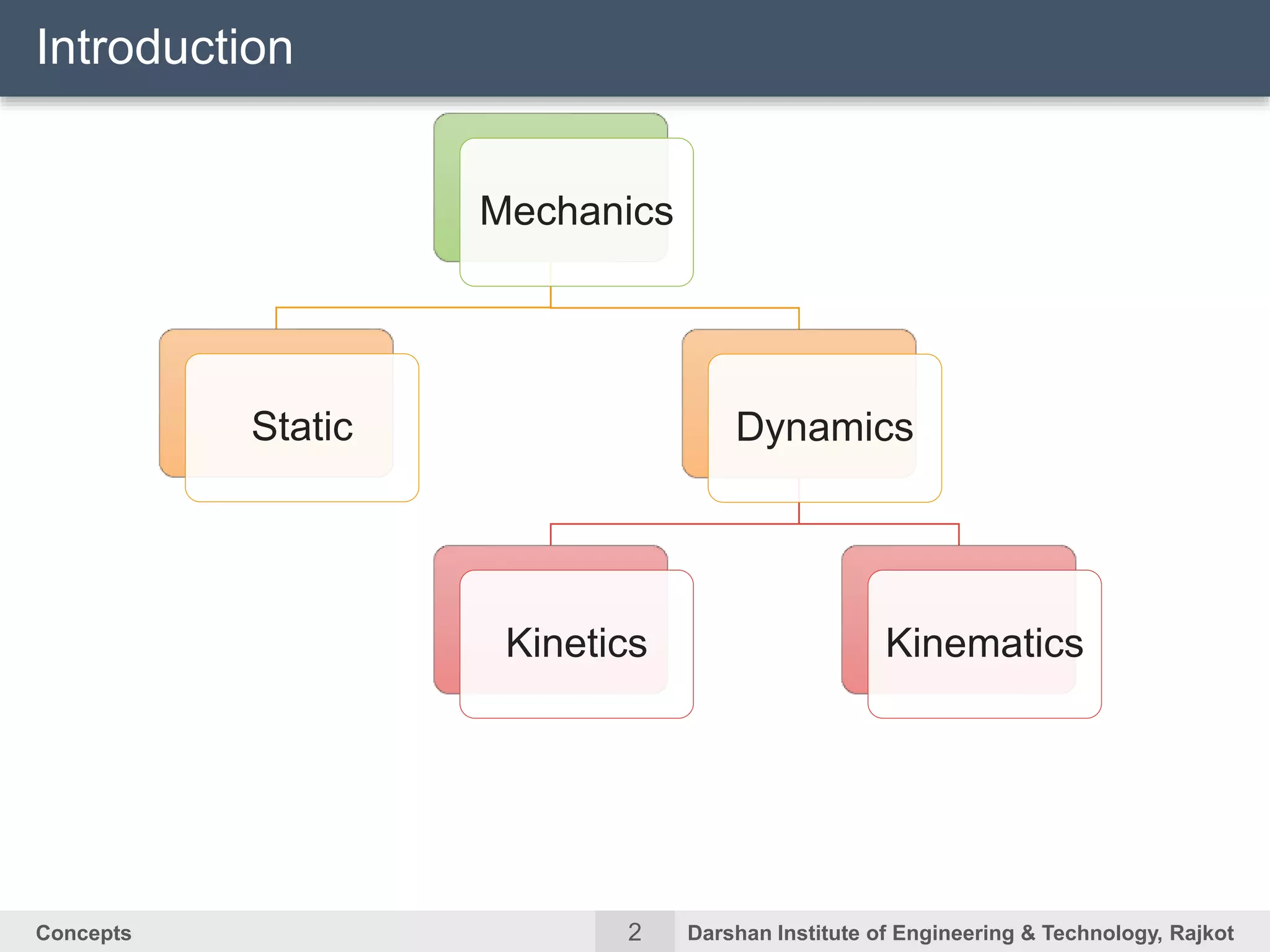
