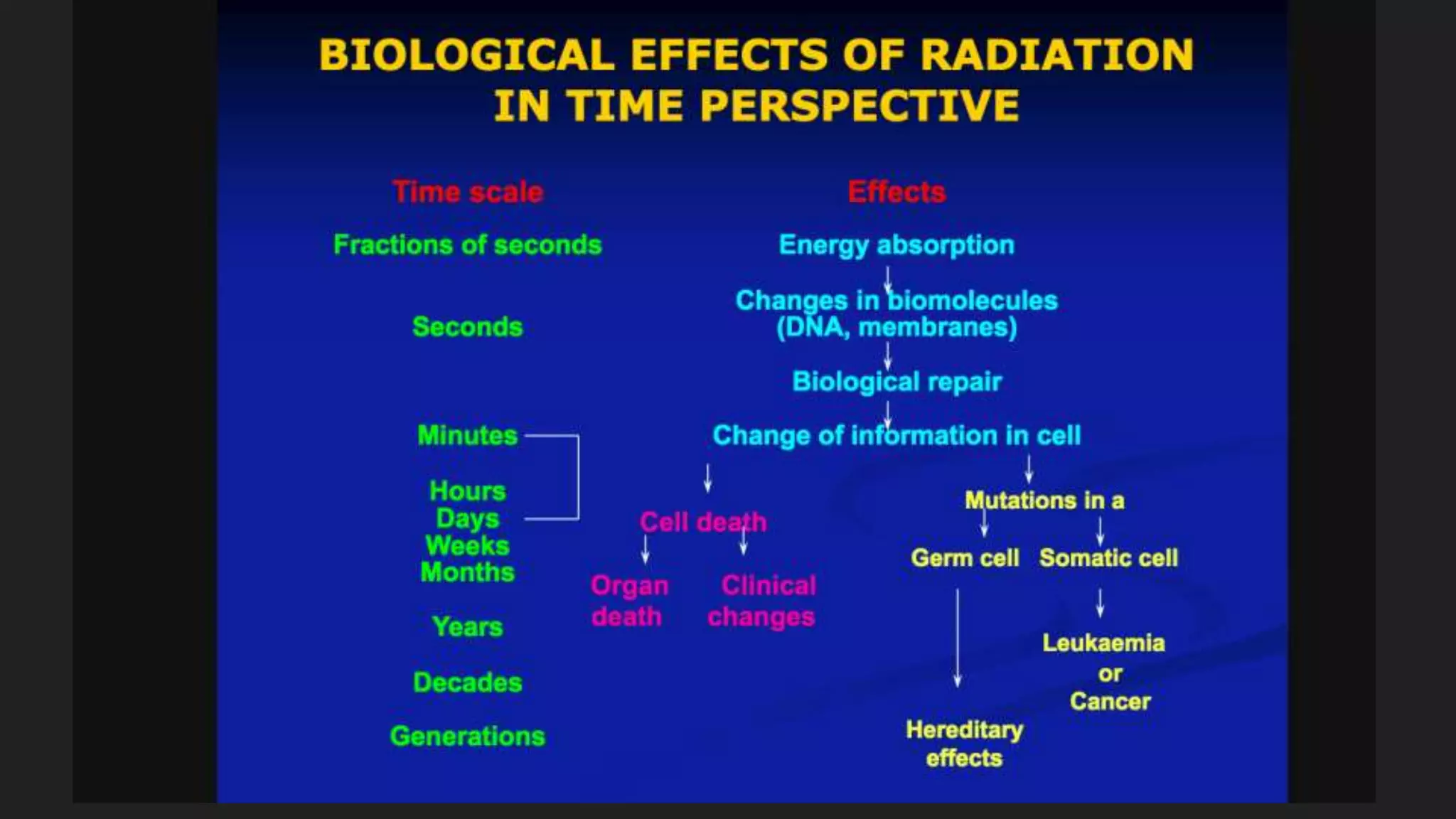
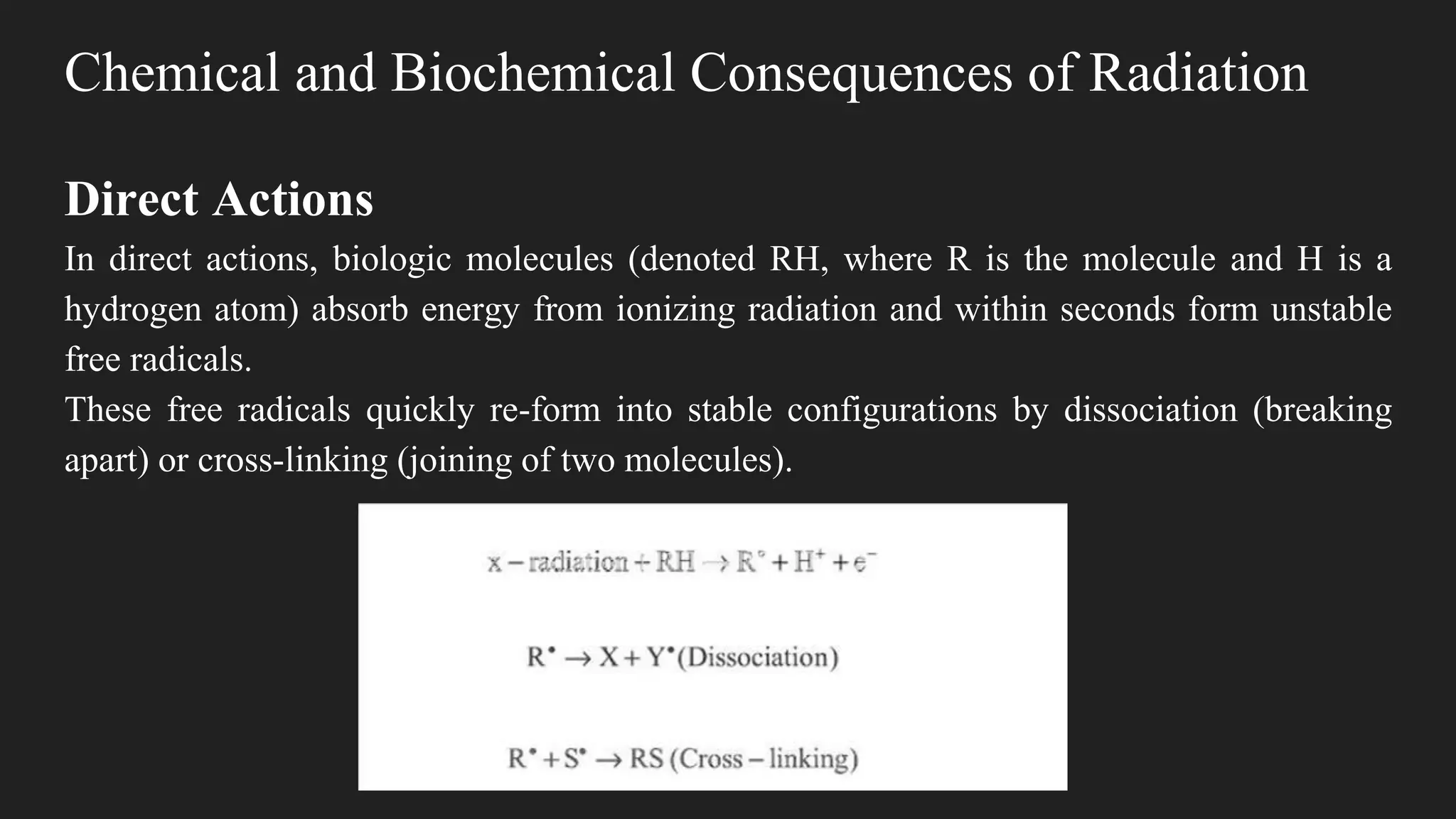
