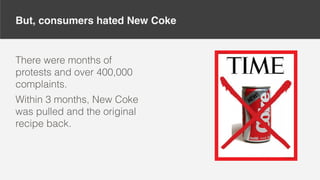
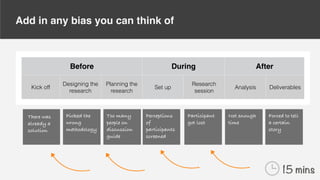
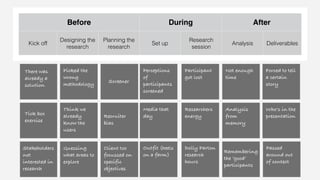
The document discusses inherent biases in research, exemplified by Coca-Cola's New Coke debacle in the 1980s, where biased design and oversight led to flawed decision-making despite extensive testing. It emphasizes the importance of recognizing and mitigating biases in research sessions, from planning to execution and analysis. Suggestions for reducing bias include challenging assumptions, using diverse participant recruitment, and avoiding leading questions.