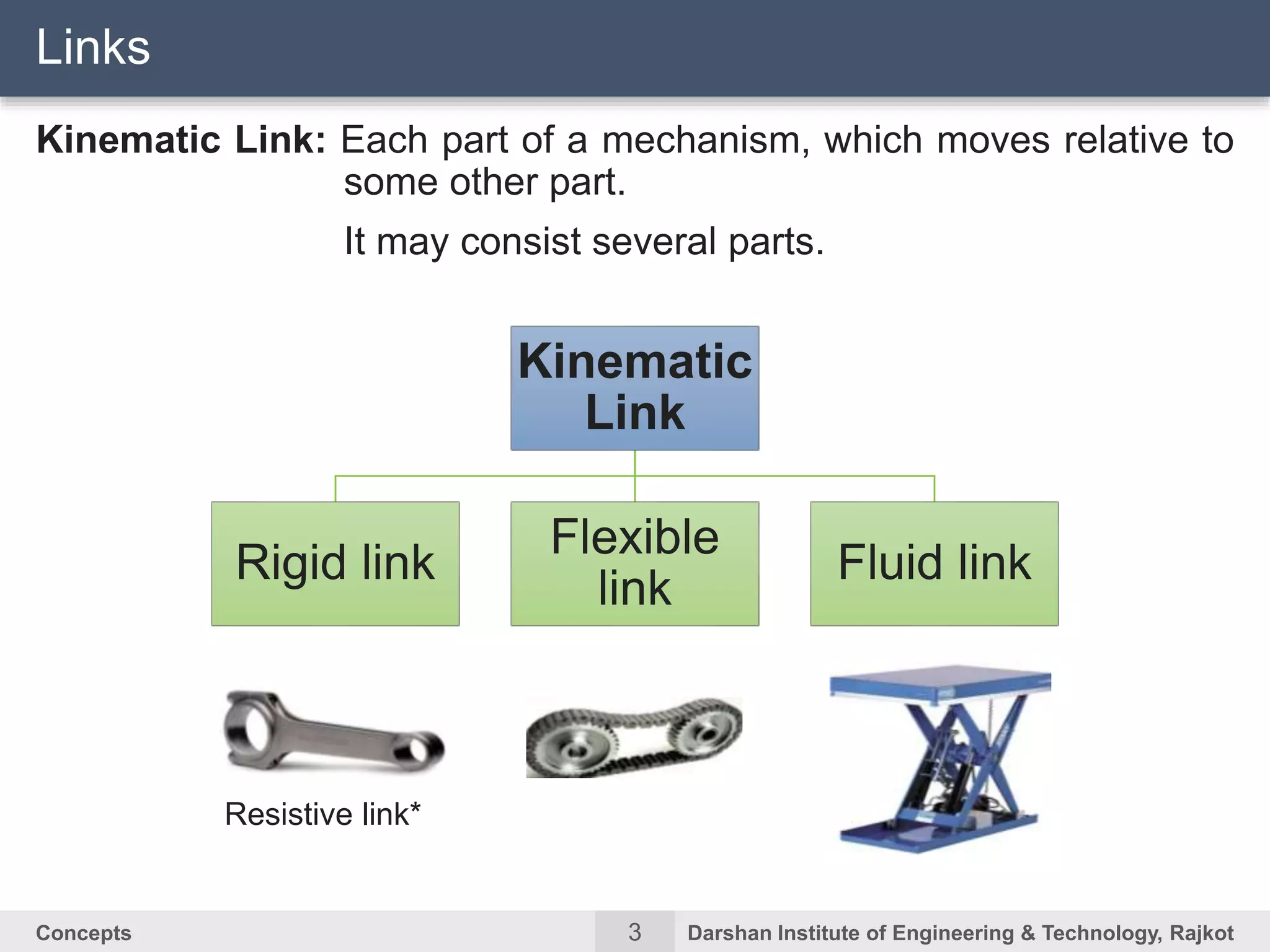
