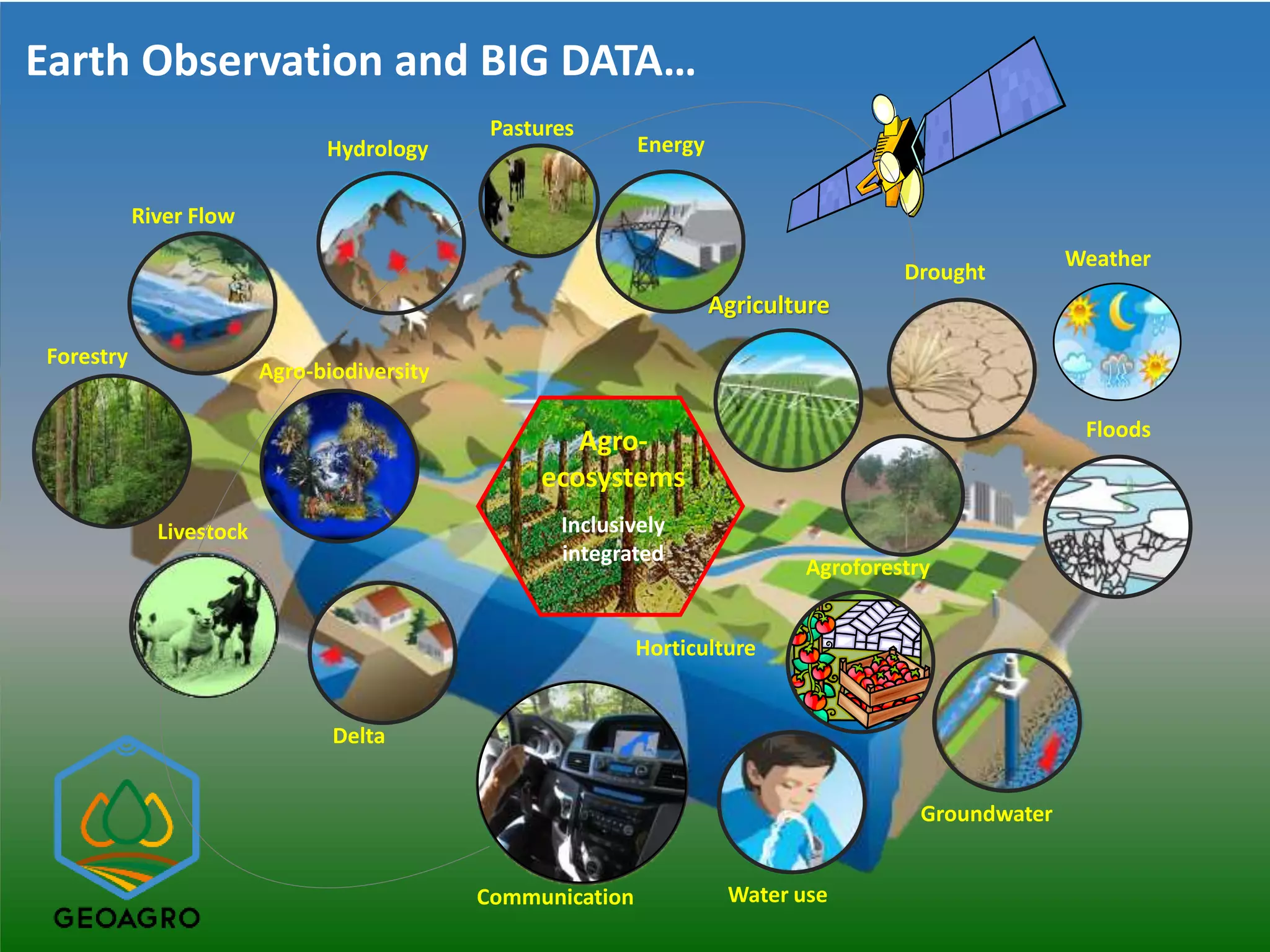
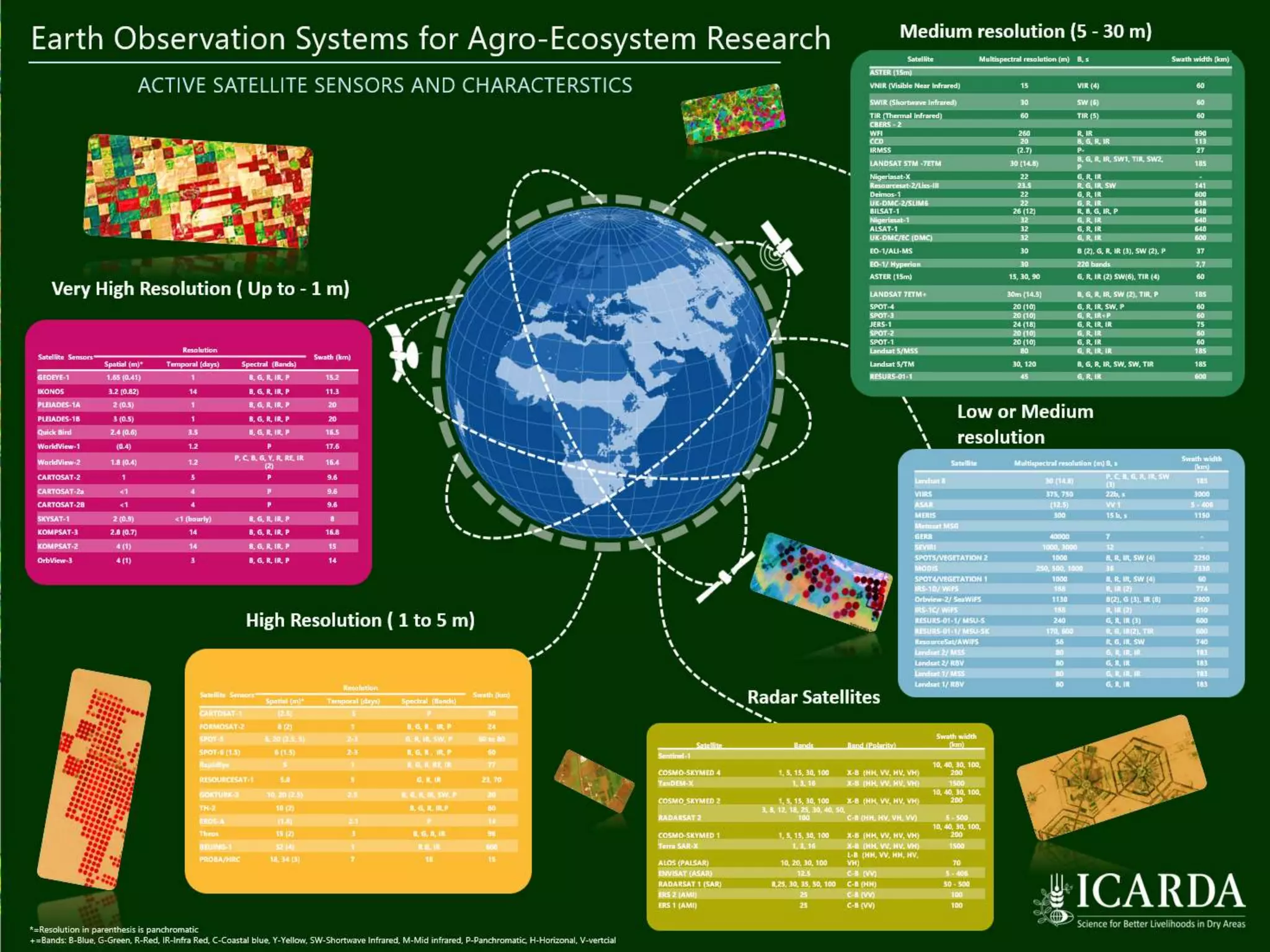
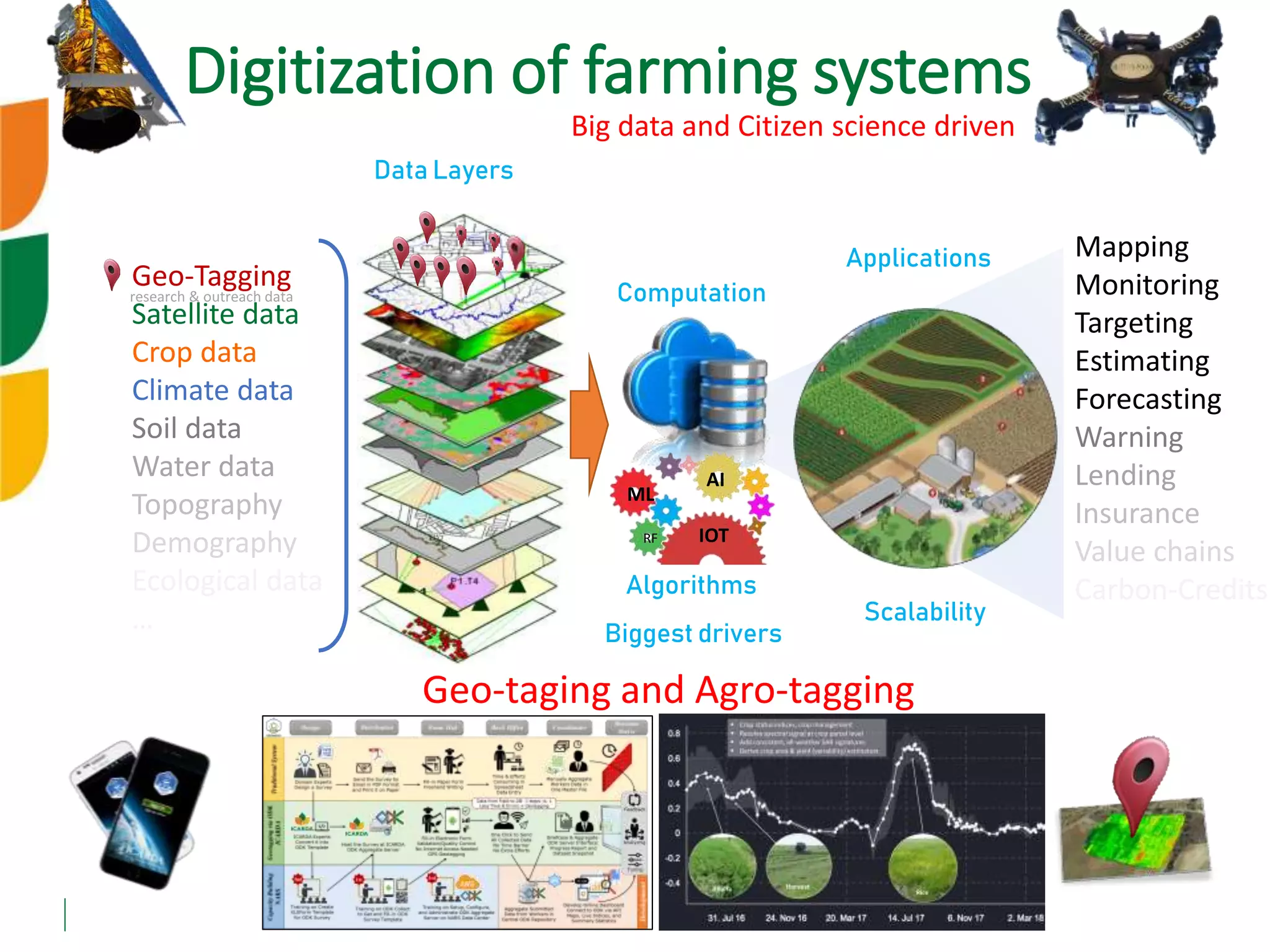
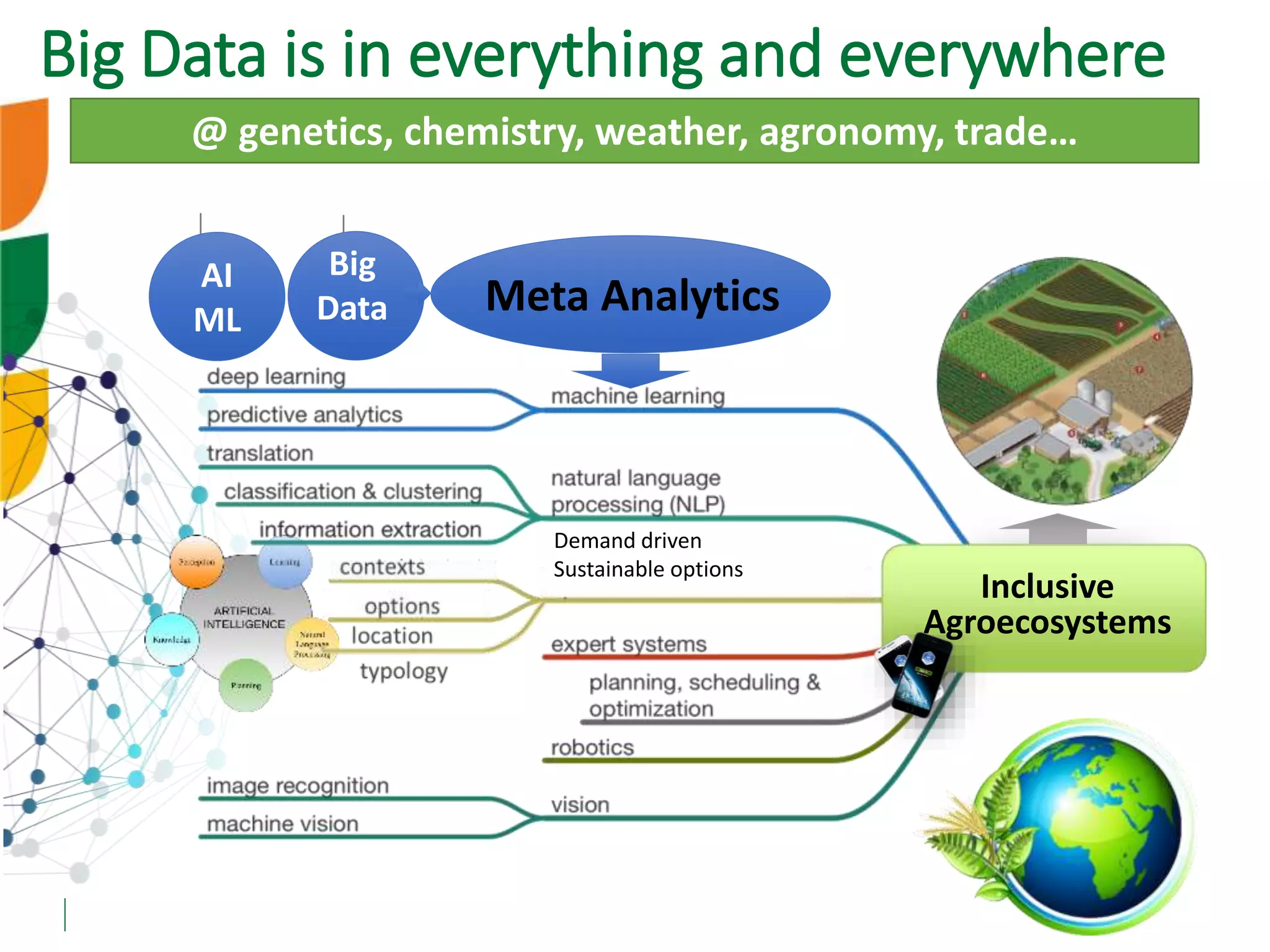
