The document summarizes several biogeochemical cycles:
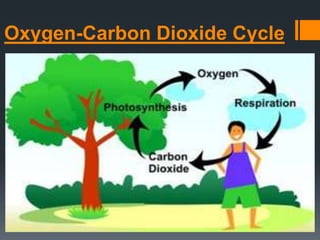
- The oxygen-carbon dioxide cycle involves the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between living things and the atmosphere through photosynthesis and respiration.
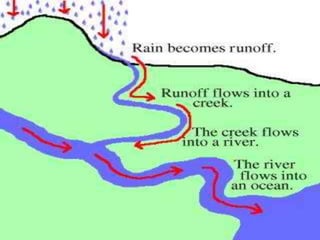
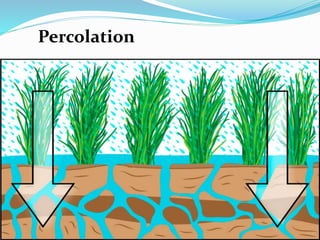
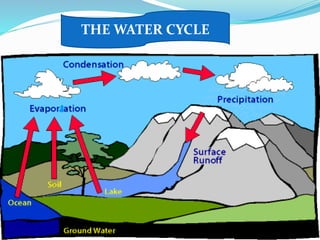
- The water cycle describes the continuous movement of water on, above, and below the Earth's surface through processes like evaporation, condensation, precipitation, and runoff.
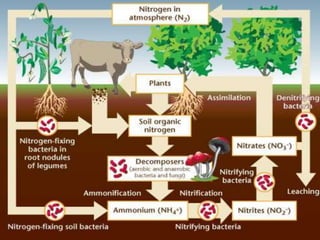
- The nitrogen cycle involves nitrogen-fixing bacteria converting nitrogen to ammonia, decay and nitrification processes, and denitrification returning nitrogen to the atmosphere.