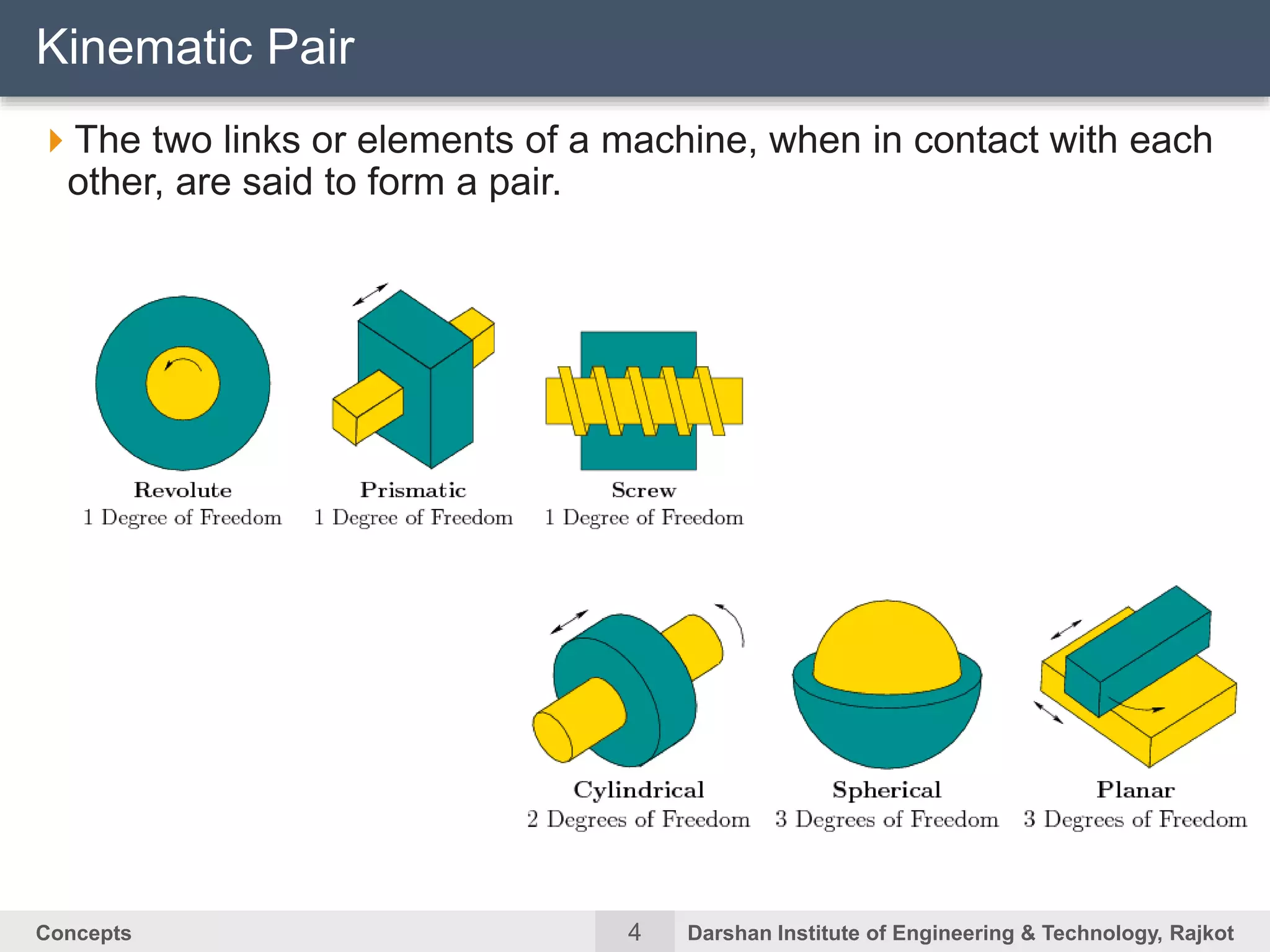
