This document provides information about leadership approaches and theories. It discusses:
- The basic approaches to leadership including defining leadership, characteristics of great leaders like empathy, honesty, direction, communication and flexibility.
- The main roles of a leader including representation, integrating efforts, soliciting support, and guiding employees.
- Different leadership styles like laissez-faire, autocratic, participative, transactional, and transformational.
- Trait theory of leadership which identifies core traits like motivation, integrity, self-confidence and knowledge. It also discusses the strengths and limitations of this theory.
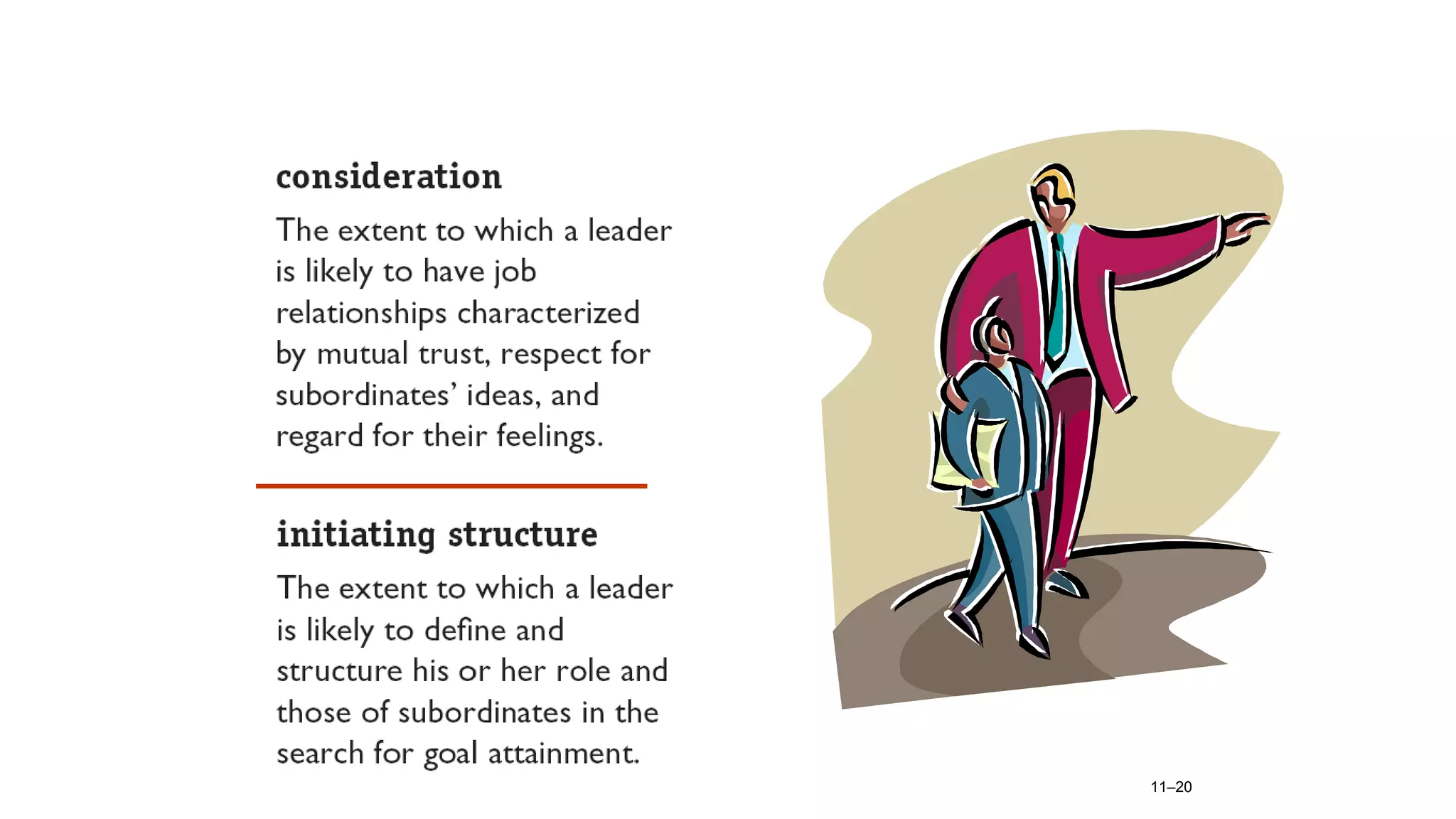
- Consideration and initiating structure dimensions of leadership behavior.
