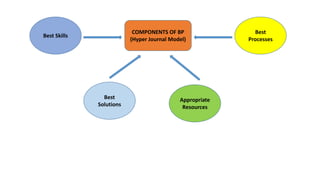
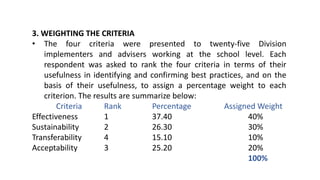
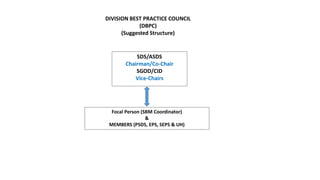
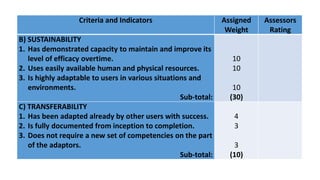
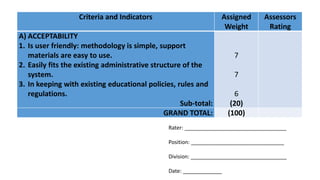
The document discusses the concepts and processes involved in identifying, documenting, and confirming best practices in education, emphasizing the importance of methodology and systematic approaches. It outlines the characteristics of best practices, their various classifications, and the necessary criteria for validation, such as effectiveness and sustainability. Additionally, the document highlights the role of school leadership, community involvement, and documentation strategies in fostering a culture of excellence within educational settings.