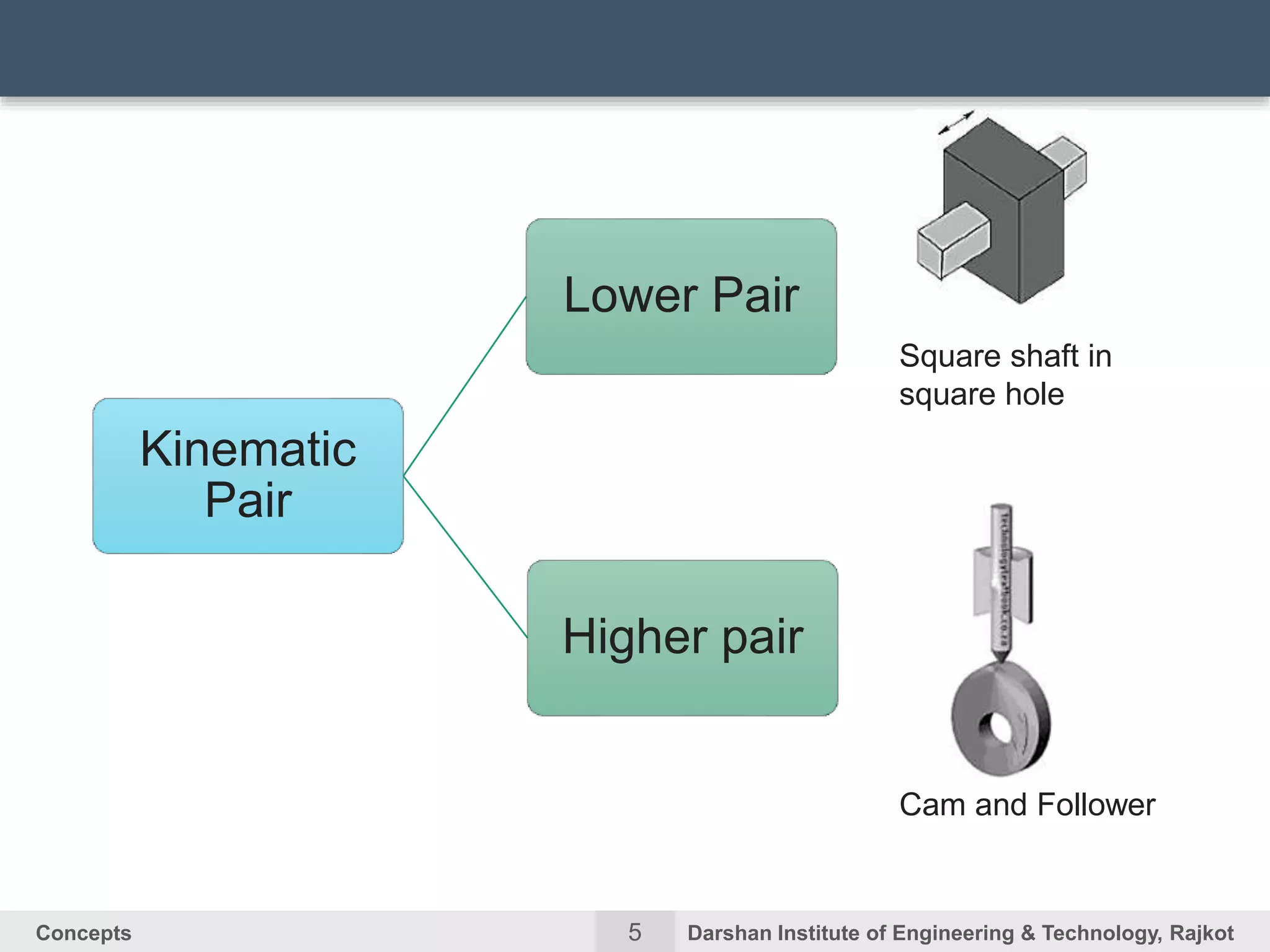