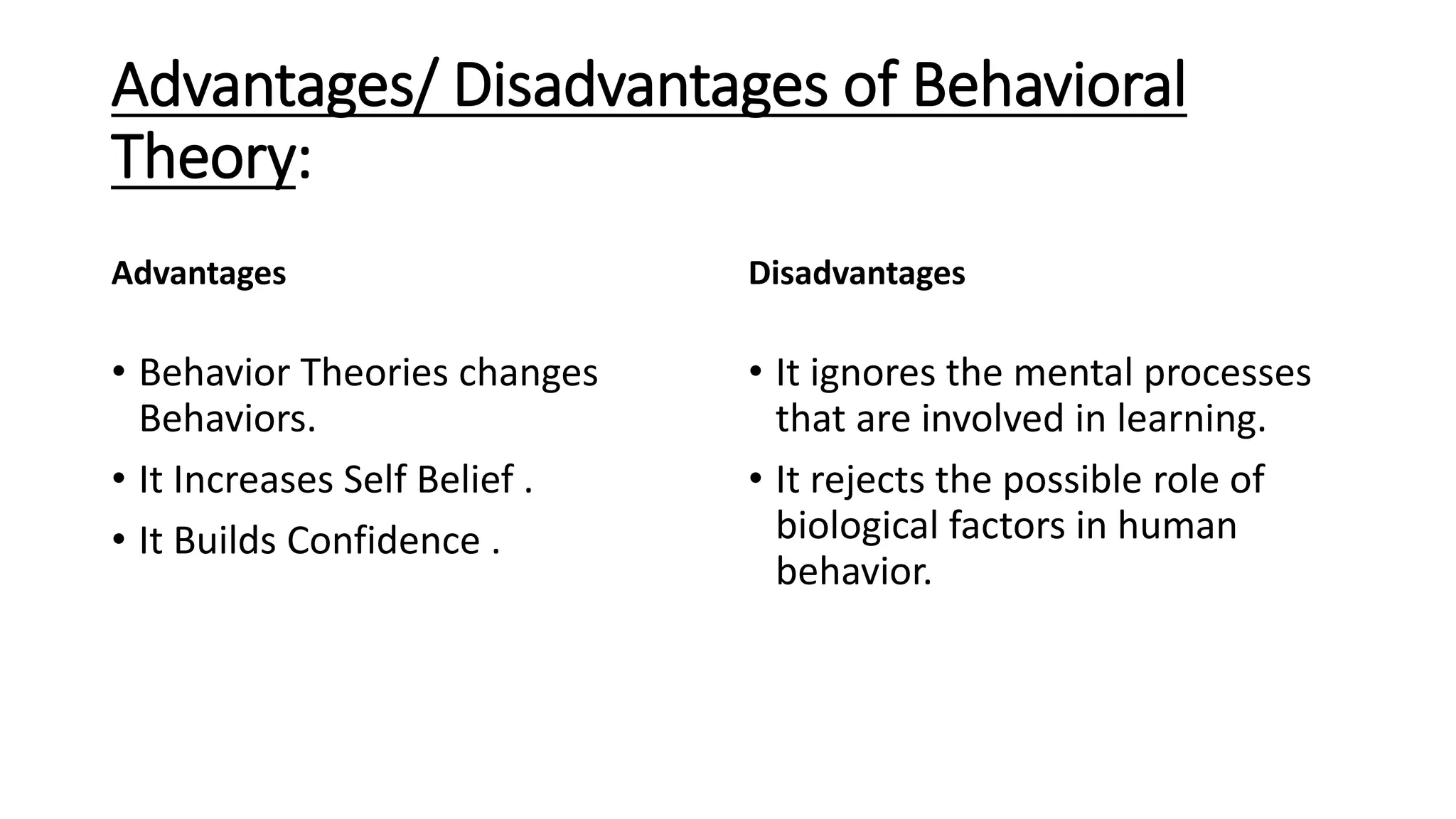
- Behavioral theories which attempt to describe