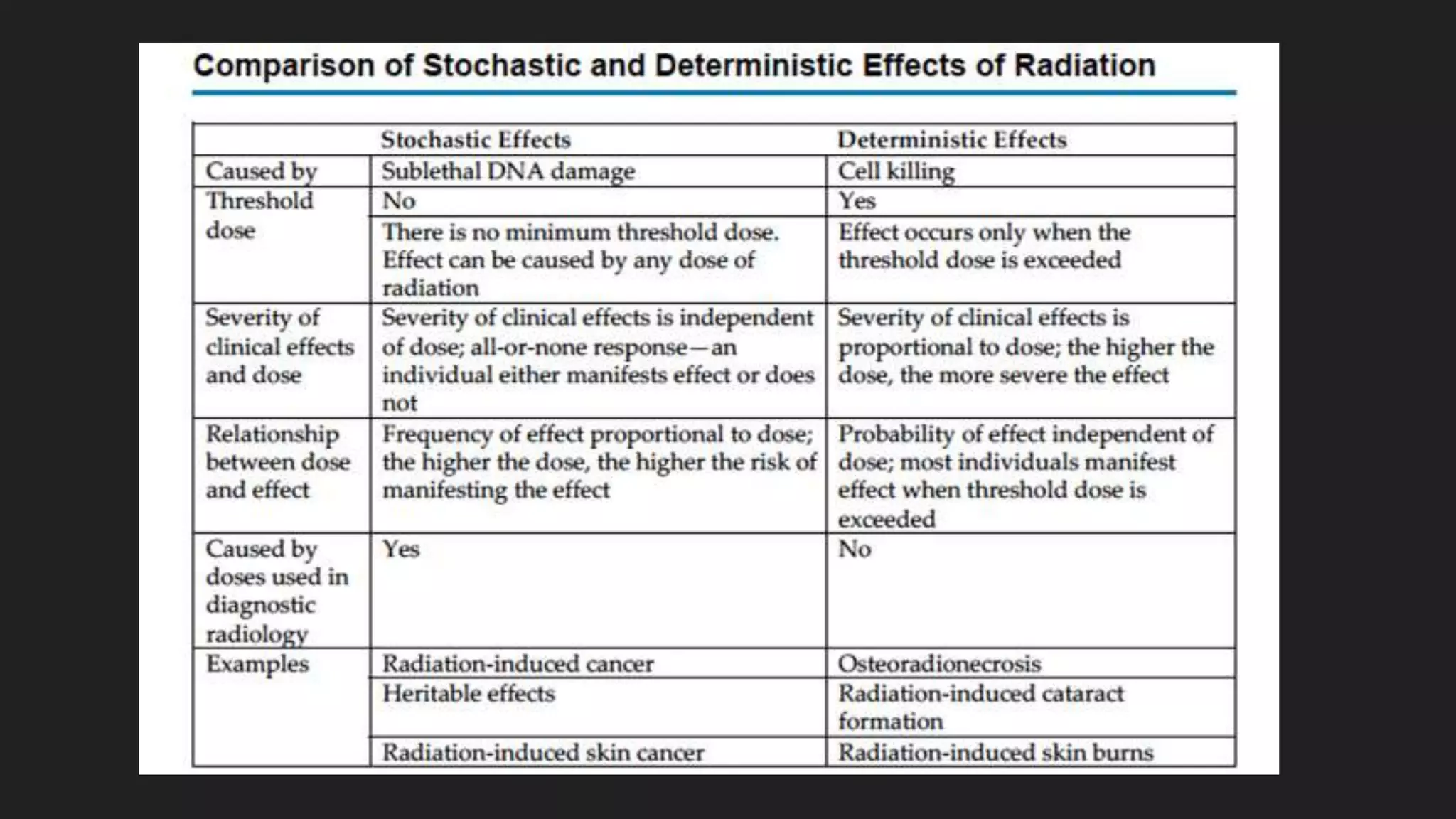
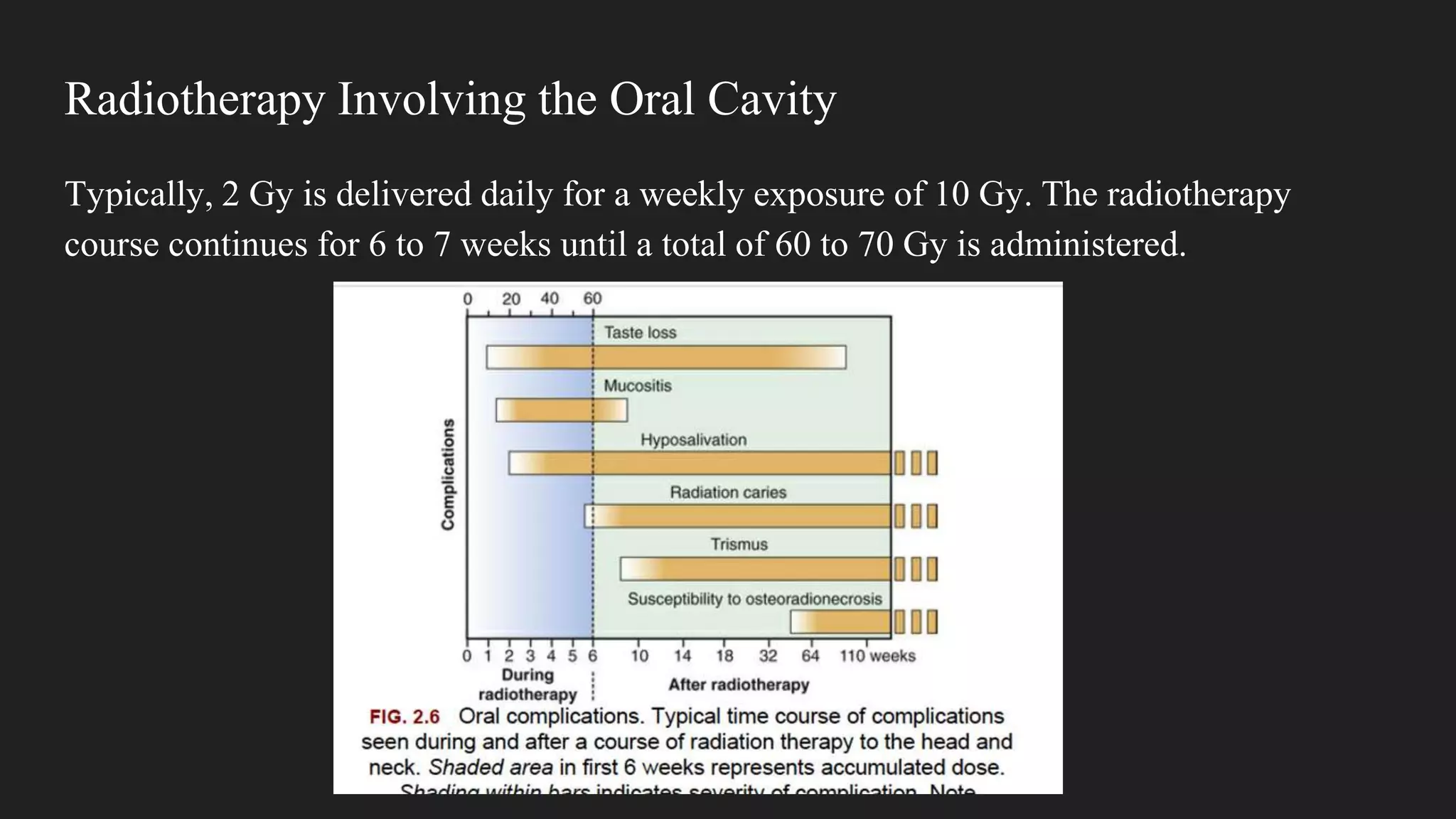
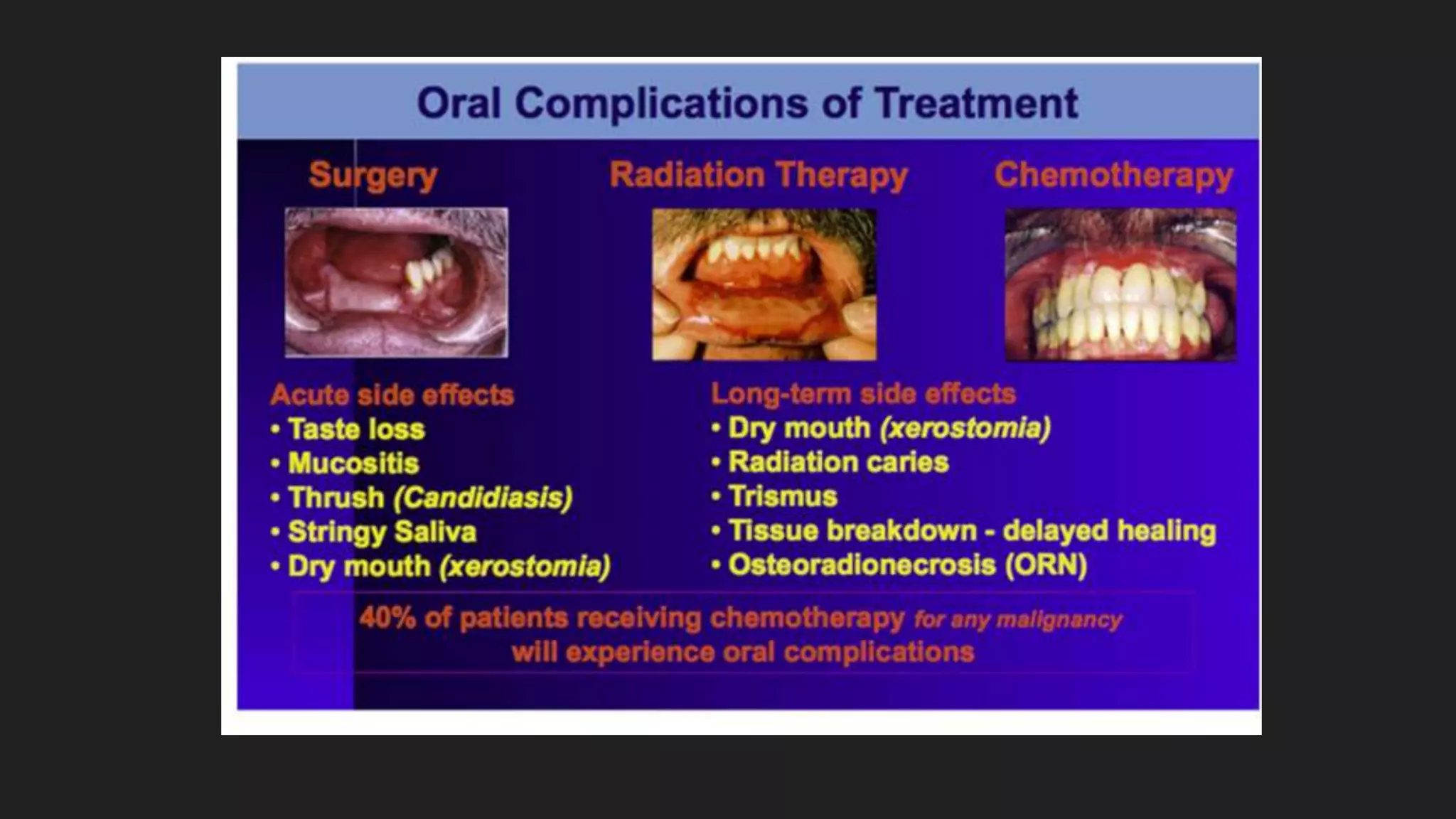