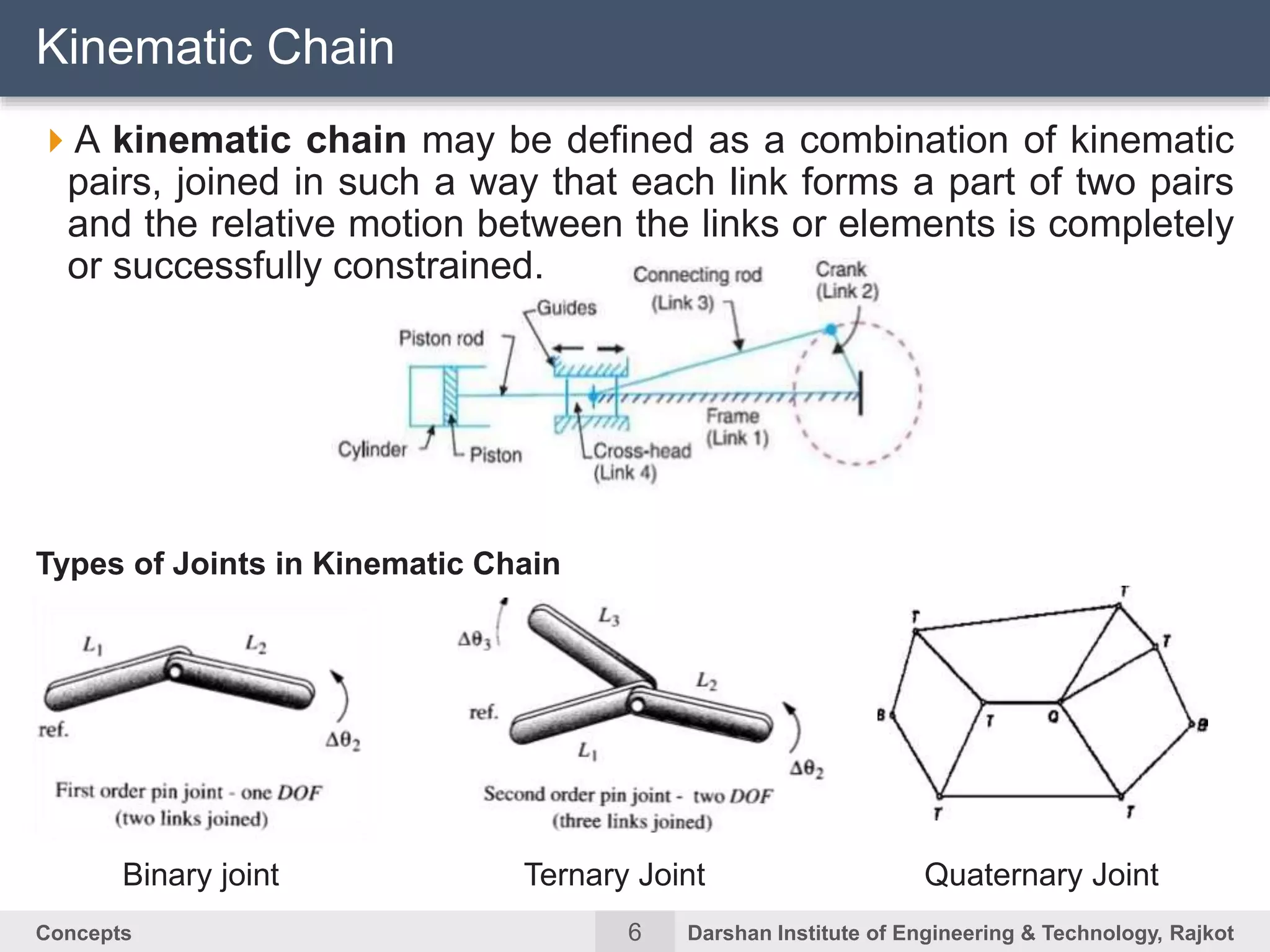
