Bio110 practice problems chap4
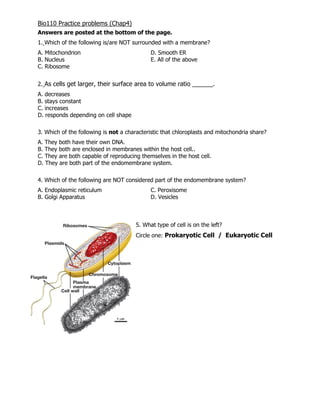
- 1. Bio110 Practice problems (Chap4) Answers are posted at the bottom of the page. 1. Which of the following is/are NOT surrounded with a membrane? A. Mitochondrion D. Smooth ER B. Nucleus E. All of the above C. Ribosome 2. As cells get larger, their surface area to volume ratio ______. A. decreases B. stays constant C. increases D. responds depending on cell shape 3. Which of the following is not a characteristic that chloroplasts and mitochondria share? A. They both have their own DNA. B. They both are enclosed in membranes within the host cell.. C. They are both capable of reproducing themselves in the host cell. D. They are both part of the endomembrane system. 4. Which of the following are NOT considered part of the endomembrane system? A. Endoplasmic reticulum C. Peroxisome B. Golgi Apparatus D. Vesicles 5. What type of cell is on the left? Circle one: Prokaryotic Cell / Eukaryotic Cell
- 2. Bio110 Practice problems (Chap4) 6. Fill in all the spaces in the plant cell below: 7. What are the functions of the following: (i) Ribosomes – (ii) Peroxisomes – (iii) Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) – (iv) Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER) – 8. Describe one advantage of compartmentalization in eukaryotic cells. 9. Which of the following is/are NOT part of, or product(s) of the Endomembrane System? Rough ER Smooth ER Nuclear envelope Ribosome Microtubules Vesicle Peroxisome Golgi apparatus Lysosome Motor proteins 10. The function of ribosomes attached to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is to ______. A. synthesize lipids for the cell and these lipids stay in the cell B. synthesize proteins for the cell and these proteins stay in the cell C. synthesize lipids for export and these lipids will leave the cell D. synthesize proteins for the cell and these proteins will leave the cell 11. The process of cells taking in large molecules is known as ______. A. endomembrane system C. endocytosis B. exocytosis D. trade deficit
- 3. Bio110 Practice problems (Chap4) 12. Which of the following is not a part of prokaryotes? A. DNA C. Cell wall B. Cell membrane D. Endoplasmic reticulum 13. Proteins synthesized by the rough ER are usually ______. A. for internal storage C. for internal regulation B. to build more membranes in the cell D. exported from the cell 14. Plant cells have ______, which are absent in animal cells. A. endoplasmic reticulum D. vesicles B. a central vacuole E. mitochondria C. Golgi apparatus 15. The smooth ER is especially abundant in cells that synthesize large amounts of ______. A. toxins D. lipids B. proteins E. nucleic acids C. enzymes 16. The endomembrane system is composed of the different membranous entities that are suspended in the cytoplasm within ________. A. fungal cells only D. animal cells only B. all eukaryotic cells E. all prokaryotic cells C. plant cells only 17. The cytoskeleton includes all of the following except ______. A. microtubules D. microfilaments B. intermediate filaments E. all of the above are included C. ribosomes 18. Ribosomes can be found _______. I. in organelles (mitochondria & chloroplasts) III. attached to the endoplasmic reticulum II. floating in the cytoplasm IV. only in eukaryotic cells A. I only D. I and II G. II, III and IV B. II only E. I, II and III C. III only F. II and III 19. The Golgi Apparatus is involved in ______. A. transporting proteins for export from the cell D. producing lysosomes B. packaging proteins into vesicles E. all of the above C. altering or modifying proteins 20. True / False (circle one) Since they have chloroplasts for energy production, plant cells lack mitochondria.
