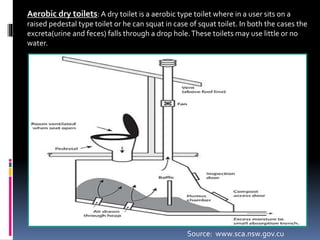
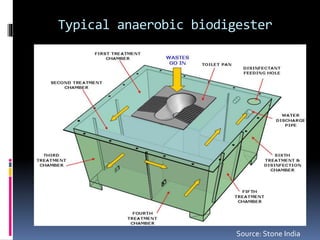
Bio-toilets are thermophilic digesting toilets that can be classified into aerobic dry toilets and anaerobic digesters, suitable for various uses including public utilities. With over 600 million people in India lacking proper sanitation, bio-toilets offer eco-friendly solutions by decomposing waste and eliminating pathogens, while also reducing the burden on sewer systems. They require less space and maintenance compared to traditional septic tanks and contribute positively to health and environmental conditions.