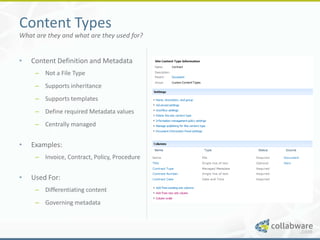
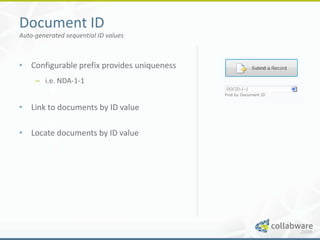
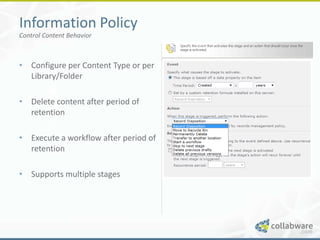
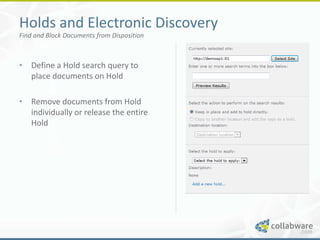
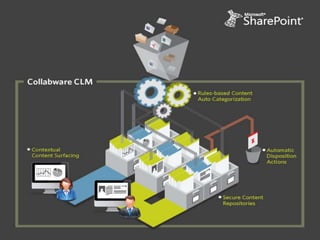
The document discusses basic records management strategies using SharePoint, detailing features and implementation approaches for managing records effectively. It highlights key components such as content types, metadata, and information policy, alongside challenges like limitations in enterprise capabilities and the need for customization. Advanced options with Collabware CLM are proposed to enhance SharePoint's functionality for records lifecycle management.