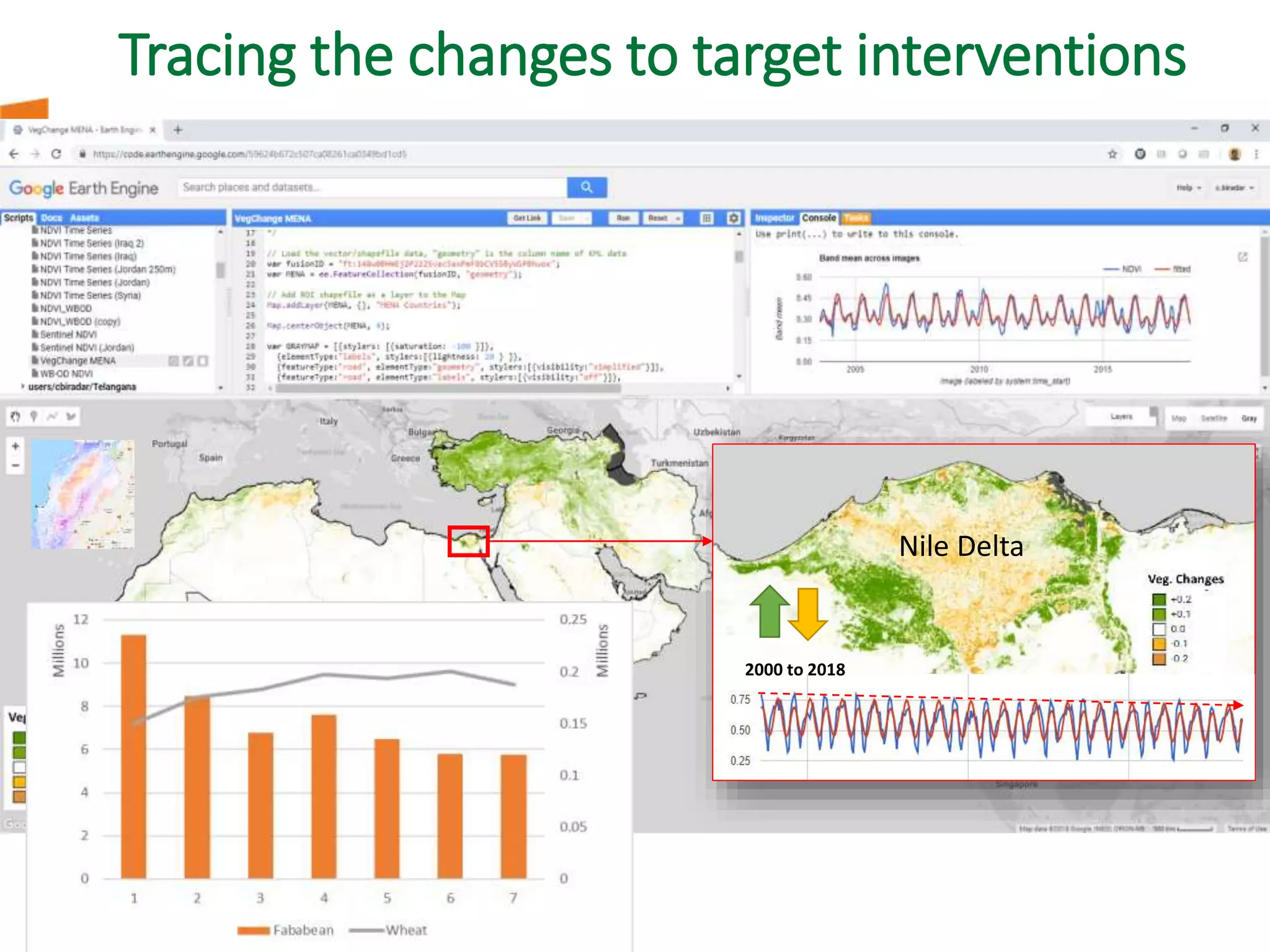
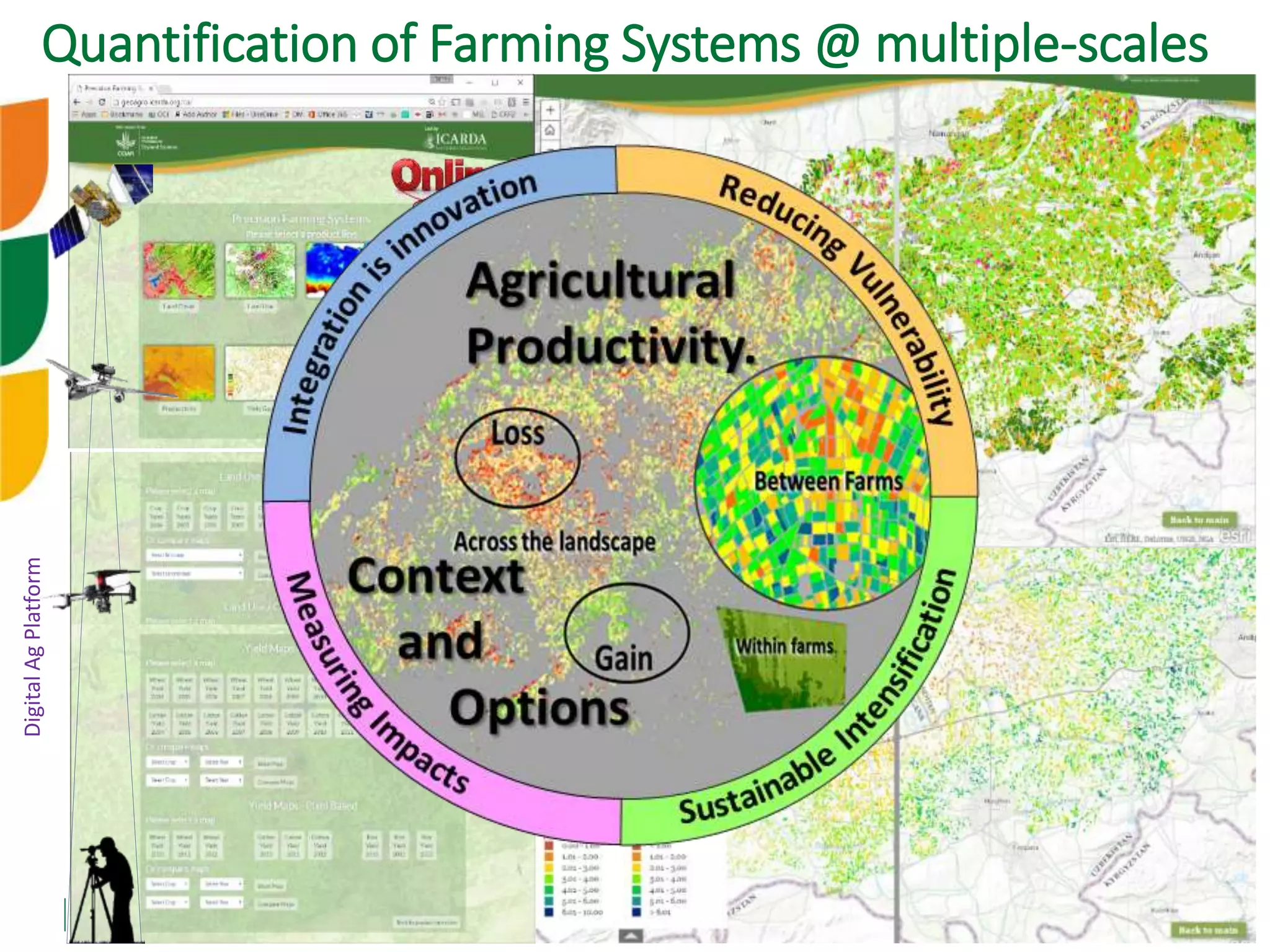
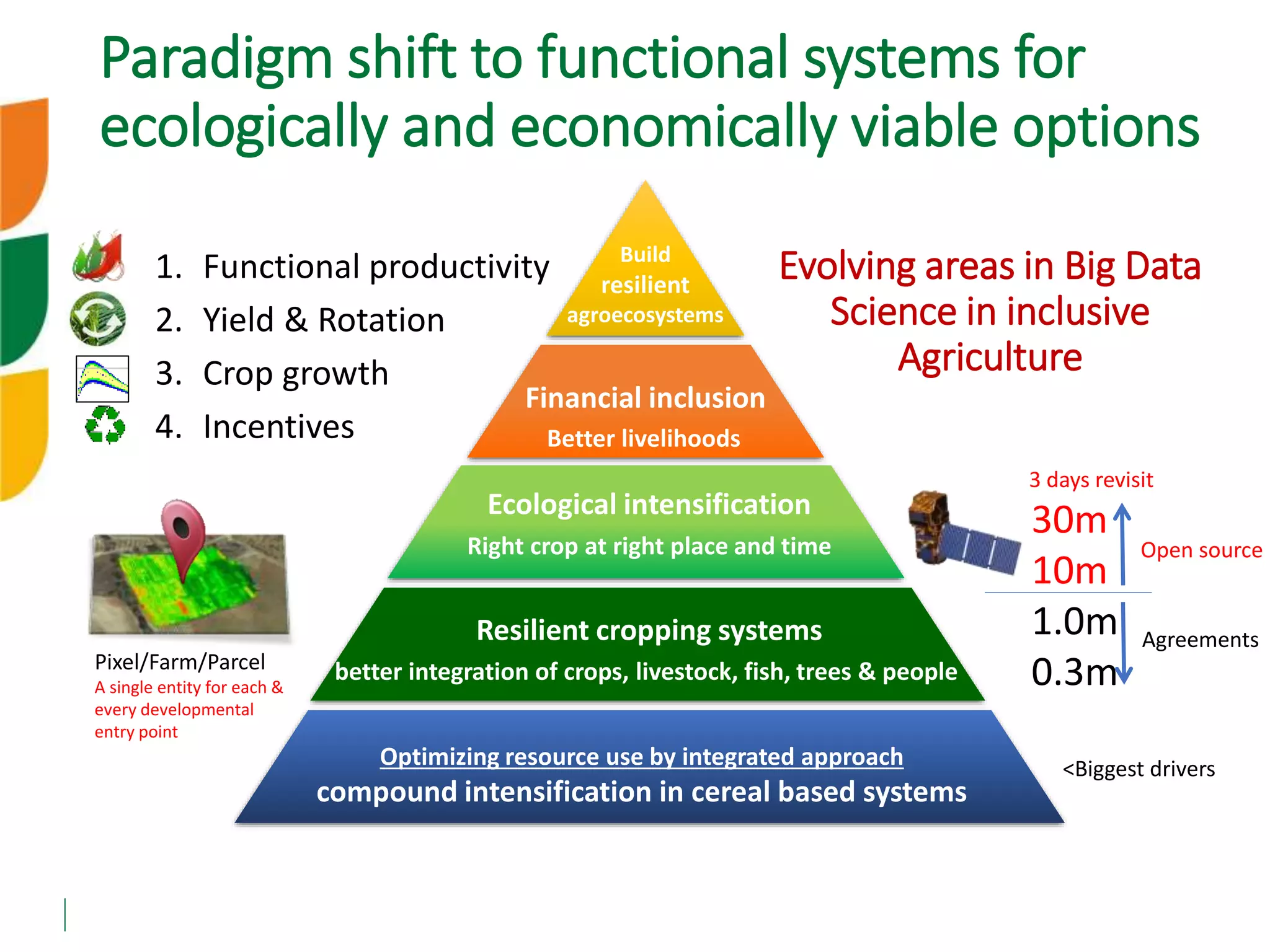
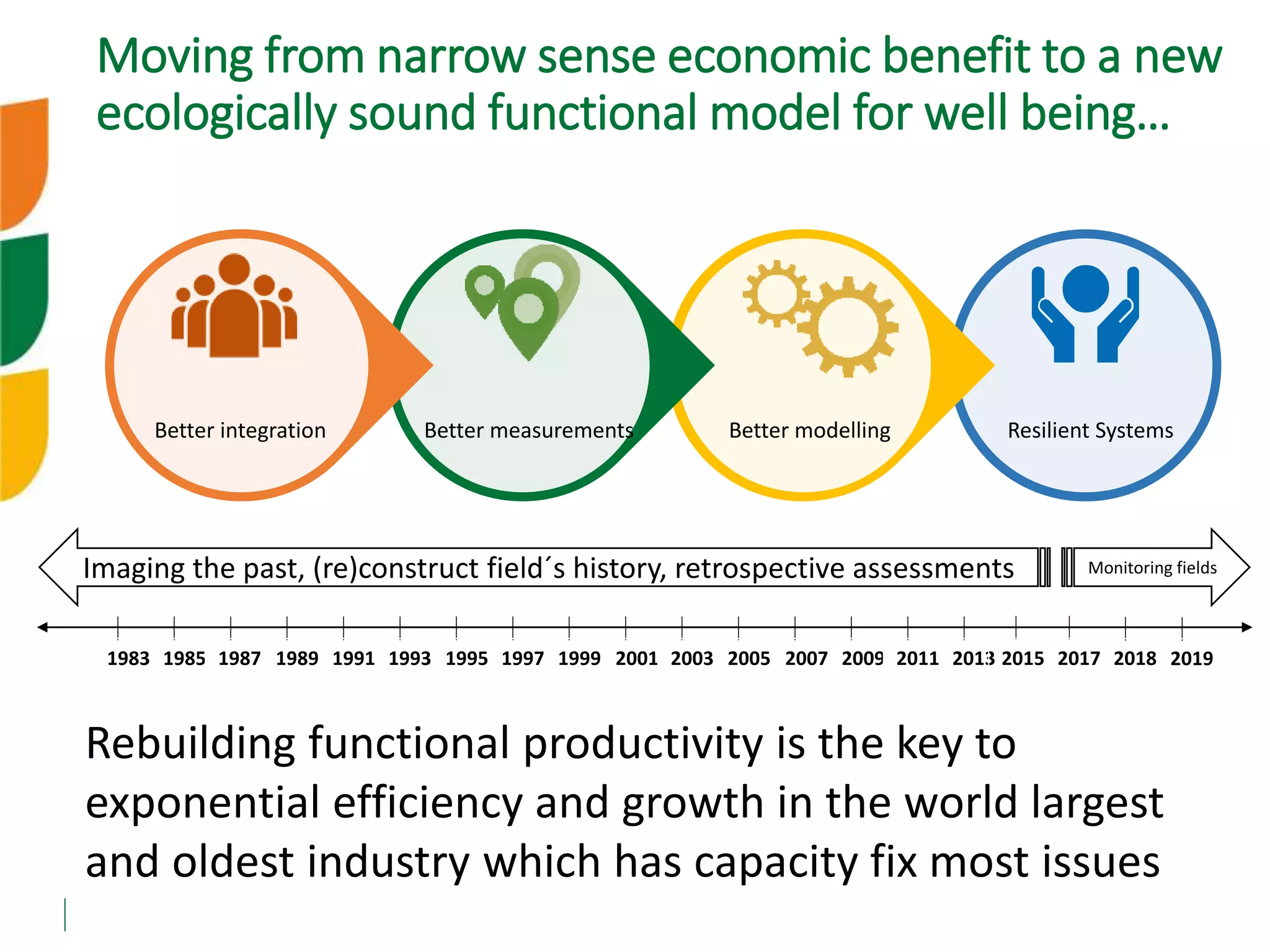
