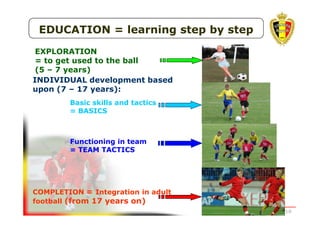
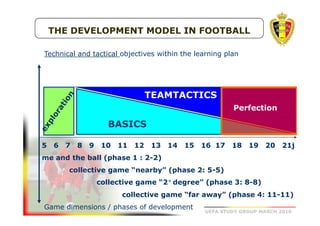
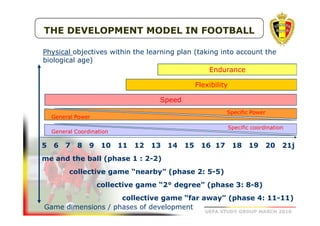
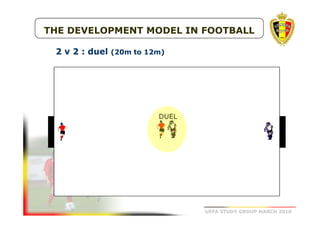
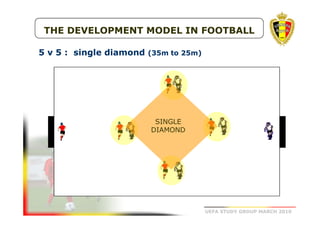
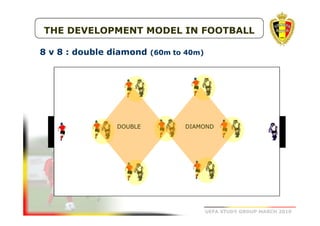
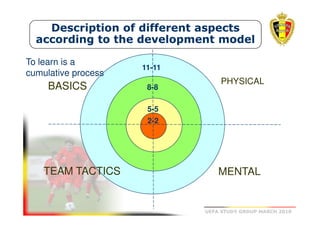
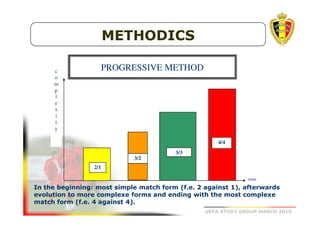
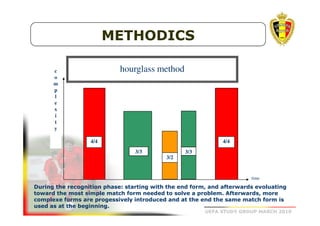
The document outlines the Belgian FA's youth development philosophy, emphasizing fun and learning through play, structured education, and a zone philosophy that improves players' understanding and decision-making. It details a continuous development model that includes technical, tactical, mental, and physical objectives across different phases of player growth. Additionally, it highlights the importance of creating a strong learning environment focused on individual player growth and decision-making.