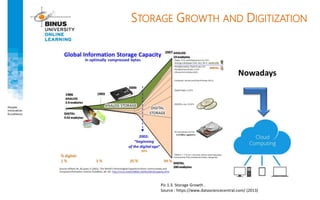
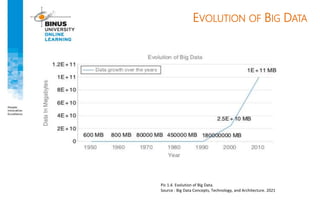
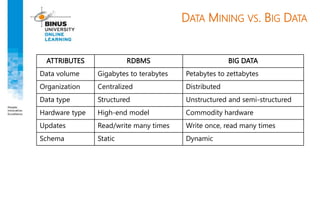
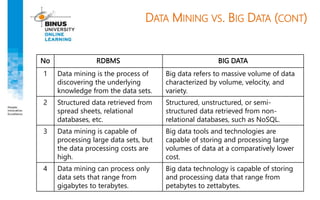
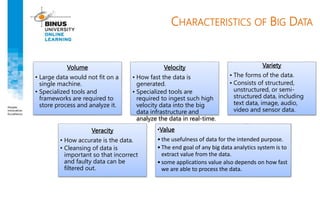
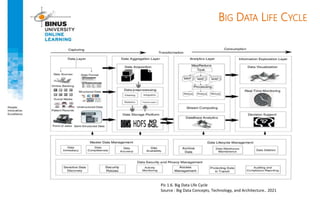
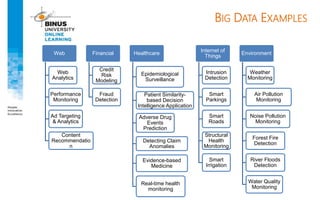
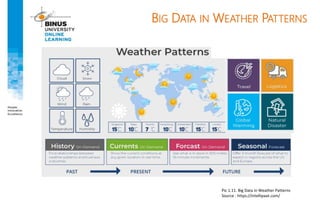
Big data refers to large, complex datasets that cannot be processed by traditional databases. It is characterized by volume, velocity, and variety. Challenges include storage, analysis, and privacy of heterogeneous data from various sources like the internet, sensors, and financial transactions. Key technologies for big data include Hadoop, HDFS, and MapReduce which allow distributed processing of large datasets across commodity servers.