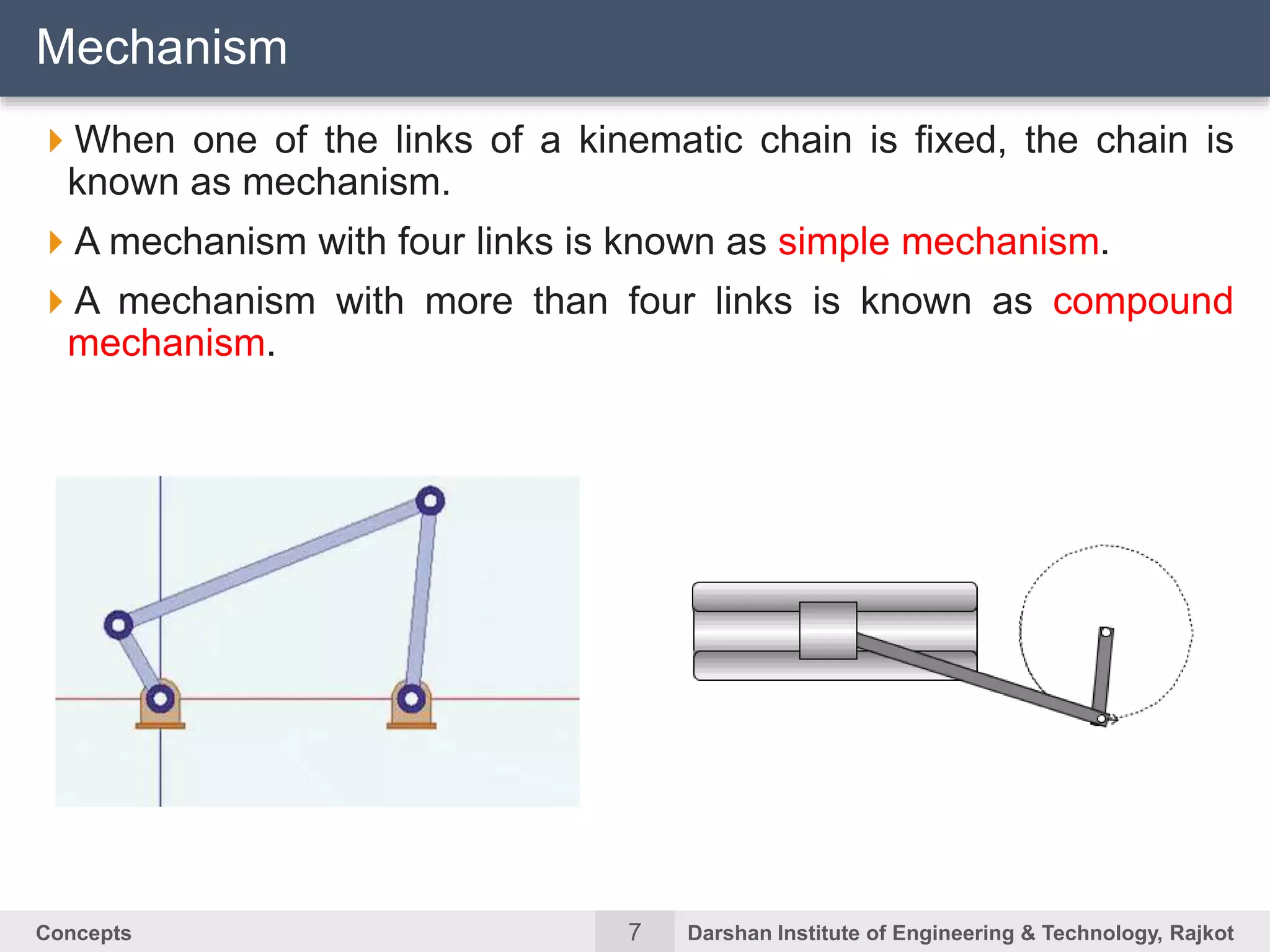
