The document summarizes key points from a workshop on developing impact pathways for projects.
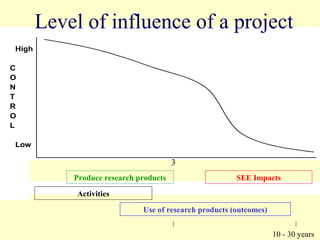
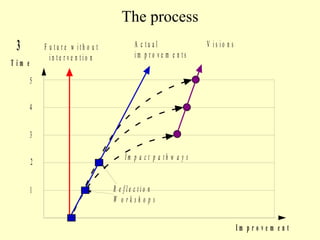
1. The workshop discussed making impact pathways (how projects create change) explicit in order to improve project practice and impact. Explicit impact pathways can help with planning, evaluation, program integration, and ex-post impact assessment.
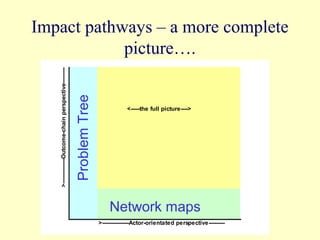
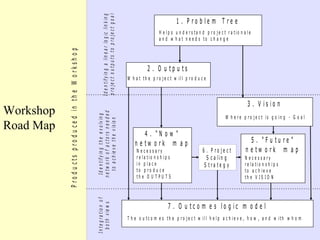
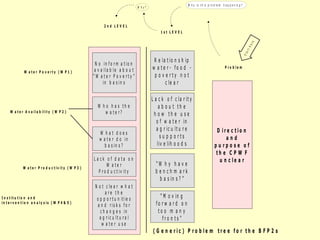
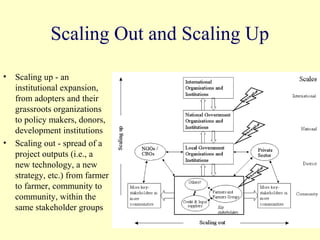
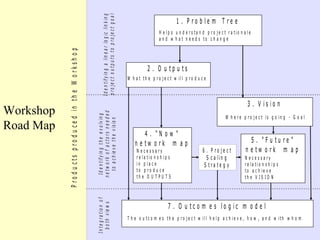
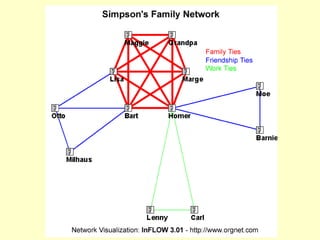
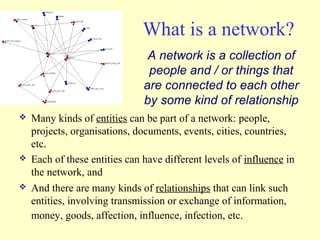
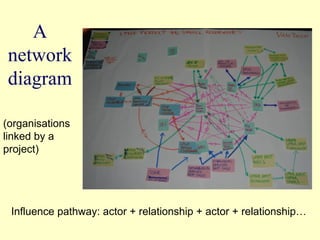
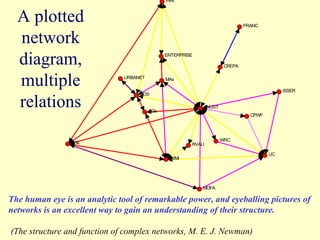
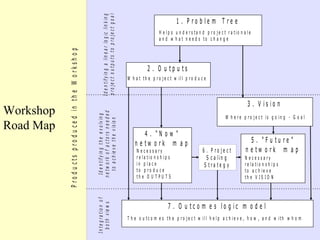
2. The workshop introduced the Pathways of Influence, Performance and Adoption (PIPA) approach for making impact pathways explicit. PIPA develops two perspectives - a problem tree showing how project outputs address problems to achieve goals, and network maps showing the relationships needed over time to achieve goals.
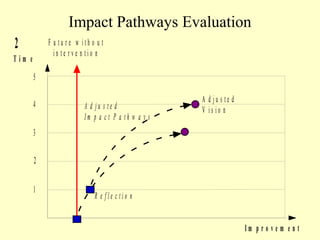
3. Integrating these perspectives provides a more complete picture of a project's theory of change from an