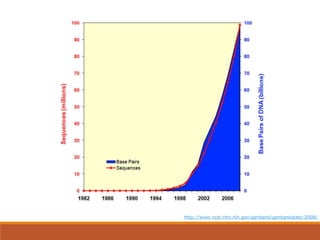
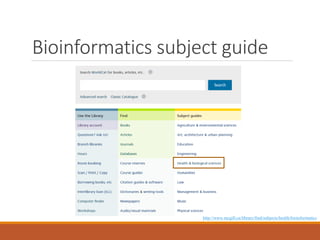
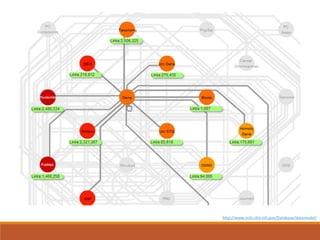
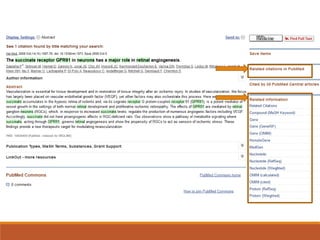
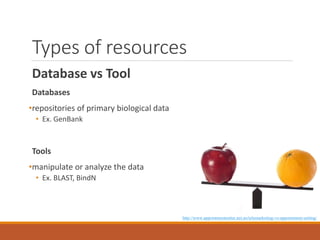
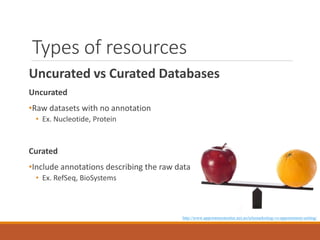
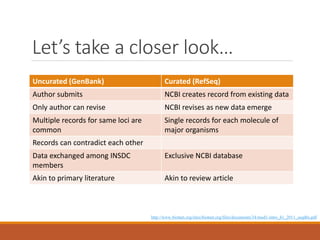
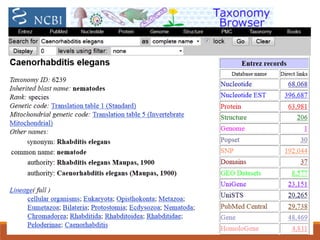
This document provides an introduction and overview of bioinformatics resources. It begins by outlining the objectives of understanding different bioinformatics databases and tools, learning how to search and navigate the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) database, and finding additional help. Definitions of bioinformatics are provided. The document then describes various applications of bioinformatics and directs the reader to a subject guide on bioinformatics resources. It proceeds to categorize major types of freely available bioinformatics resources as databases versus tools, and as curated versus uncurated databases. Specific examples like GenBank, BLAST, and RefSeq are outlined. The document concludes by providing contact information for questions.


![Bioinformatics is…
“…us[ing] computers to store, retrieve,
analyze or predict the composition or the
structure of biomolecules”
-Bioinformatics.org
“…the integration of computers, databases
and software into research projects that
address large biological questions, or
problems”
-UBC, What is Bioinformatics?
http://web.archive.org/web/20041210092942/http://bioinformatics.org/faq/
http://www.bioteach.ubc.ca/what-is-bioinformatics/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bioinformaticsresourcesprimer-140223185142-phpapp01/85/Bioinformatics-resources-a-primer-3-320.jpg)