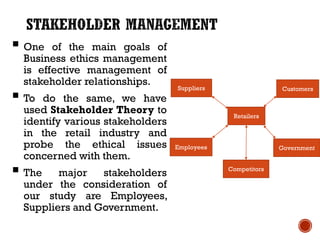
The document discusses ethical issues in the Indian retail industry related to employees, suppliers, and the government. It notes that global retailers are known to overwork employees and pay low wages without proper benefits. Large retailers can also force down supplier prices to increase their profits. There are concerns that foreign retailers will lobby and pressure the Indian government, potentially influencing regulations in a way that raises ethical issues. Suggestions are made around protecting employee rights and developing frameworks to avoid monopolistic practices with suppliers.






![SUPPLIER RELATED ISSUES
• A big retailer has enough muscle power to determine the
supplier prices and if the need be to lower the same to
increase their own share of the pie.
• Pressure of large companies on retailers: e.g. ITC allegedly
forces its retailers to put their cigarette packets face-wise
while that of competitors edge-wise [cigarette companies
are not allowed to advertise their product].
• Under stocking products of certain suppliers by retailers,
giving unequal opportunity to certain suppliers.
• The Utilitarian Theory states that the action should be
morally right if it results in the greatest amount of good for
the greatest number of people.
• In this case, the focal firm would gain the maximum utility
at the cost of other stakeholders like farmers, SMEs and
standalone suppliers.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/beppt-130411005549-phpapp02/85/Ethical-issues-after-walmarts-entry-in-Indai-8-320.jpg)