1) Ionizing radiation interacts with biological molecules like DNA and water to cause damage through direct and indirect actions within seconds to hours.
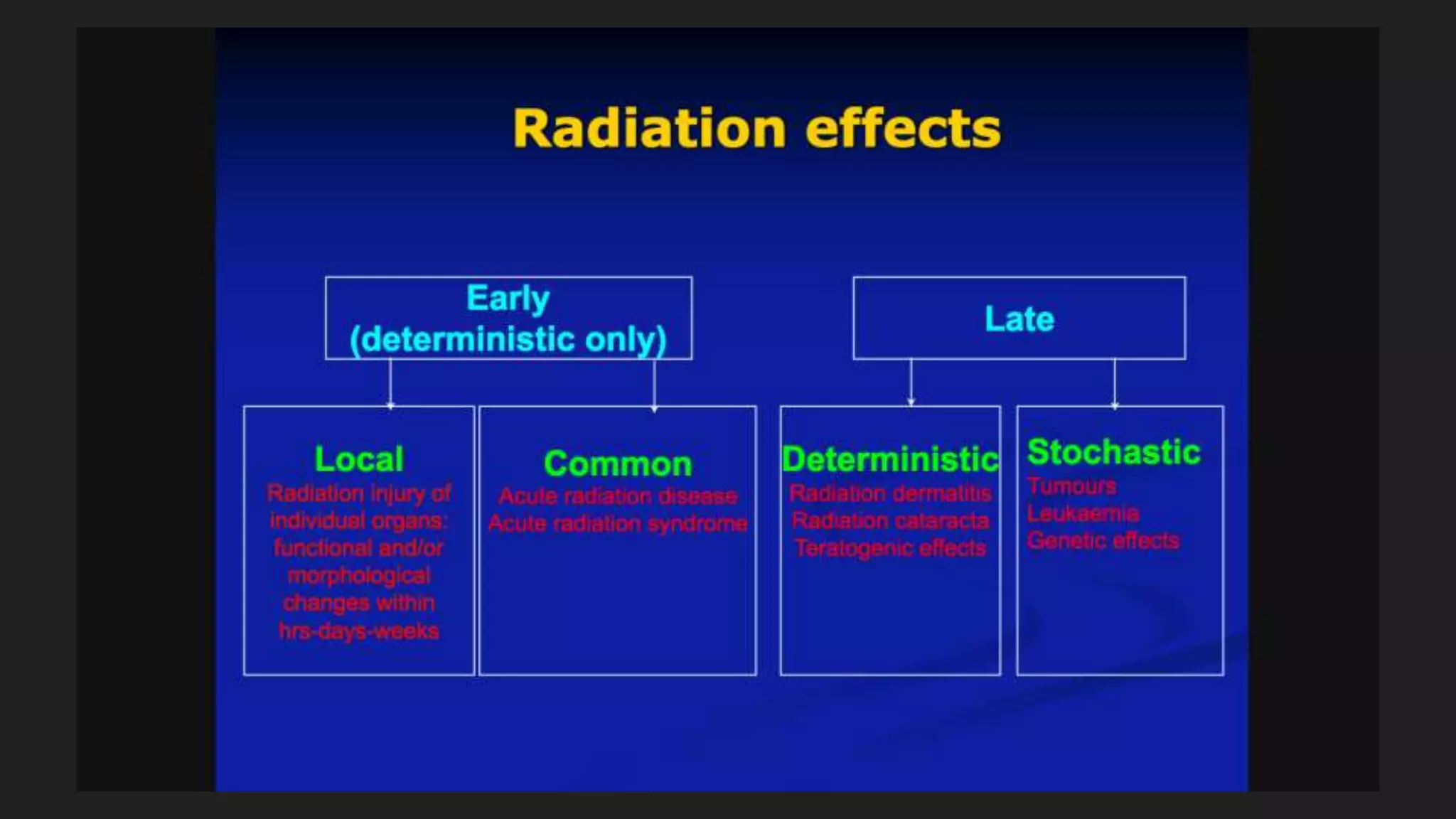