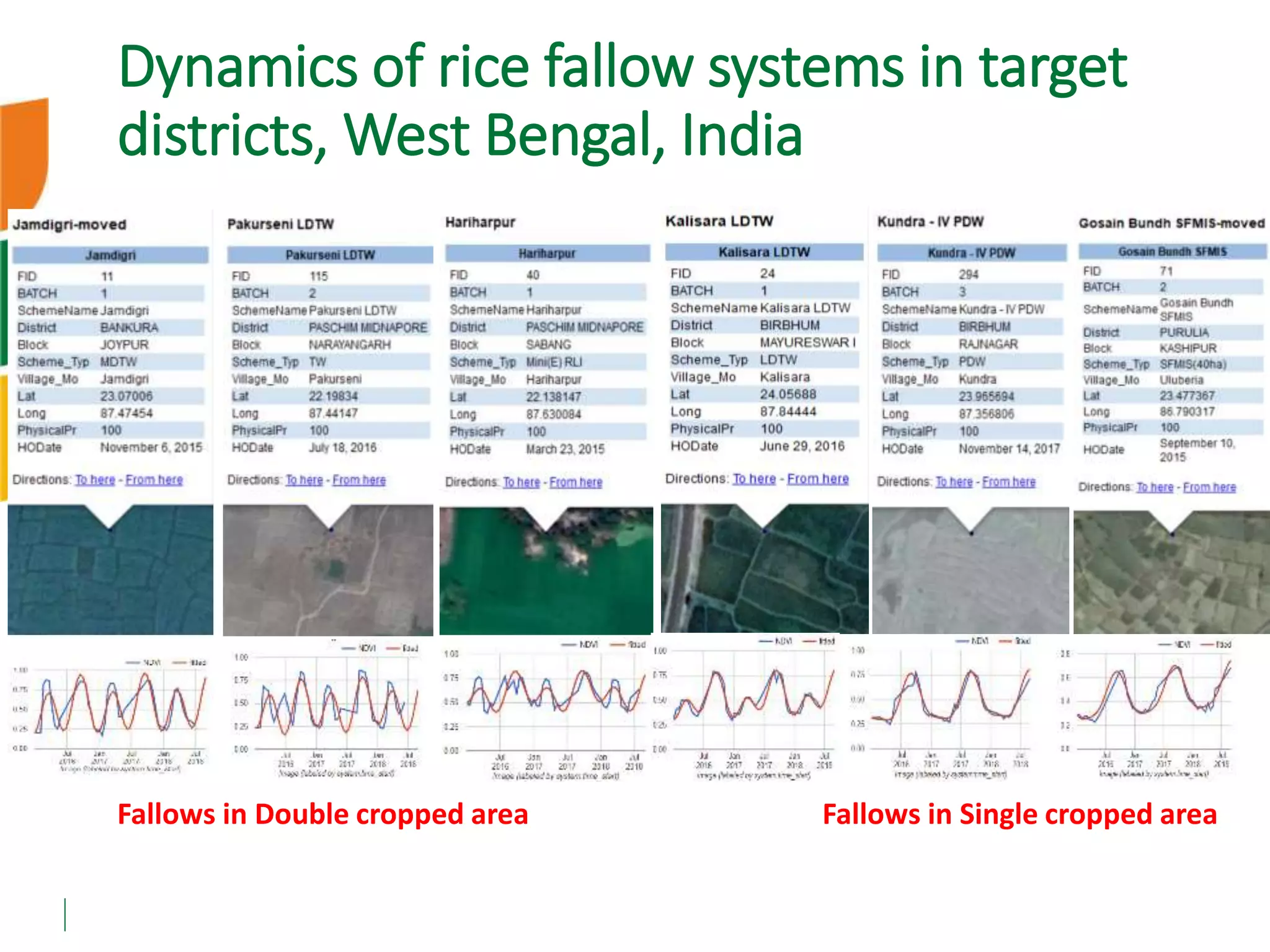
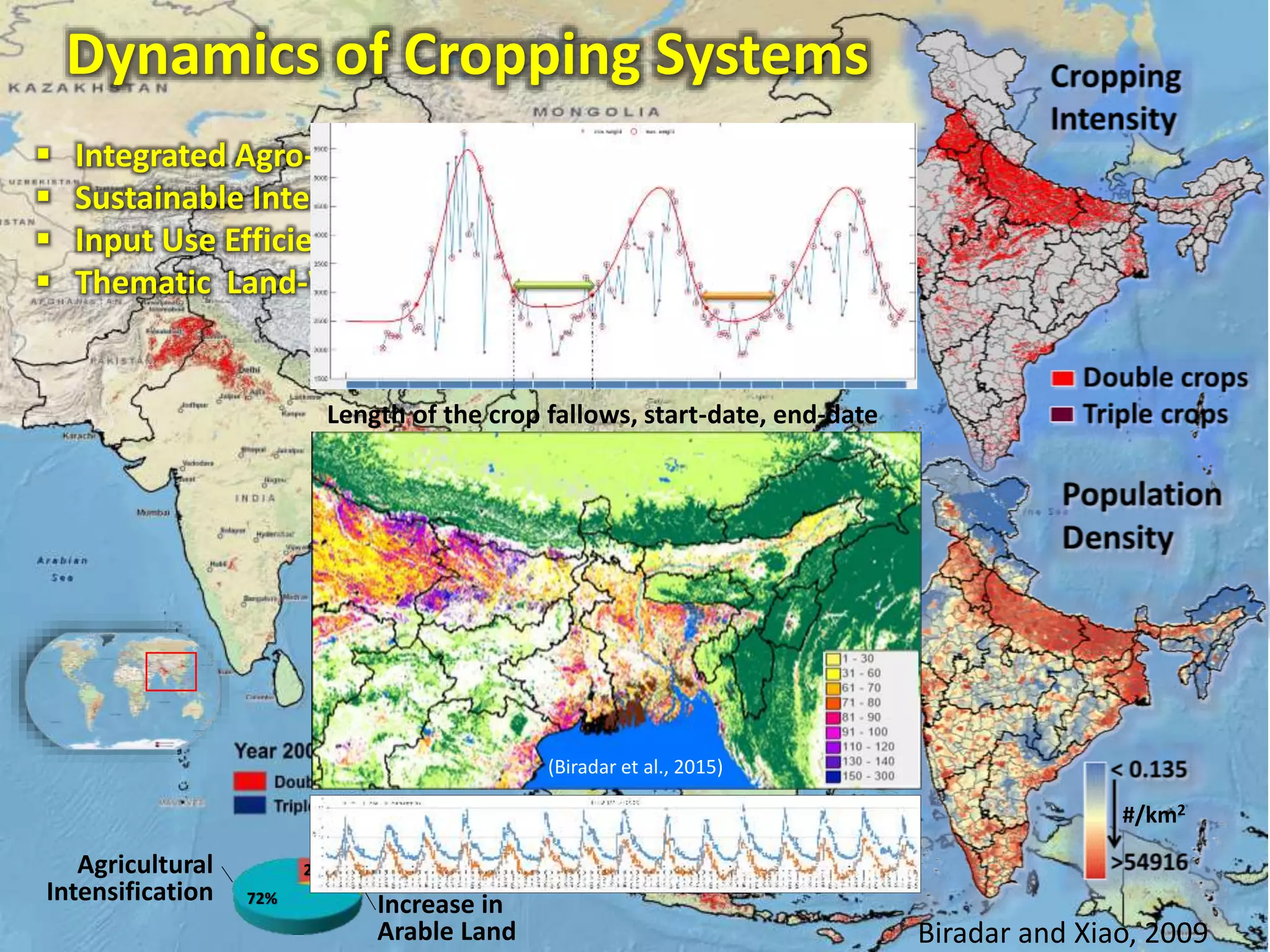
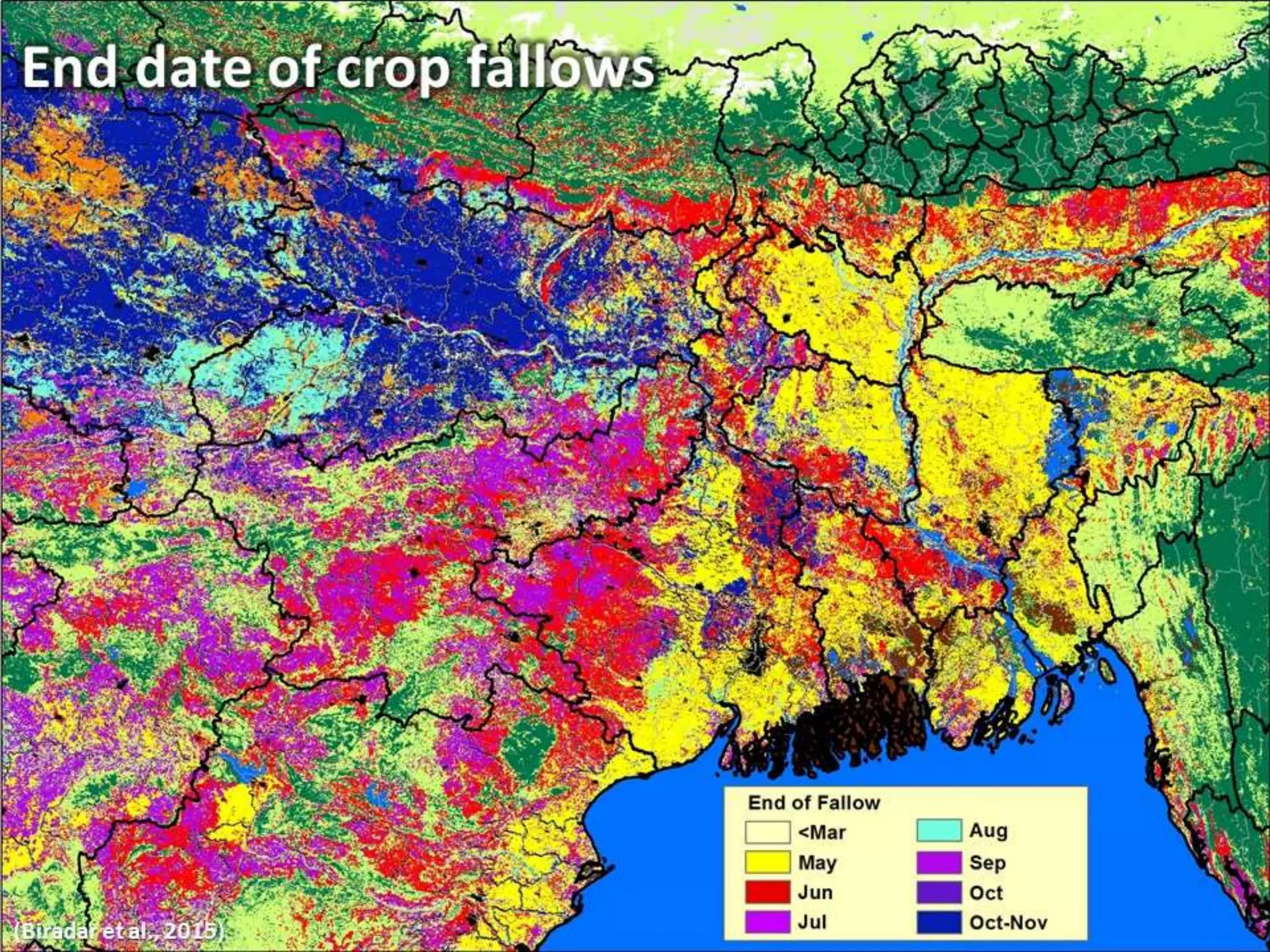
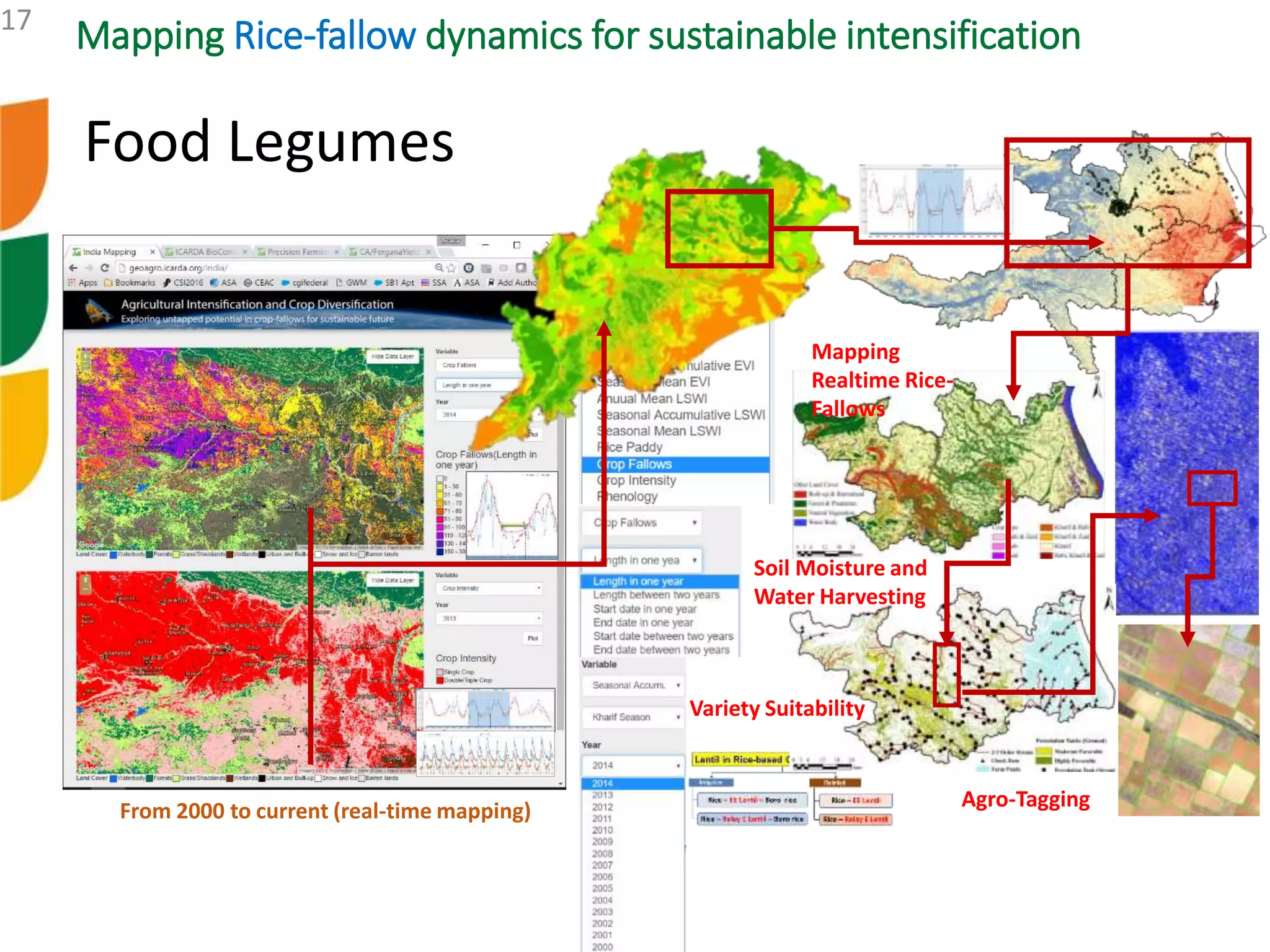