- 4. Bio110 Practice problems (Chap4) 21. True / False (circle one) The microtubules of cilia and flagella are organized in a characteristic 9+2 pattern, which allows them to slide past one another. 22. Fill in the blanks in the box below. Use the following terms: Lysosomes Plasma membrane Centriole Microtubules Chloroplasts Centrosome Mitochondria Cytoskeleton Peroxisomes Vacuole Smooth ER Nuclear pore Ribosome Chromosomes Golgi apparatus DNA Microfilaments Nuclear envelope Endomembrane system Rough ER Cell component Function a. Membrane enclosing the nucleus; separates it from the cytoplasm b. Extensive system of interconnected network of membranes and vesicles that processes proteins, lipids and lysosomes bound for the cell (such as lysosomes) or for export c. Membrane-enclosed sacs that processes, modifies and packages proteins from the ER on their way to their destination d. Organelle that contain enzymes for digestion of complex molecules e. Genetic material of the cell tightly-wound around DNA-binding proteins, located the nucleus. f. Bilayer made of phospholipids with embedded protein molecules surrounding all cells, separating cytoplasm from the outside g. Organelle responsible for conversion of sunlight energy into chemical energy (carbohydrates) h. General support structure for cell, responsible for crawling, and swimming motion of cell i. Organelle responsible for converting chemical energy into cellular energy, ATP j. Component of cytoskeleton that serve as tracks for organelle movement, separating divided chromosomes. k. Membranous compartment that stores mainly water, found only in plants l. Site where proteins are assembled and modified before they head to the Golgi Apparatus via vesicles m. Complex where microtubules are synthesized, contains centrioles. 23. Put Koch's Postulates in the proper order. (1) The microbe can be isolated and grown in pure culture outside of the host. (2) The same microorganism must then be isolated from the inoculated animal. (3) The microbe is present in every animal with the disease, and absent in healthy ones. (4) The cultured microorganism must cause the same disease in inoculated animals. A. 1, 2, 3, 4 C. 3, 1, 4, 2 B. 3, 4, 1, 2 D. 3, 2, 4, 1
- 5. Bio110 Practice problems (Chap4) 24. How does ethanol (alcohol) kill bacterial cells? A. By disrupting cell membrane phospholipids followed by cell dehydration and death. B. By denaturing cell membrane proteins followed by cell dehydration and death. C. By denaturing mitochondrial membrane proteins followed by mitochondrial death. D. By disrupting mitochondrial membrane phospholipids followed by mitochondrial death. 25. Which of the following is NOT the definition of a haplotype? A. It is a collection of SNPs inherited together from our parents. B. It is a collection of SNPs which are physically-linked on a chromosome. C. It is usually a single unique SNP. D. It distinguishes the genome of an individual from the genome of others. 26. How do SNPs arise? A. By CRISPR gene editing. C. By radiation such as UV and X-rays. B. By random mutation during DNA replication. D. All of the answers are correct. 27. Which of the following best describe a clone? A. The DNA of the clone is identical to the DNA of one of the parents. B. Clones can occur naturally. C. Clones can be created in labs. D. All of the answers are correct. 28. What is another name for producing genetically identical copies of living organisms? A. Gene editing C. Reproducing B. Cloning D. Mating 29. How are adult stem cells different from embryonic stem cells? A. Unlike embryonic stem cells, adult stem cells are not able to differentiate into all cell types. B. Adult stem cells can perform more functions than an embryonic stem cell can. C. It is less ethical to use adult stem cells than embryonic stem cells. D. Adult stem cells can differentiate into more cell types than embryonic stem cells. 30. Aside from technical difficulties in safely clone or gene edit cells, what other issues have to be considered in whether to allow human cloning or gene editing? A. Ethical issues. C. High rates of abnormalities in subjects. B. Moral issues. D. All of the above. 31. True / False (circle one) It is now safe to use cloning and CRISPR-Cas9 to edit genes in the human genome without any drawbacks.
- 6. Bio110 Practice problems (Chap4)