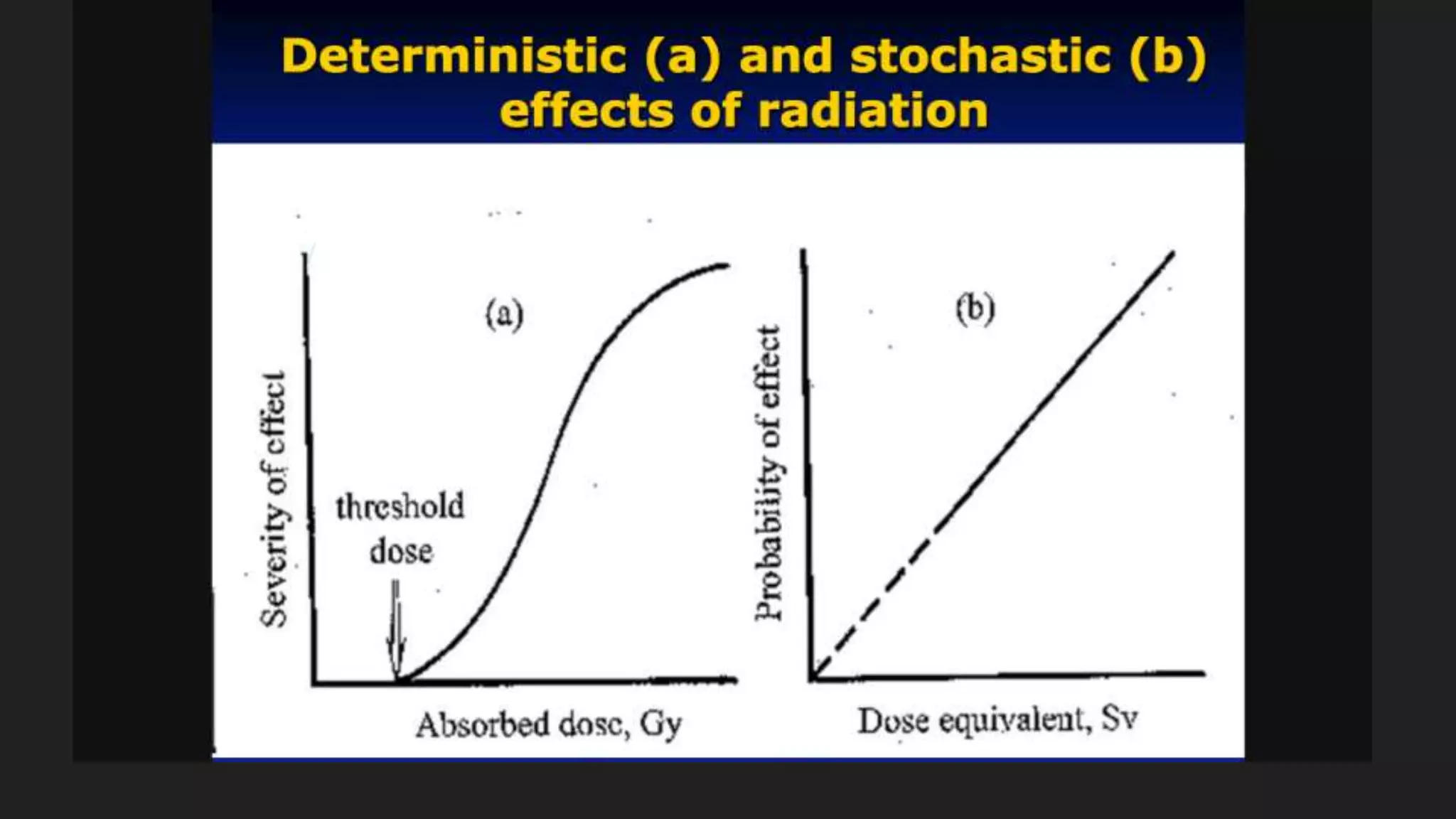
2) This damage can manifest as cell death, mutations, and cancer over time from hours to generations depending on the extent of damage.
