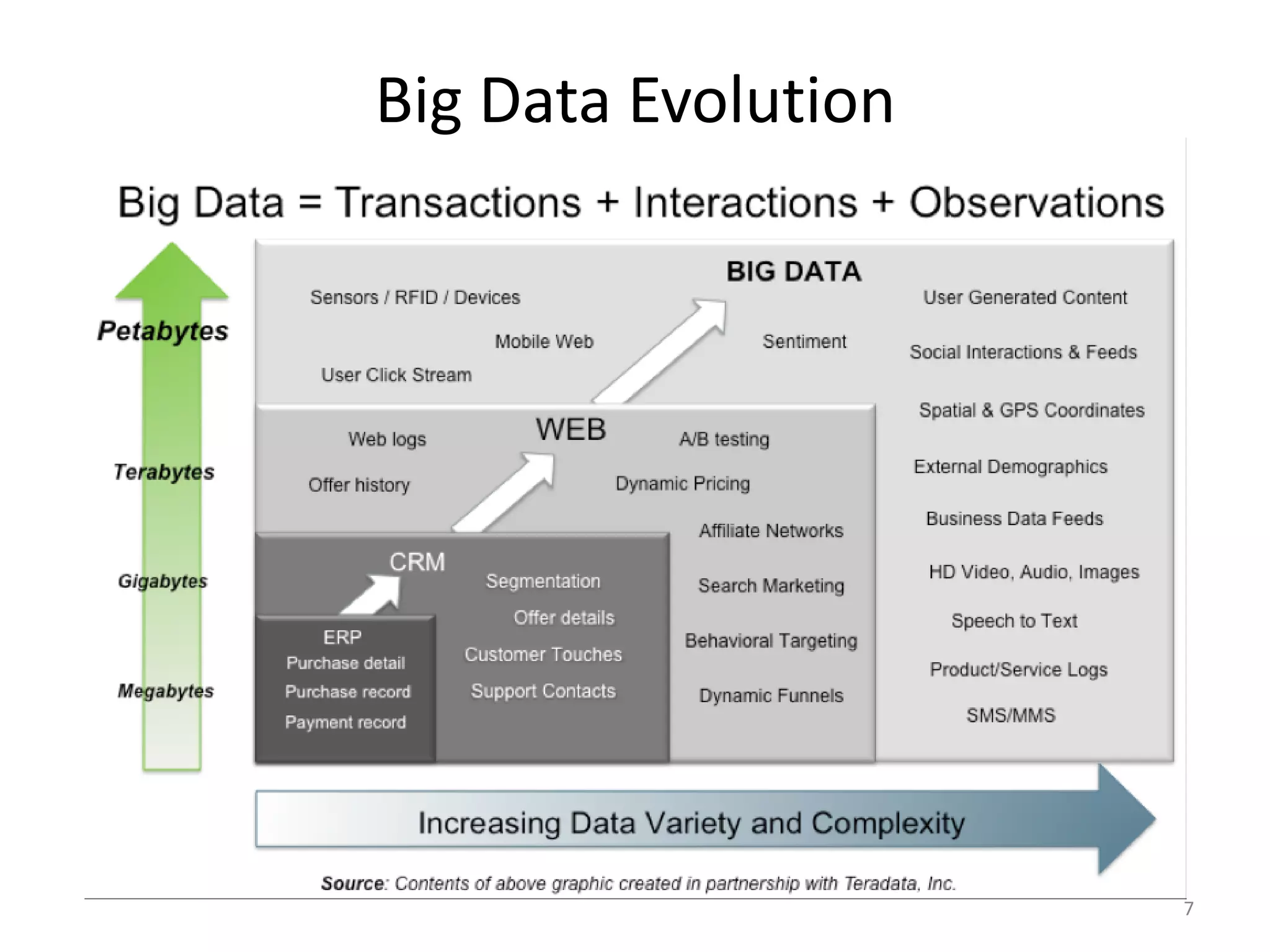
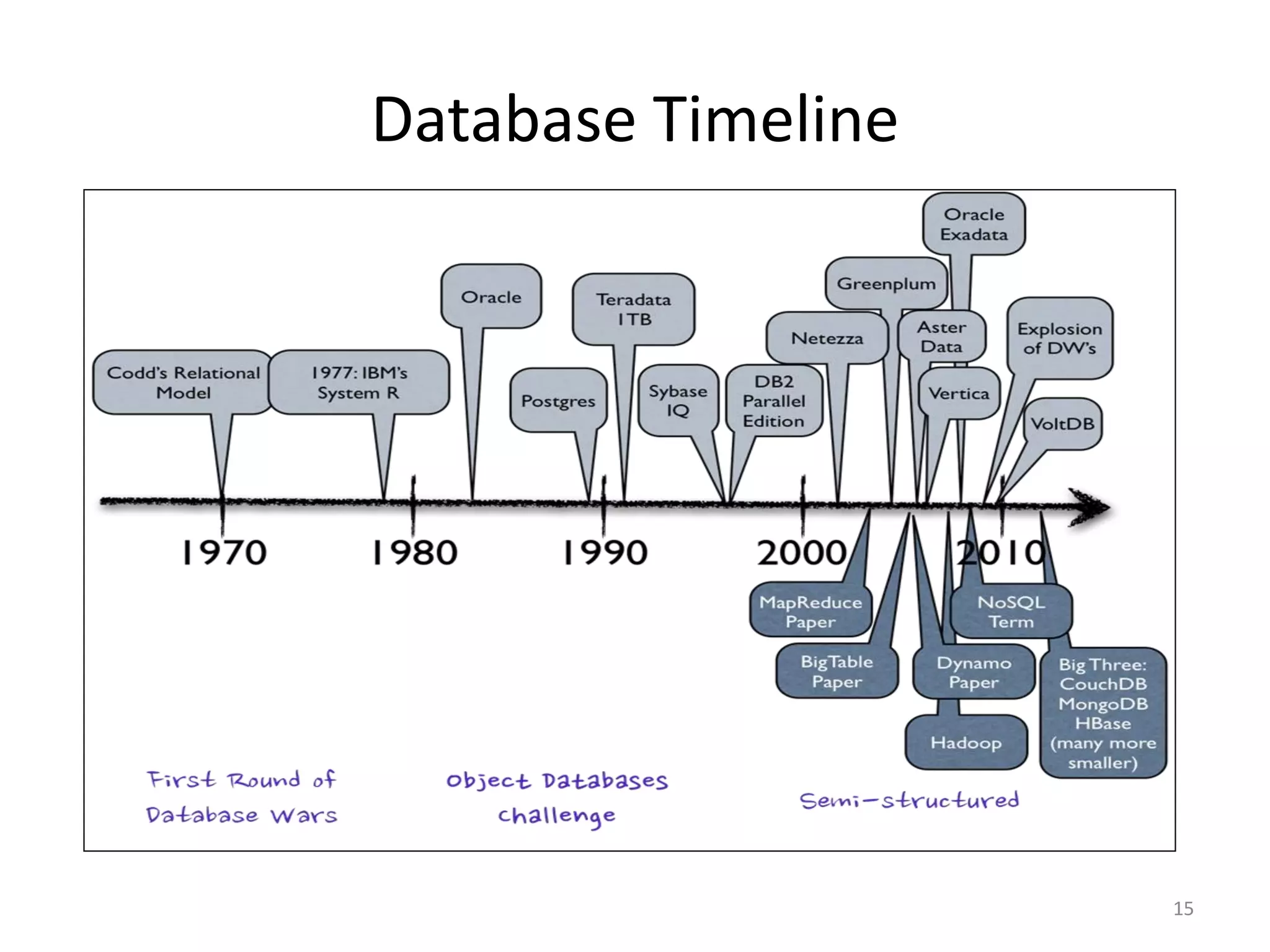
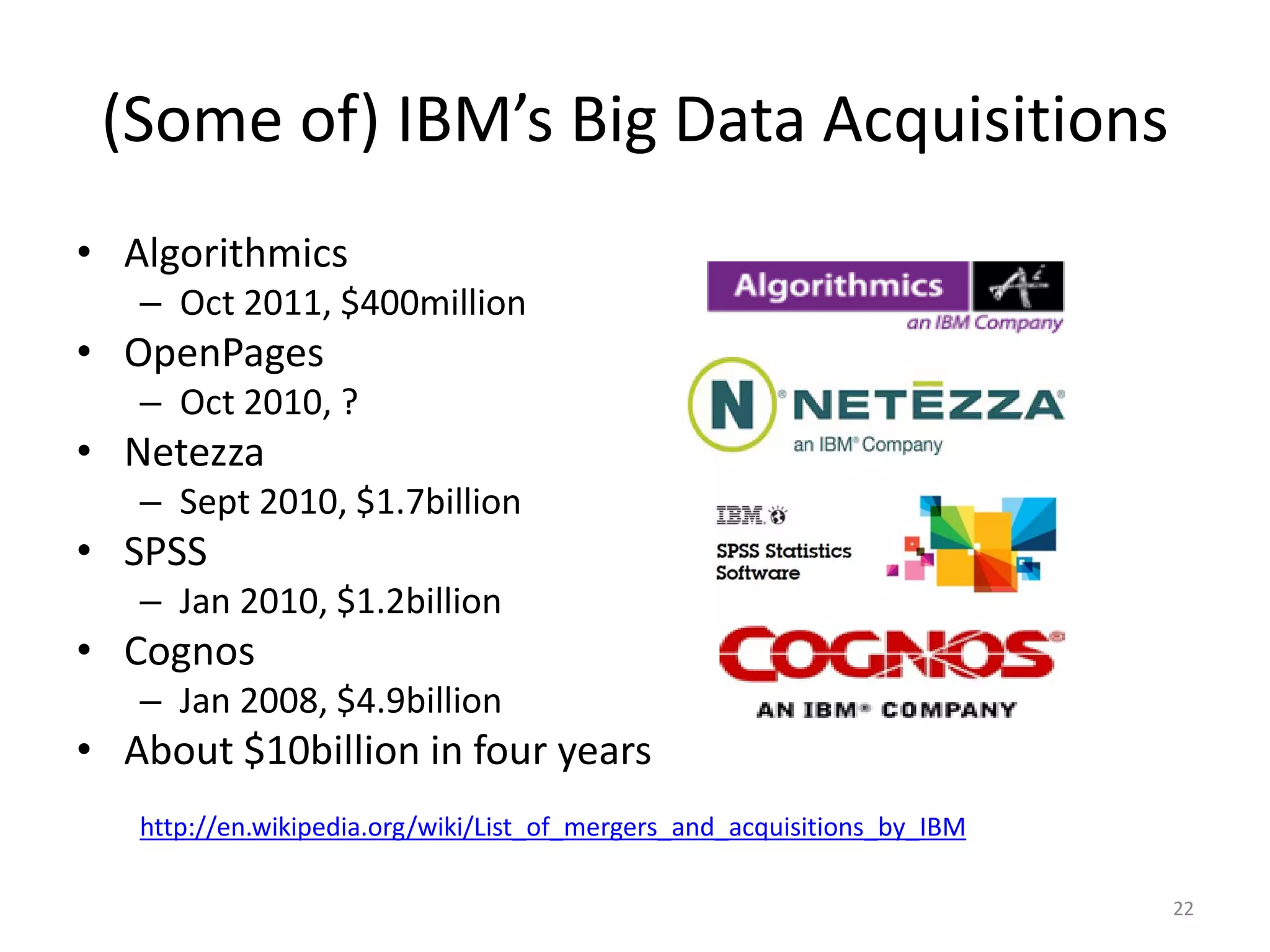
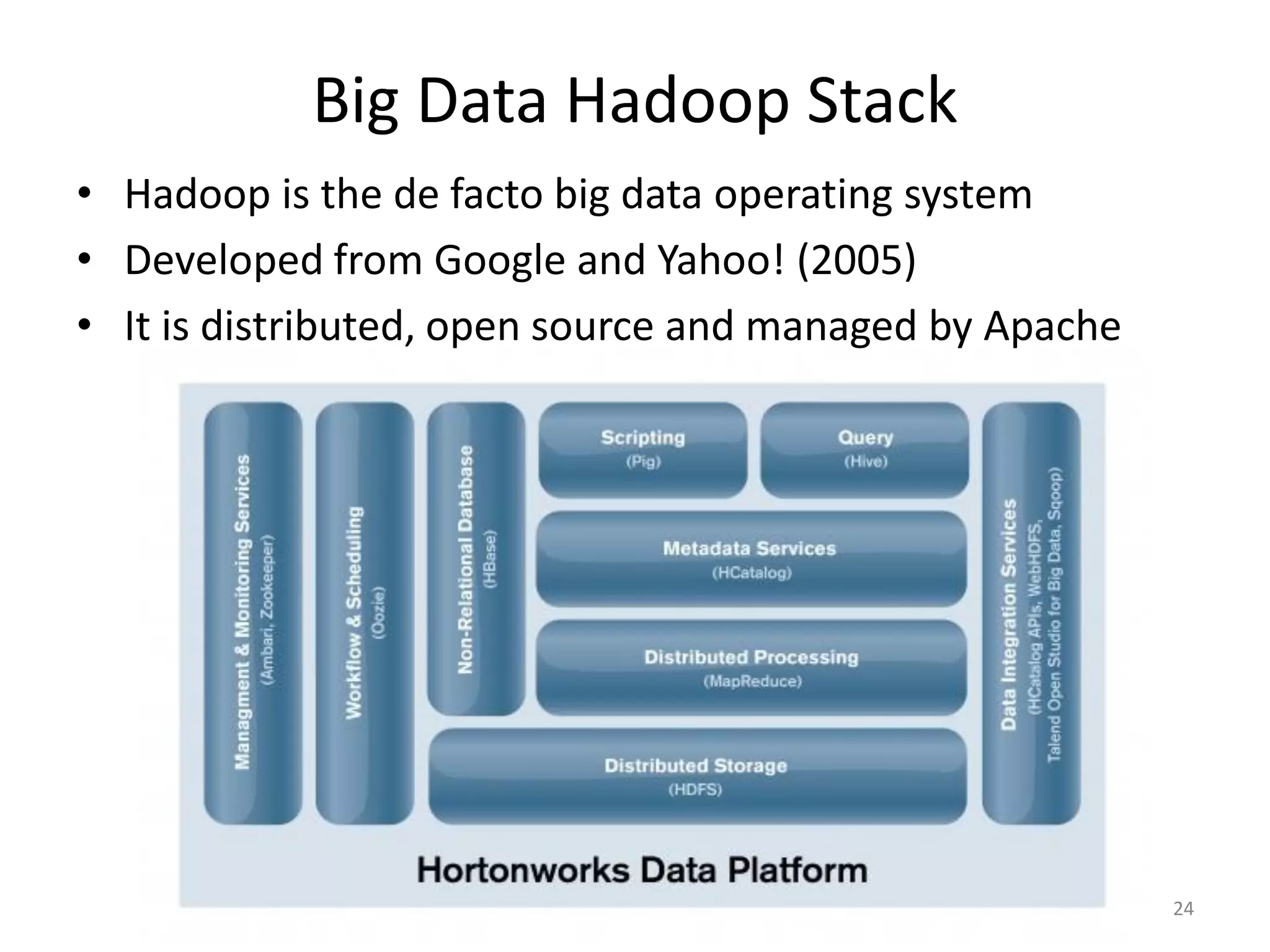
This document provides an overview of big data, including its definition, sources, databases, and analytics. It defines big data as large datasets greater than terabytes in size that are increasingly being collected from various sources such as science, social media, government and more. It notes that most data is unstructured. It also discusses the evolution of databases from relational SQL databases to non-relational NoSQL databases and Hadoop. Finally, it outlines the major tools and technologies used for big data analytics, including MapReduce, Hadoop, and machine learning.