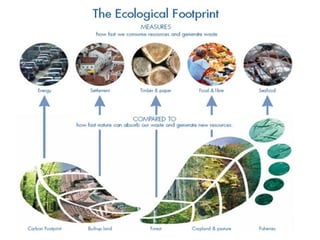
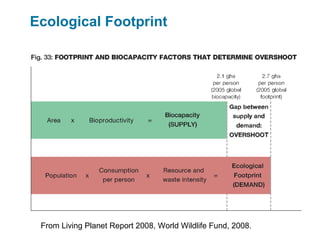
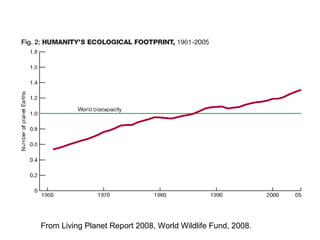
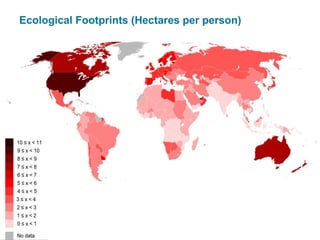
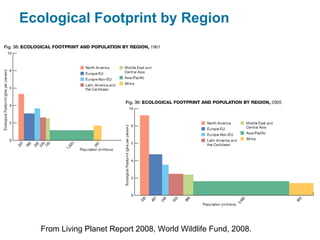
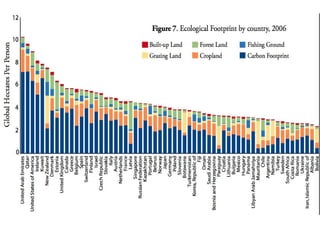
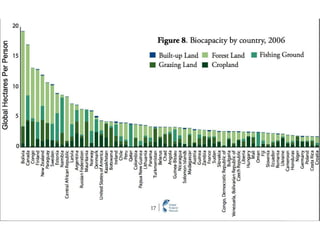
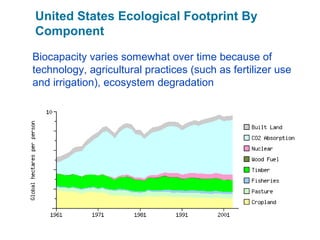
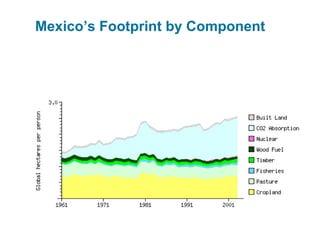
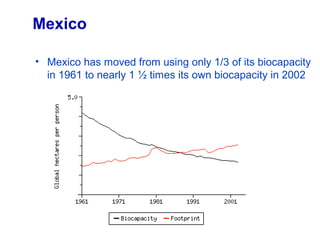
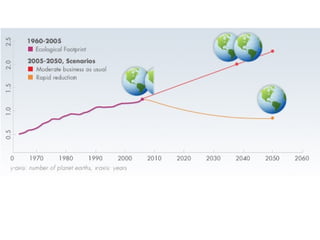
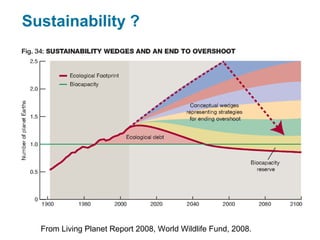
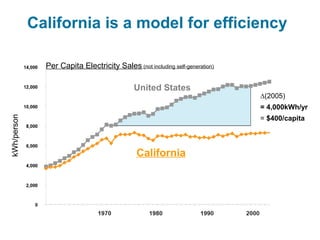
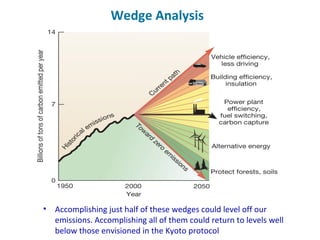
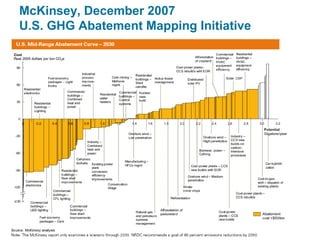
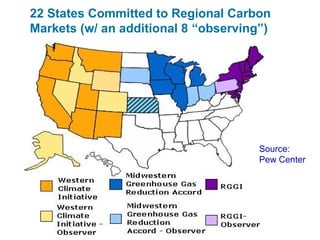
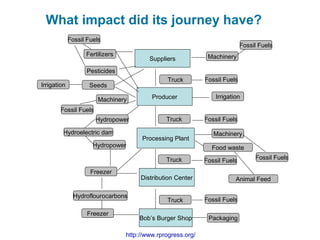
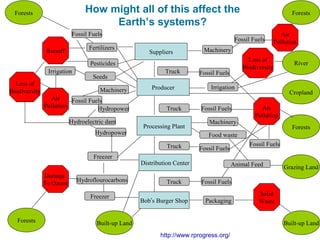
Ecological footprints measure the extent of biologically productive land and sea area required to produce the resources an individual, population or activity consumes and to absorb the corresponding waste, using prevailing technology levels. They are measured in global hectares, where one hectare represents the world average productivity. Current estimates indicate that humans are overshooting Earth's carrying capacity by 25-50% and that at current population growth and consumption rates, we will need 1.5 Earths by 2030 to sustain our footprint.