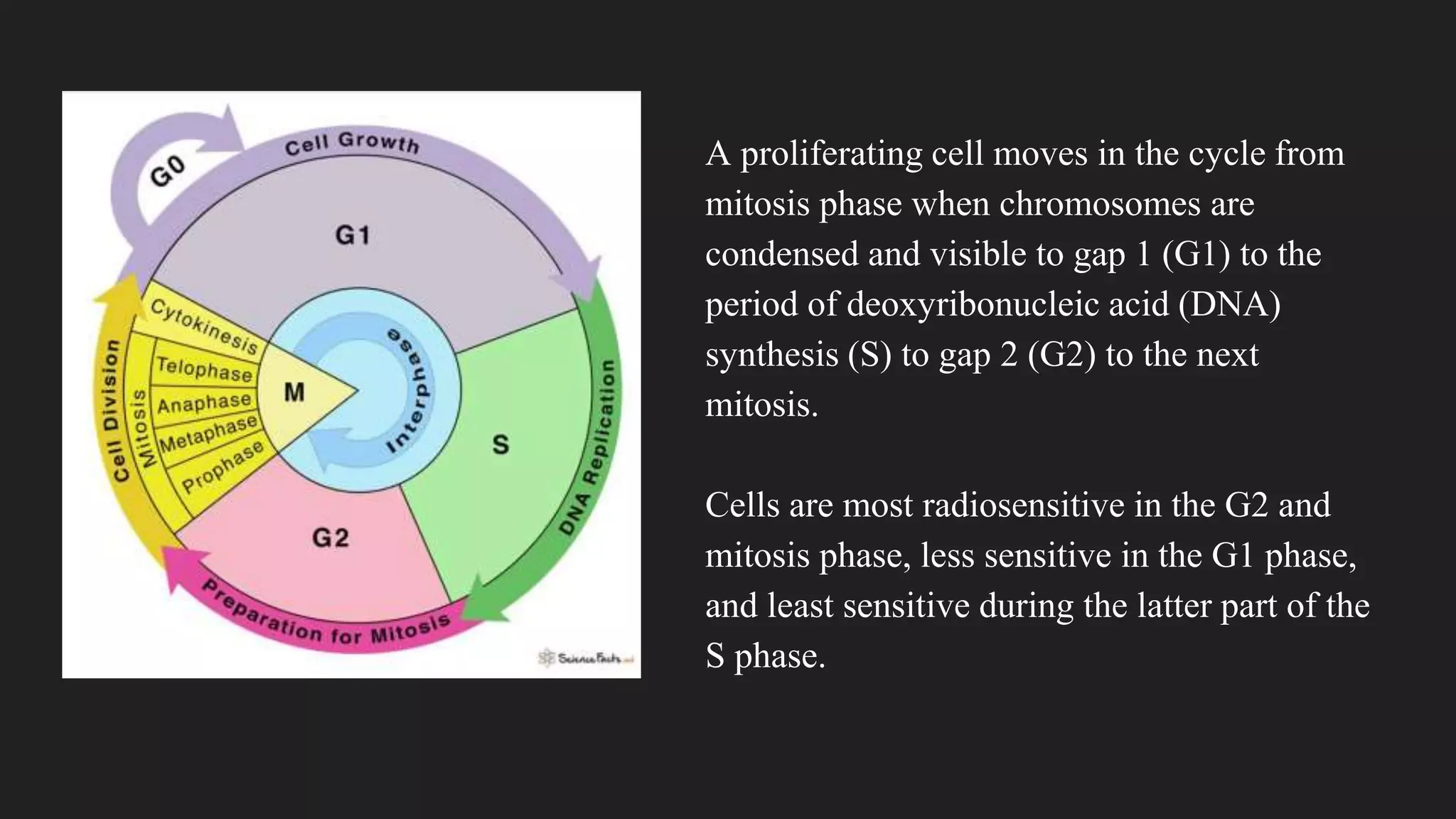
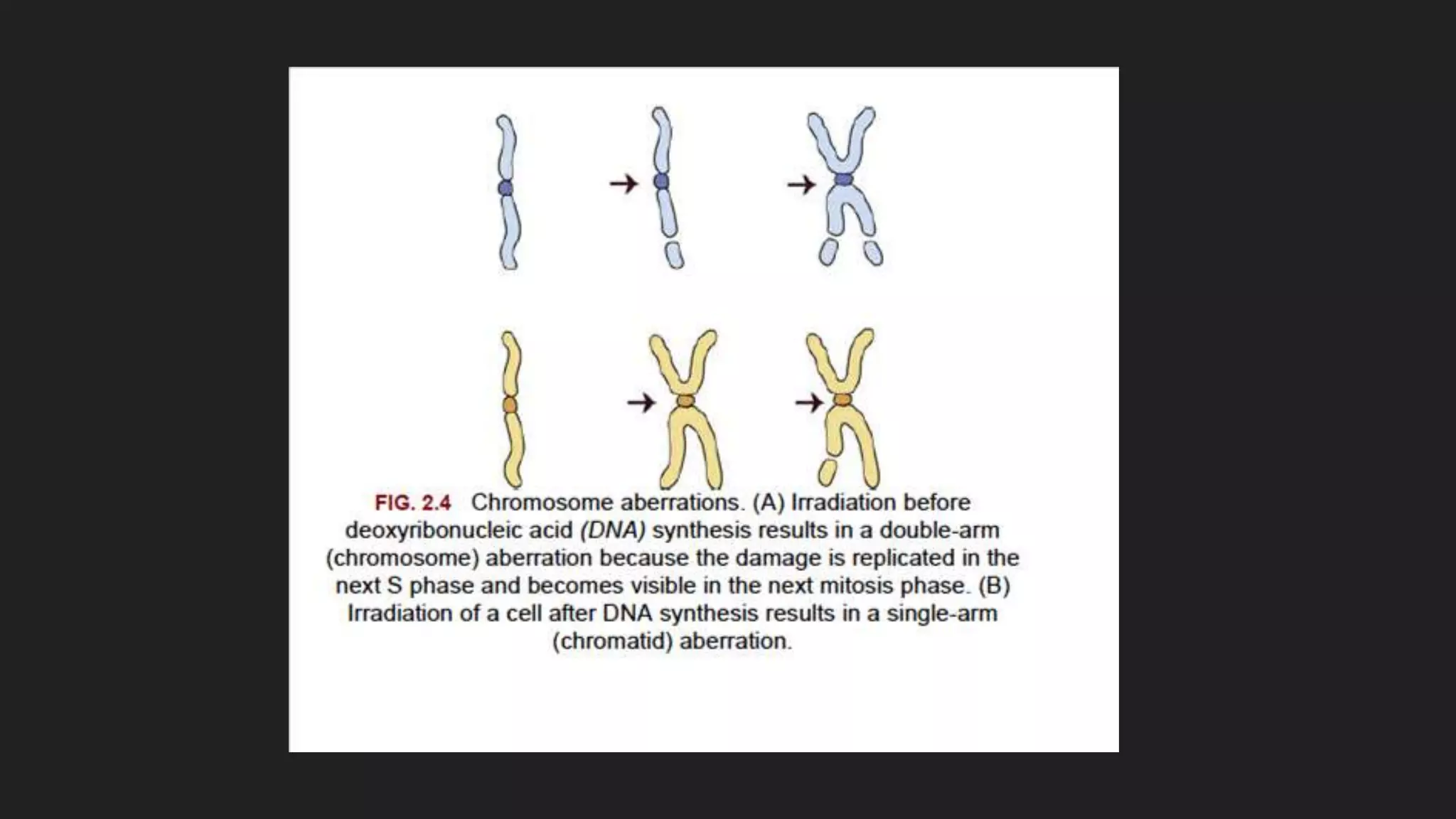
3) Radiation damages cells most during the G2 and mitosis phases of the cell cycle and causes cell death primarily through mitotic catastrophe and chromosomal abnormalities, except in lymphocytes and salivary glands where apoptosis is more common.