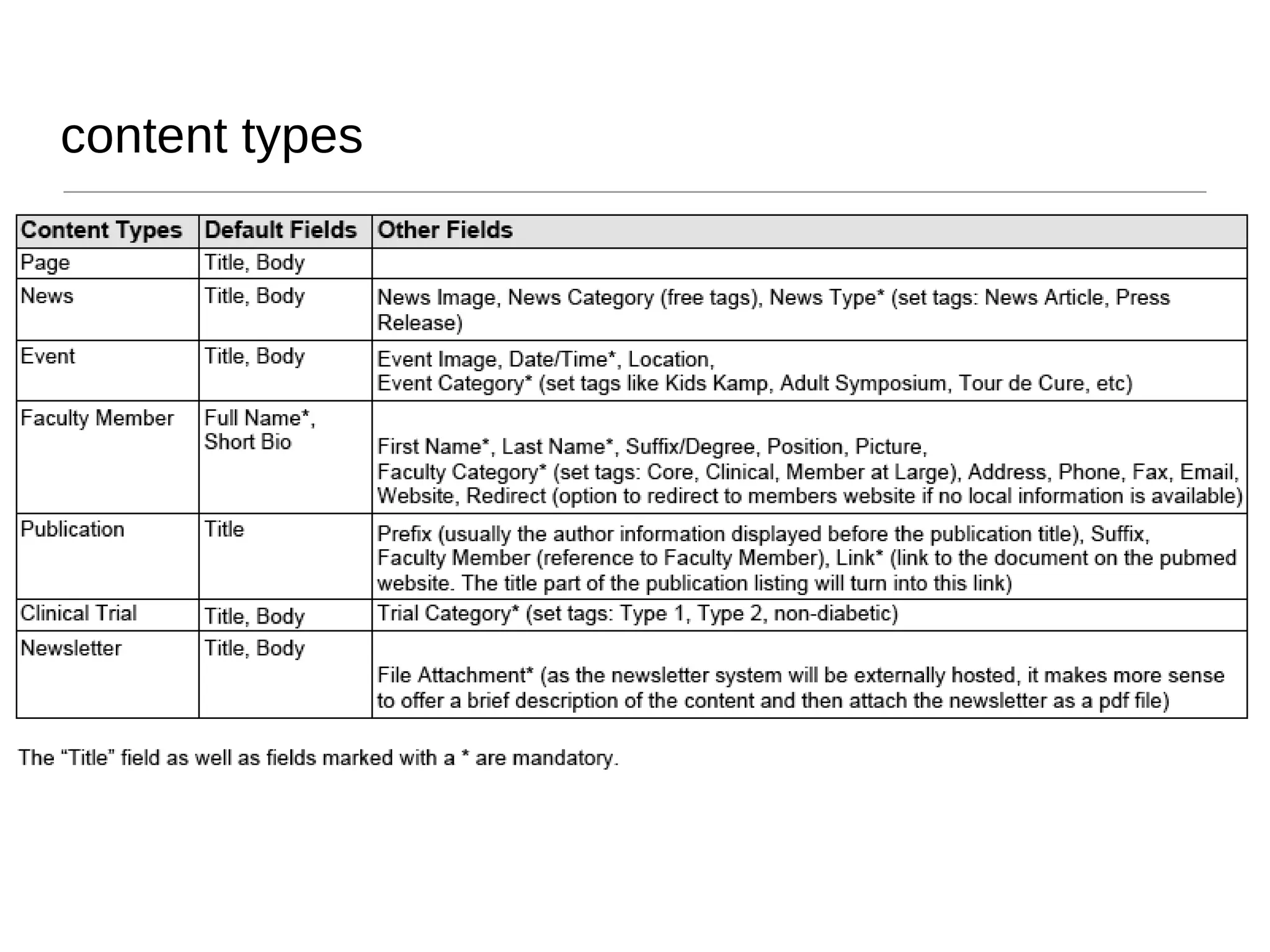
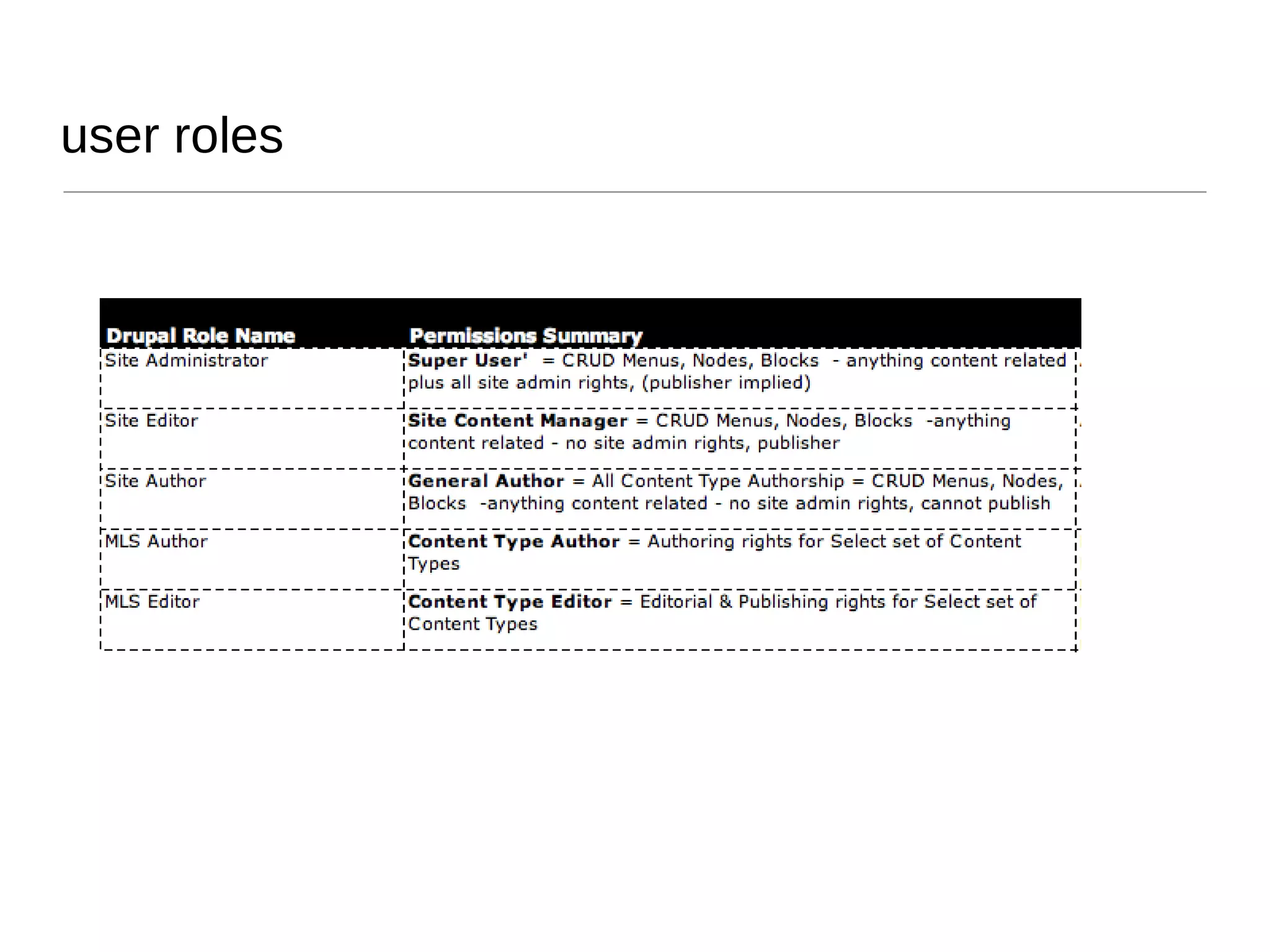
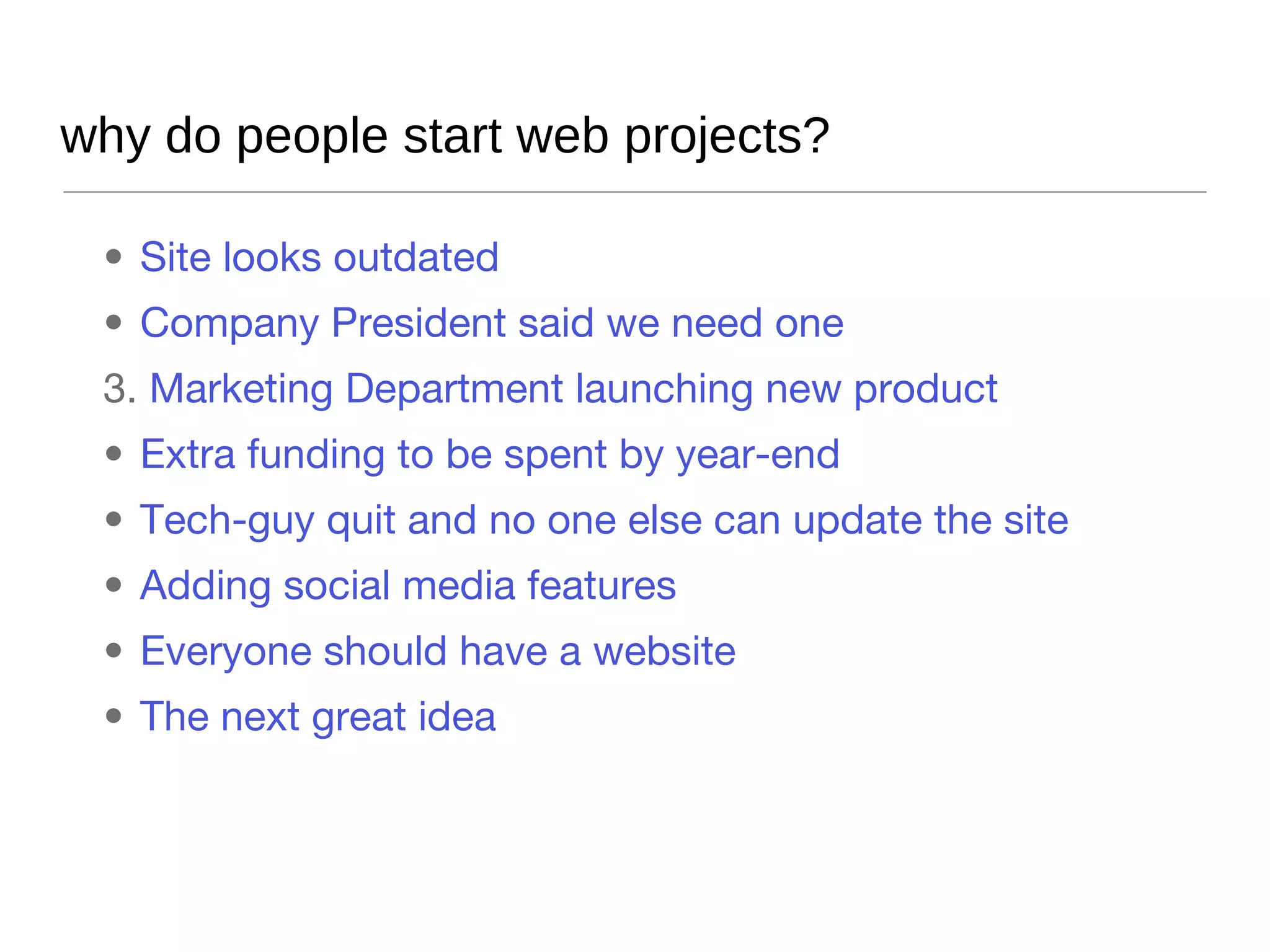
The presentation by Vanessa Turke addresses the challenges of managing client expectations in Drupal projects, focusing on the significance of customer satisfaction and quality. It underscores the importance of clear communication, project planning, and risk management in delivering value, as well as the detrimental effects of poor quality and scope changes. Additionally, the presentation emphasizes understanding client needs, maintaining project clarity, and effectively closing projects to ensure long-term success.














![what do clients expect? “ In a competitive and depressed economic climate, [your customers] want to know that any IT project they undertake will deliver a significant return on investment.” (Project management researchers, Reich, Gemino, Sauer (2010) SFU)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/managing-client-expectations-100424200907-phpapp02/75/Beyond-Budget-and-Scope-Managing-Client-Expectations-and-Delivering-Value-15-2048.jpg)




![what is value? “ [value is] the relationship between the consumer's perceived benefits in relation to the perceived costs of receiving these benefits.” ~wikipedia](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/managing-client-expectations-100424200907-phpapp02/75/Beyond-Budget-and-Scope-Managing-Client-Expectations-and-Delivering-Value-21-2048.jpg)