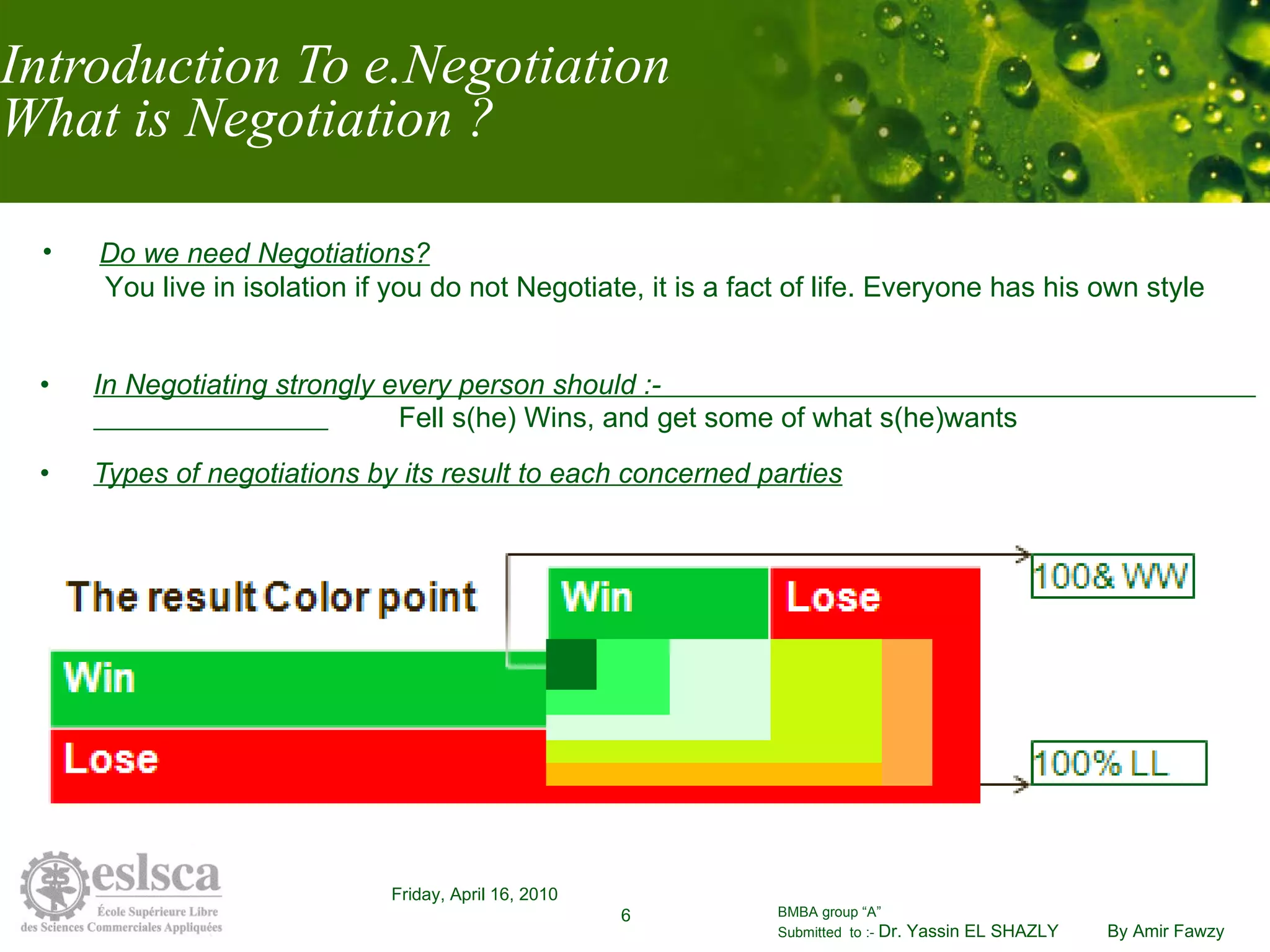
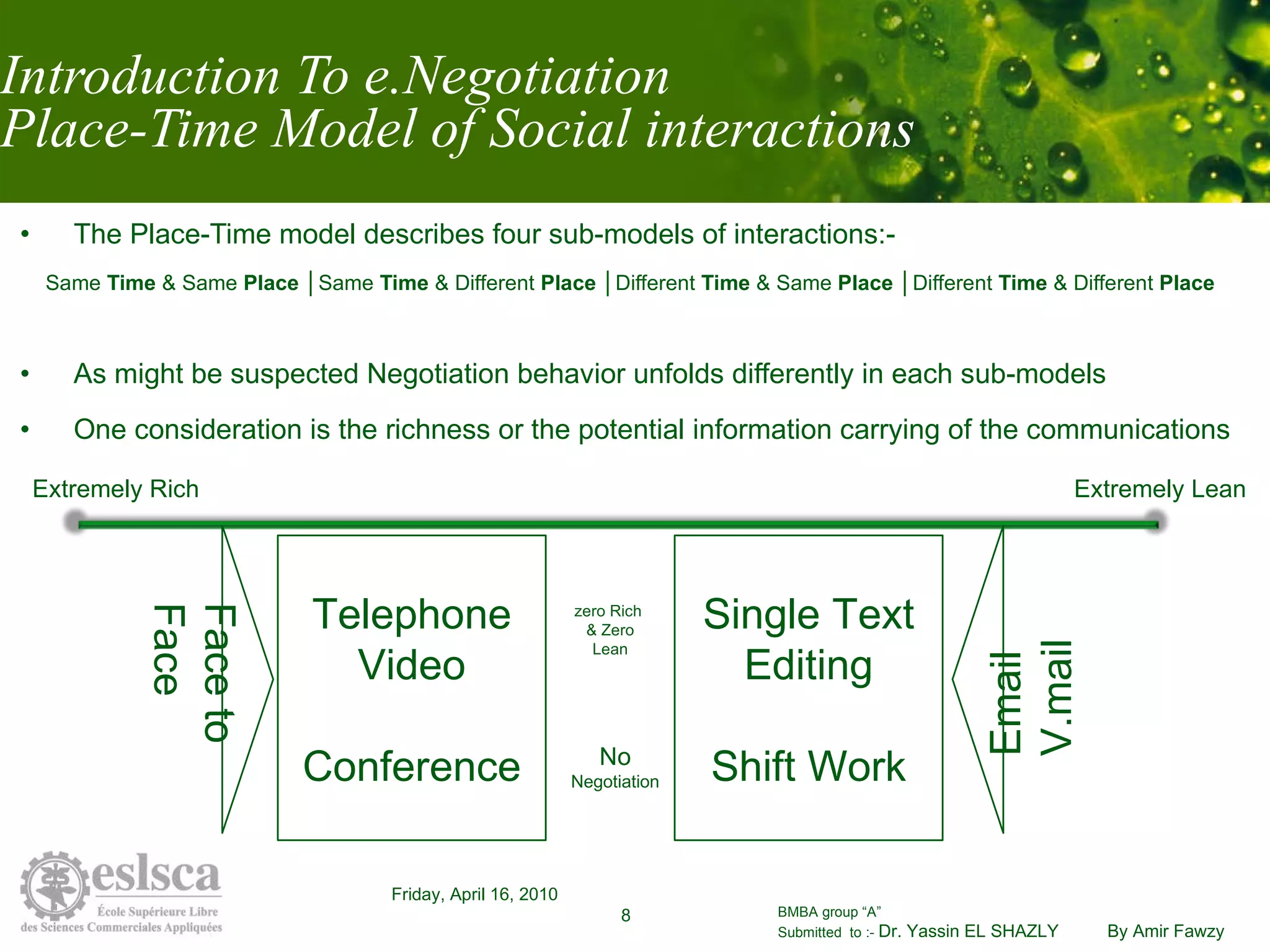
This document discusses how information technology affects negotiation behavior. It begins by defining negotiation and exploring a model of social interactions. It then examines how IT influences social behavior and trust in online negotiations. Finally, it proposes strategies for enhancing technology-mediated negotiations, such as initial face-to-face meetings or videoconferences to build rapport when fully online negotiation is necessary. The document concludes by noting that e-negotiation is not a replacement for traditional negotiation and that a blended approach may be most effective.