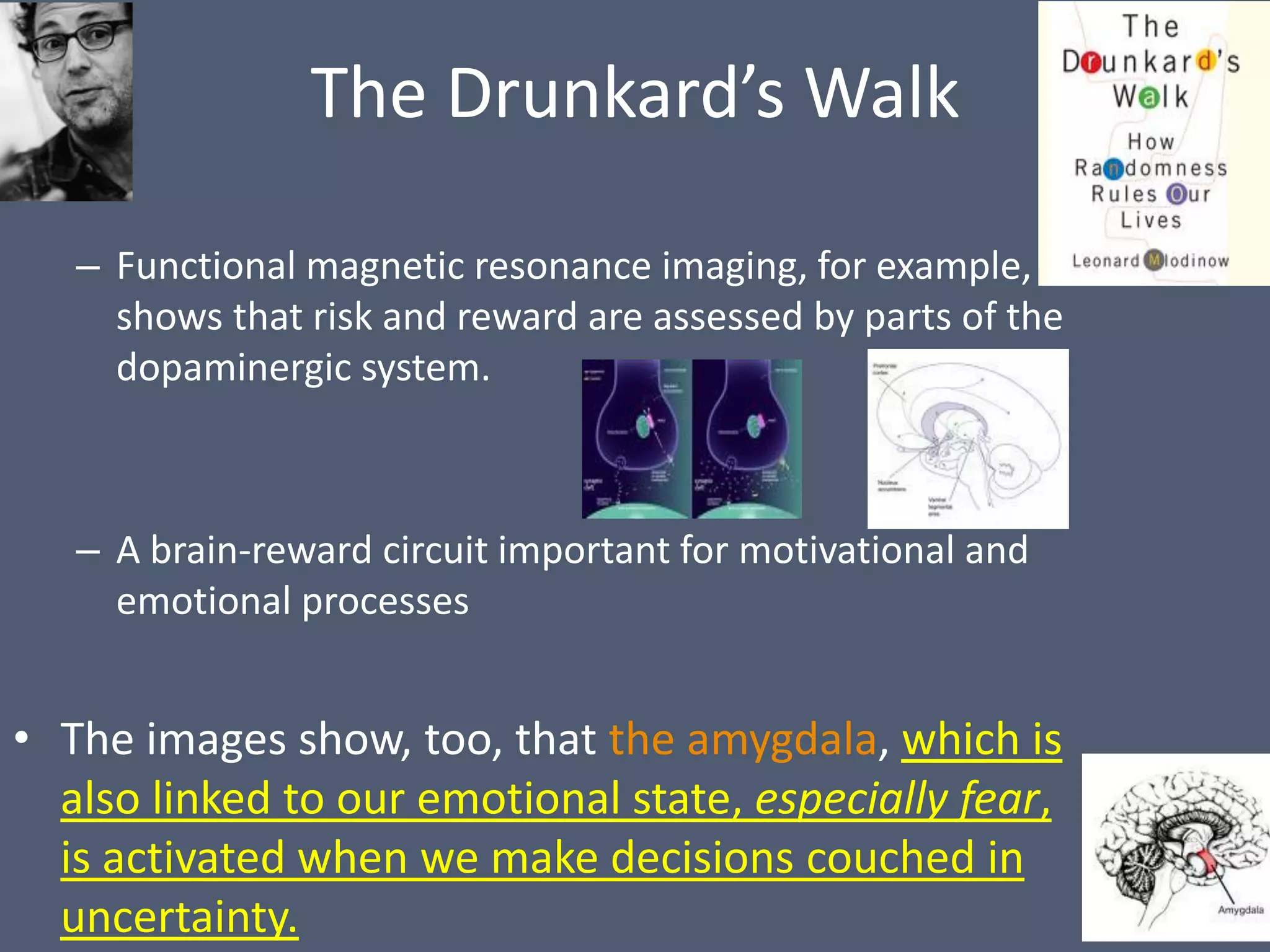
The document discusses various cognitive biases and heuristics that influence human decision-making, such as the planning fallacy in which people underestimate costs and overestimate benefits, and optimism bias which can motivate action but also lead to false beliefs. It also examines loss aversion bias and how optimism can help protect against the paralyzing effects of fearing losses more than valuing gains. A number of heuristics are explored, including the affect heuristic where emotional reactions can drive behavior over cognitive risk assessments.























![ Financial - Rule of 72 A rule of thumb for exponential growth at a constant rate. An
approximation of the "doubling time" formula used in population growth, which says divide 70 by
the percent growth rate (the actual number is 69.3147181 from the natural logarithm of 2, if the
percent growth is much much less than 1%). In terms of money, it is frequently easier to use 72
(rather than 70) because it works better in the 4%-10% range where interest rates often lie.
Therefore, divide 72 by the percent interest rate to determine the approximate amount of time to
double your money in an investment. For example, at 8% interest, your money will double in
approximately 9 years (72/8 = 9).
Tailors' Rule of Thumb A simple approximation that was used by tailors to determine the wrist,
neck, and waist circumferences of a person through one single measurement of the
circumference of that person's thumb. The rule states, typically, that twice the circumference of a
person's thumb is the circumference of their wrist, twice the circumference of the wrist is the
circumference of the neck, and twice around the neck is the person's waist. For example, if the
circumference of the thumb is 4 inches, then the wrist circumference is 8 inches, the neck is 16
and the waist is 32. An interesting consequence of this is that — for those to whom the rule applies
— this simple method can be used to determine if trousers will fit: the trousers are wrapped
around the neck, and if the two ends barely touch, then they will fit. Any overlap or lack thereof
corresponds to the trousers being too loose or tight, respectively.
Marine Navigation A ship's captain should navigate to keep the ship more than a thumb's width
from the shore, as shown on the nautical chart being used. Thus, with a coarse scale chart, that
provides few details of near shore hazards such as rocks, a thumb's width would represent a great
distance, and the ship would be steered far from shore; whereas on a fine scale chart, in which
more detail is provided, a ship could be brought closer to shore.[1]
Statistics The Statistical Rule of Thumb says that for most large data sets, 68% of data points will
occur within one standard deviation from the mean, and 95% will occur within two standard
deviations. Chebyshev's inequality is a more general rule along these same lines and applies to all
data sets.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biasesapril2012-120814140201-phpapp01/75/Biases-april-2012-25-2048.jpg)