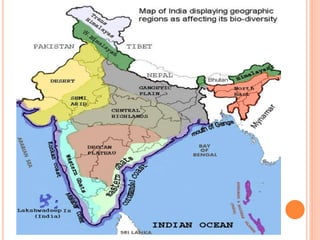
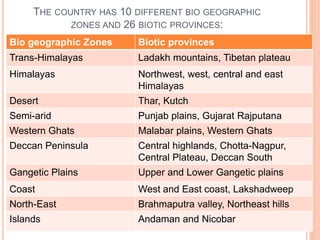
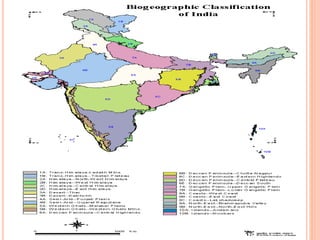
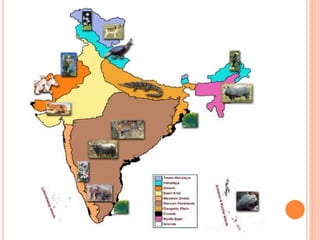
India has 10 major biogeographic zones based on geography, climate, vegetation and wildlife:
1) Trans-Himalayan region north of the Great Himalayas has sparse vegetation but the richest wild sheep and goat community and snow leopard.
2) Himalayas have very dense forests and grasslands and are home to monal, wild sheep, mountain goats, ibex, panda, and snow leopard.
3) Semi-arid areas between deserts and Western Ghats have thorn forests and support species like lions, birds, jackals, and buffaloes.
4) Western Ghats are one of the world's unique biological regions with high endemism