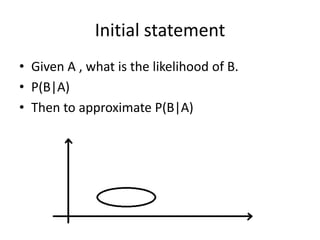
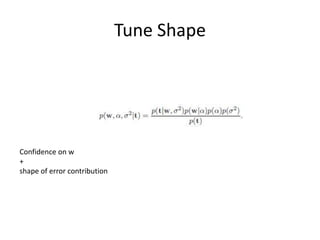
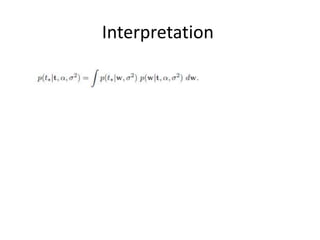
1. Bayesian methods can be used to approximate the probability of B given A (P(B|A)) by treating it as a function (f(A;w)) of the exemplars A and weights w, where the weights are unknown.
2. A Bayesian model is set up where the model/basis shapes are normally distributed, the confidence weights are independent, and there are precision tuners on the basis and weights.
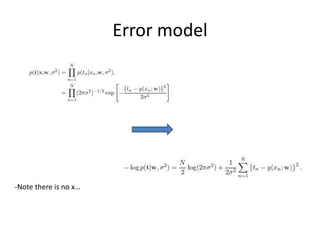
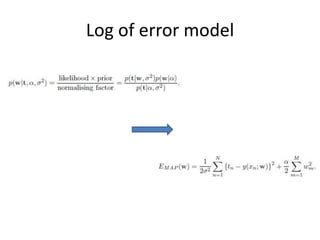
3. Complexity control through regularization adds a penalty term (E_w) to the standard regression error term (E_d) controlled by a hyperparameter (lambda) to solve overfitting.