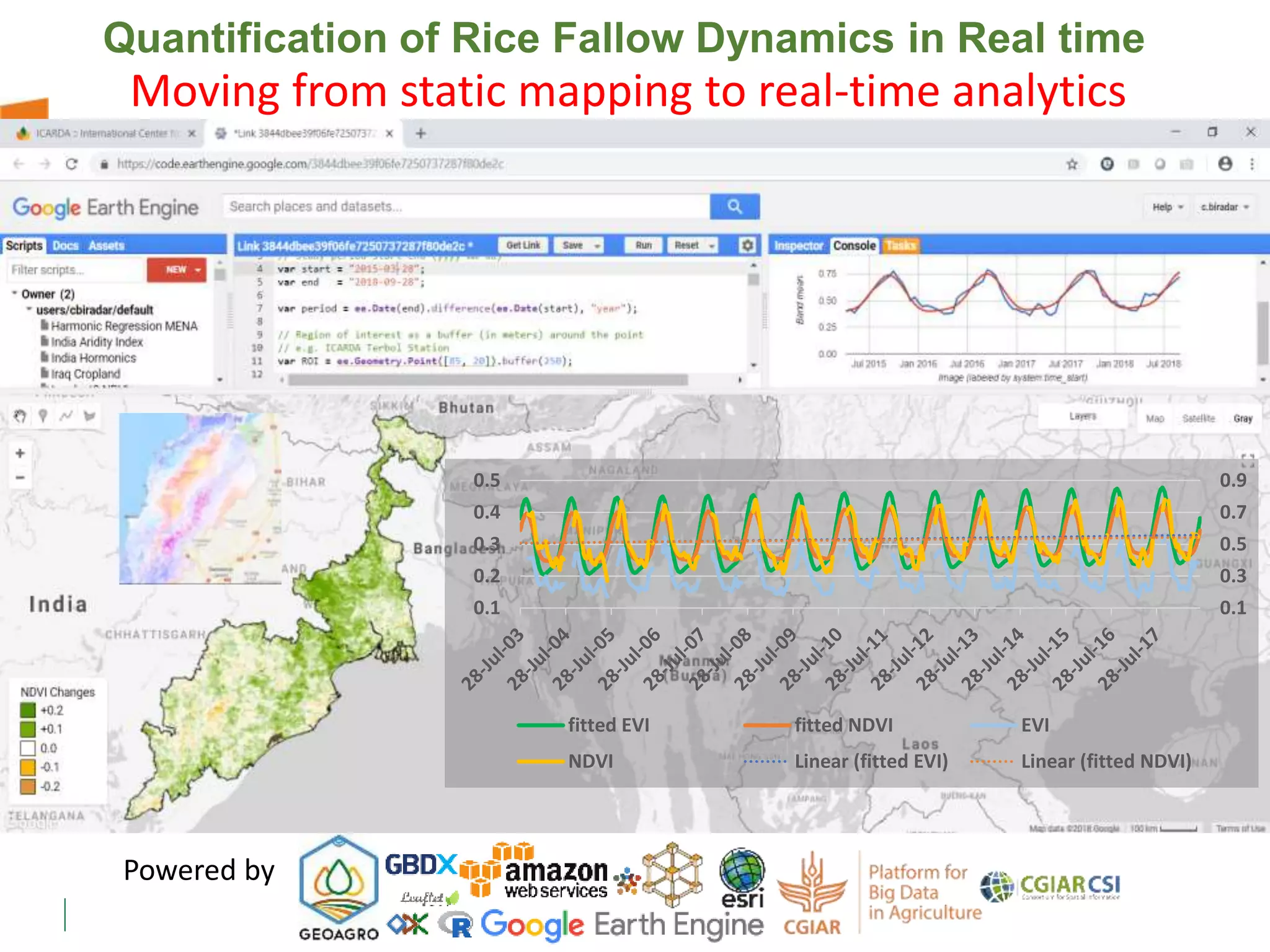
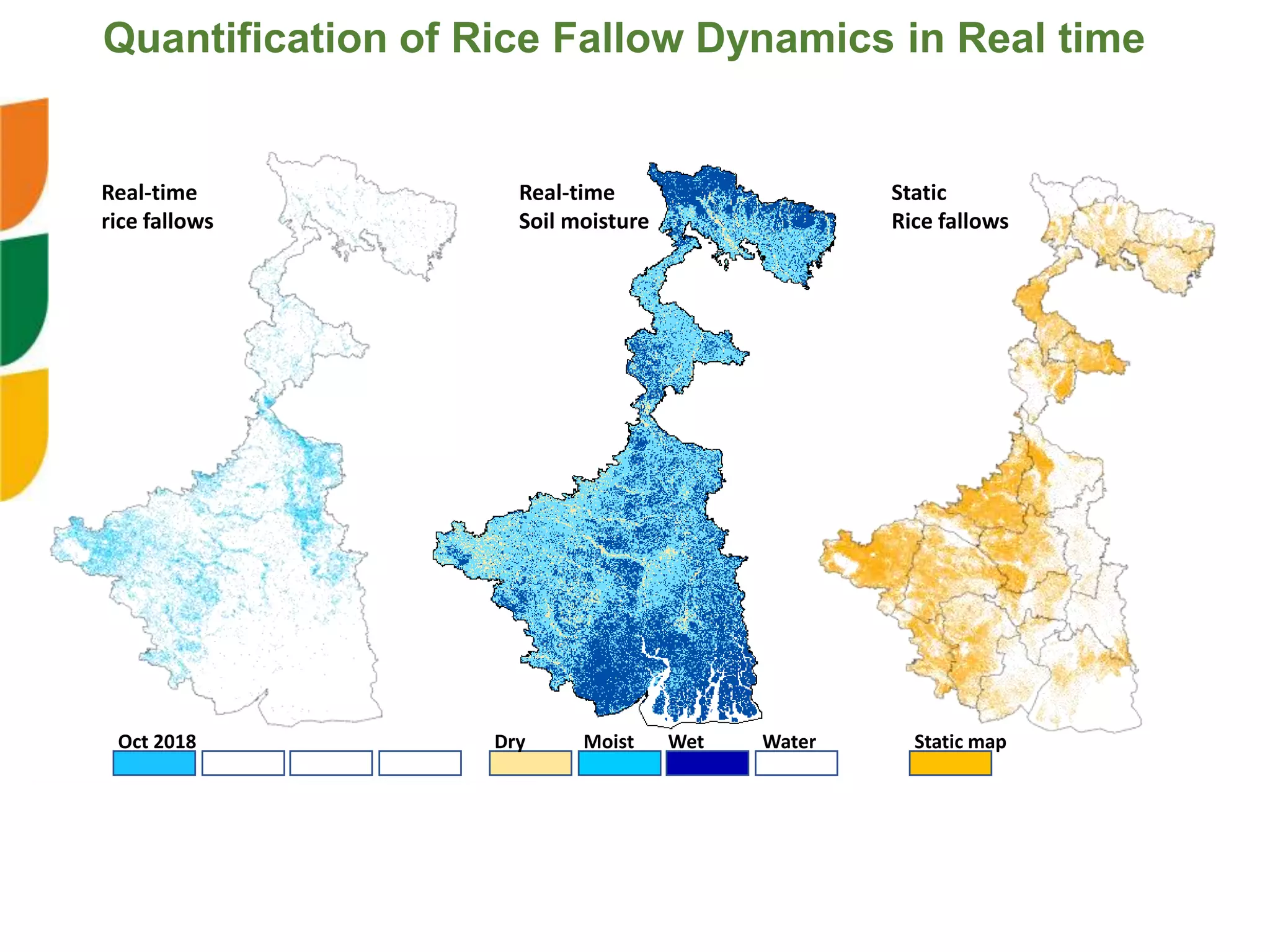
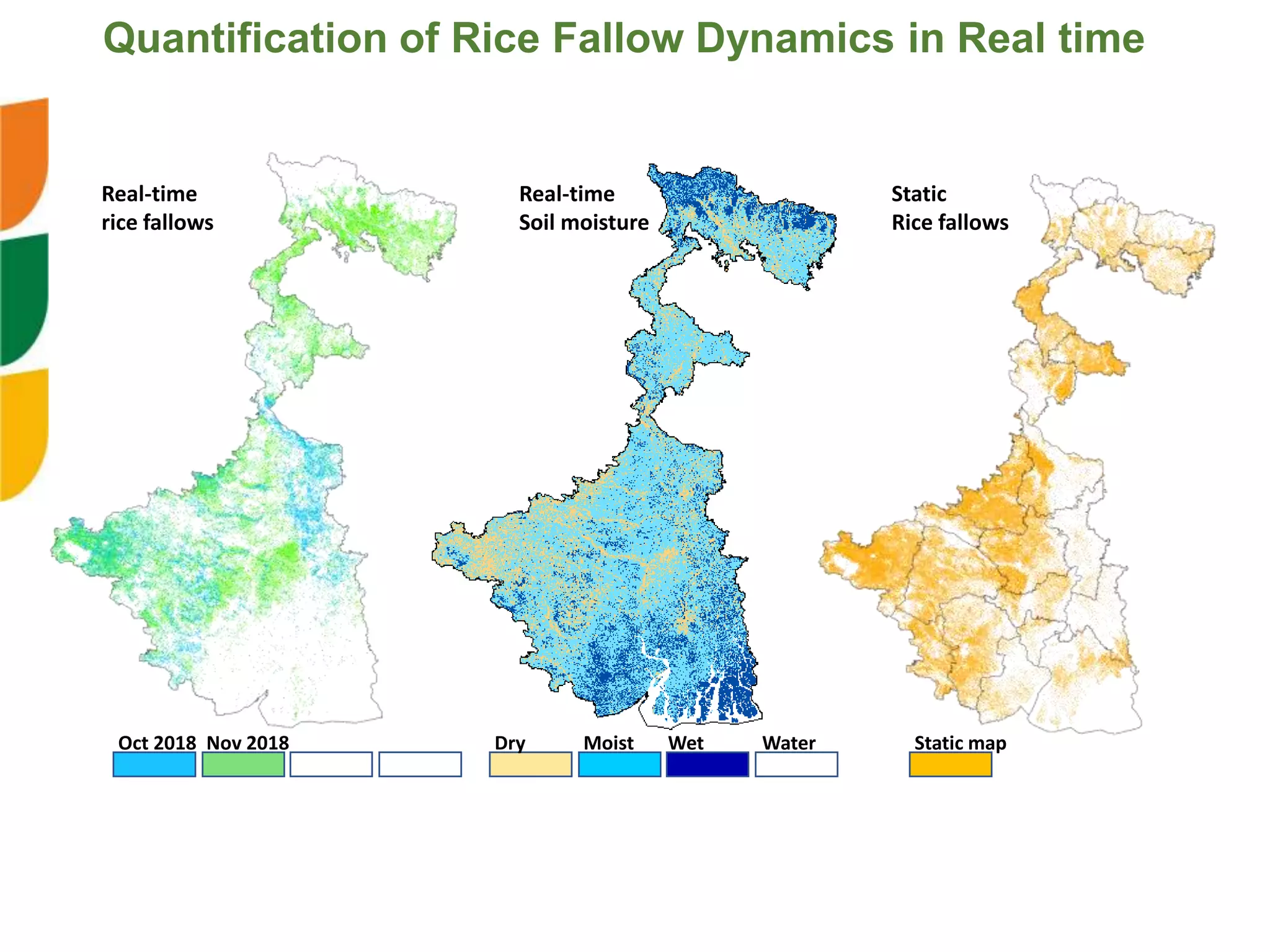
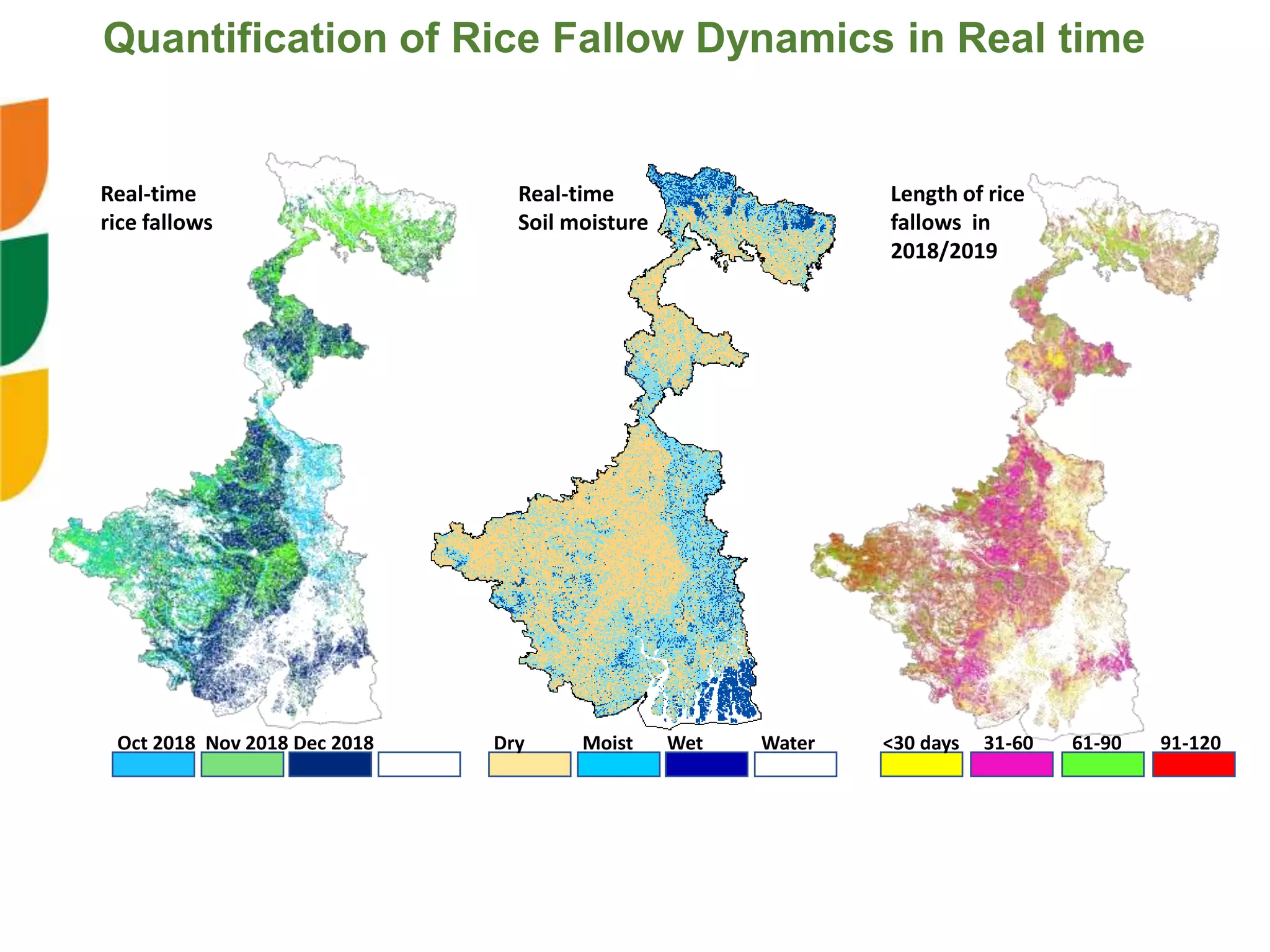
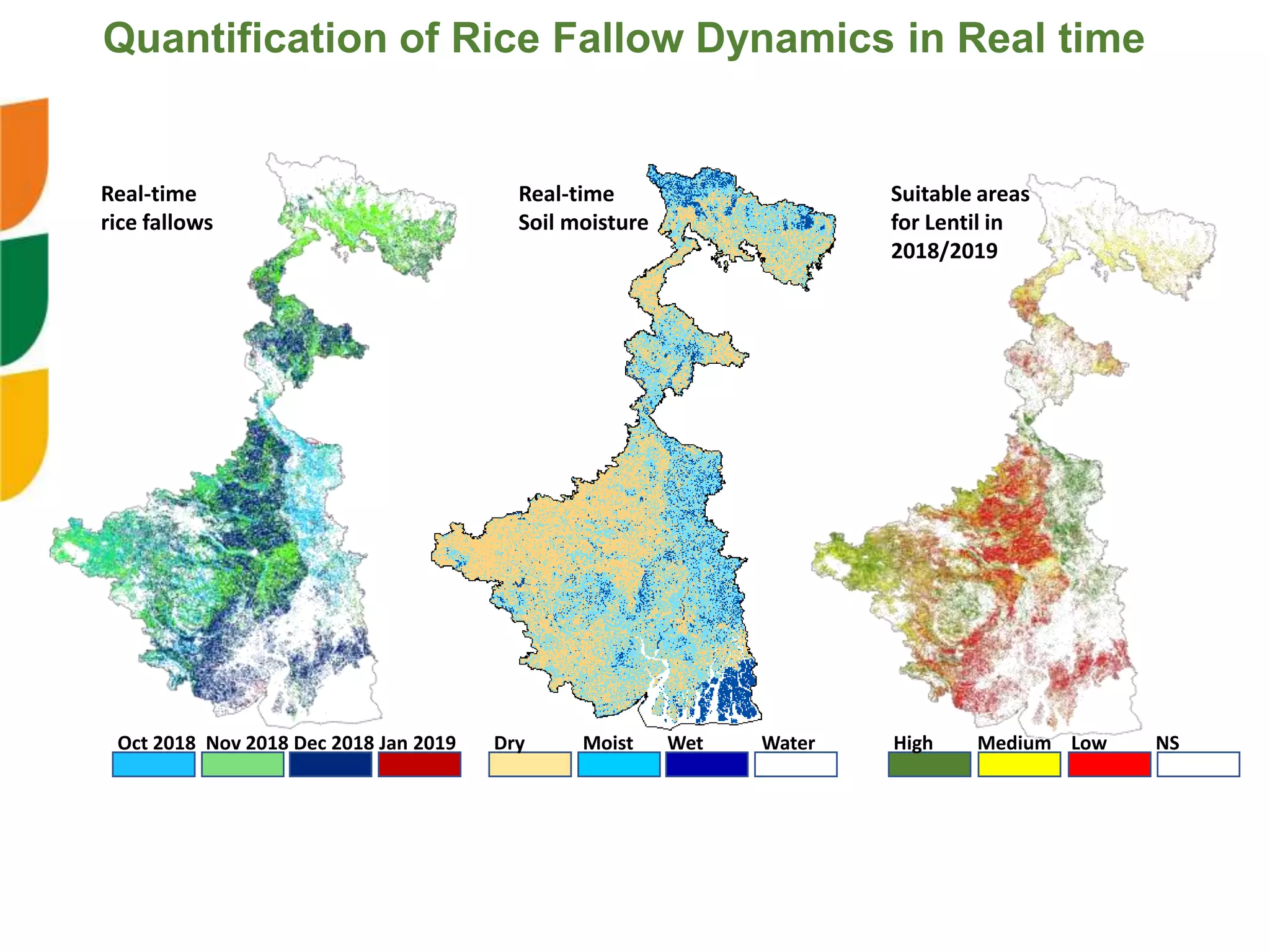
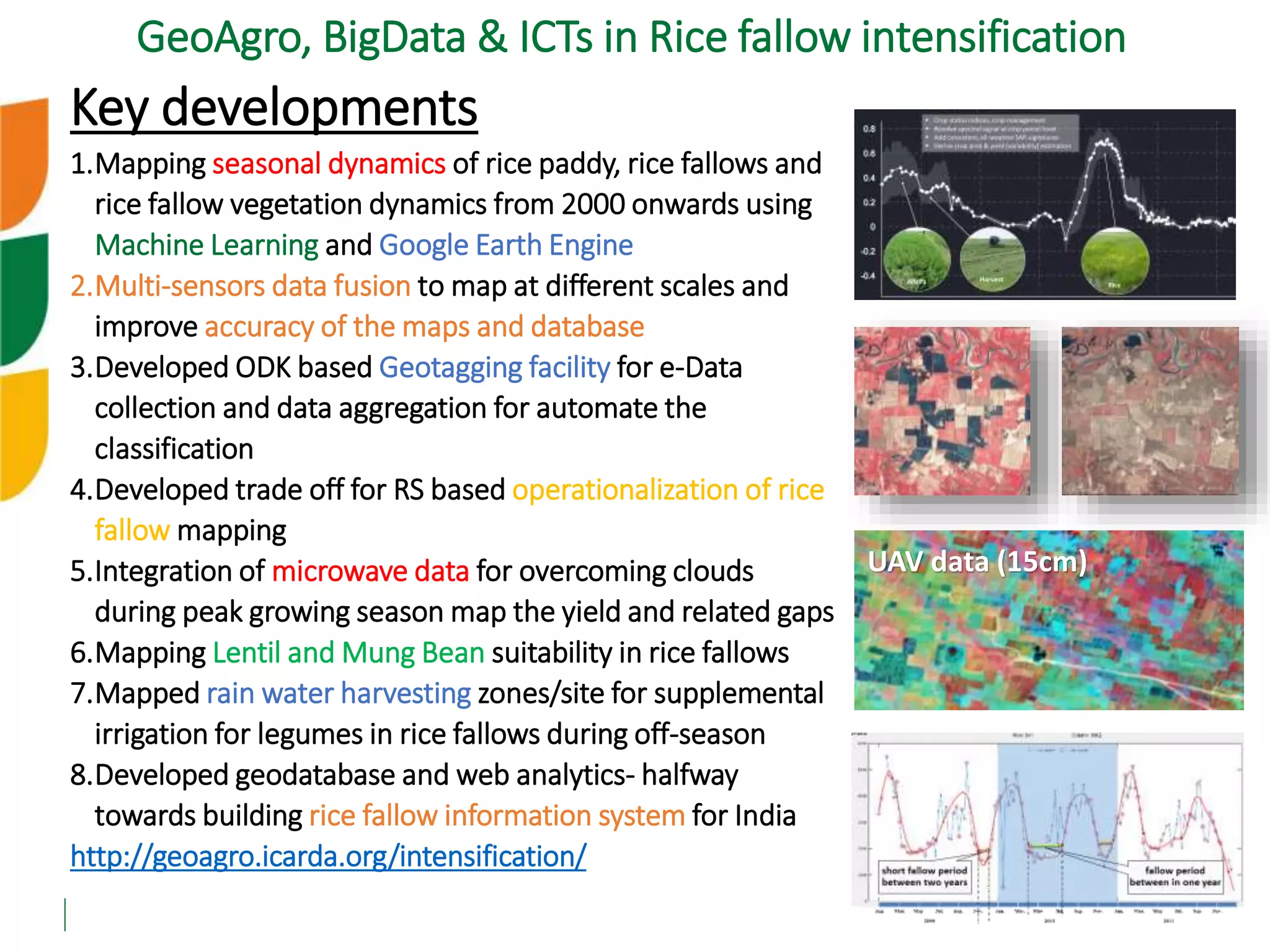
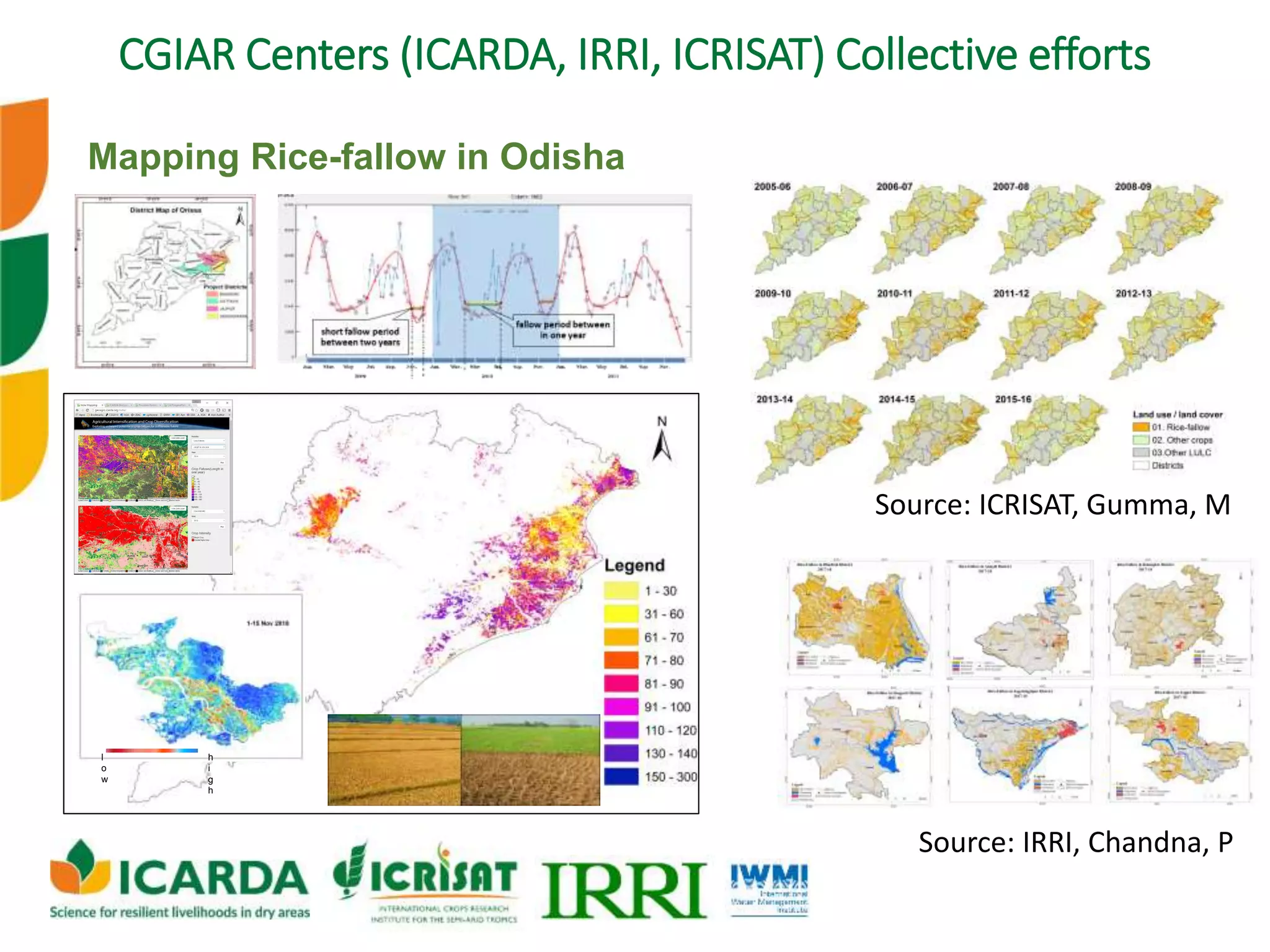
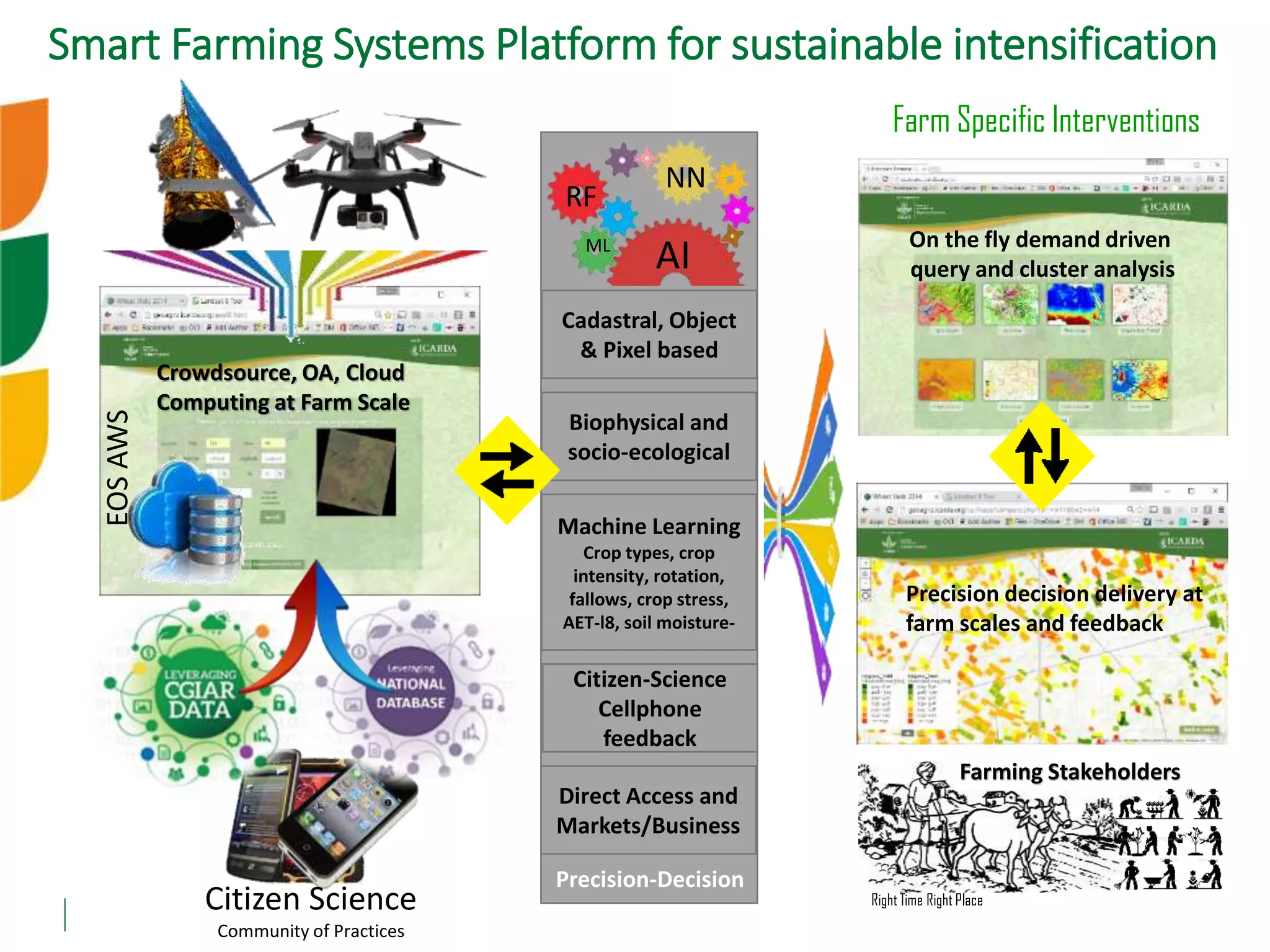
The document outlines ICARDA's strategies for enhancing agricultural productivity through big data and digital technologies aimed at promoting agroecological intensification. It emphasizes the need for integrated systems and targeted interventions to improve resource use efficiency, resilience, and sustainability in farming practices. Key developments include real-time mapping of rice-fallow dynamics and the implementation of machine learning and geotagging for improved agricultural decision-making.