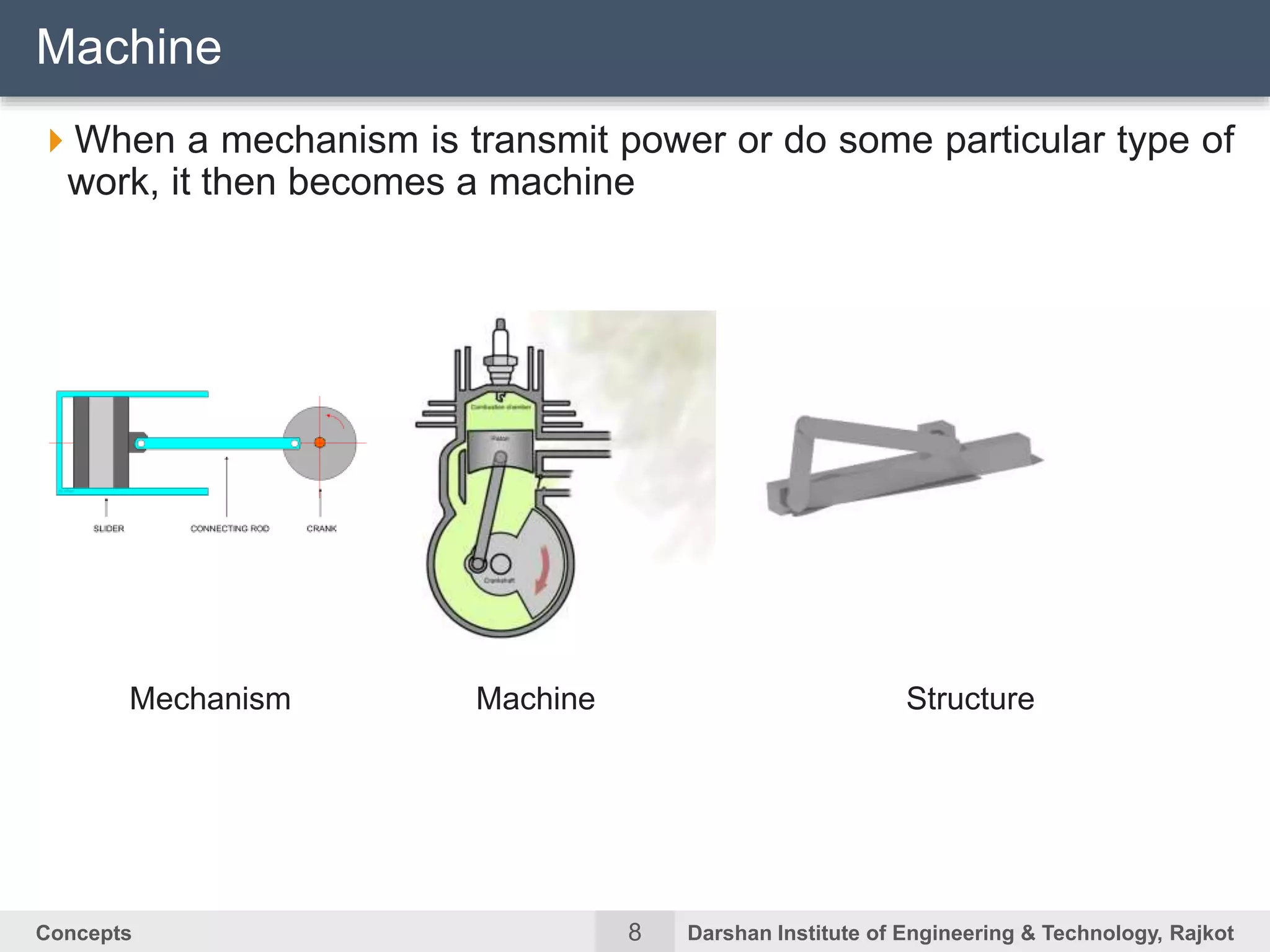
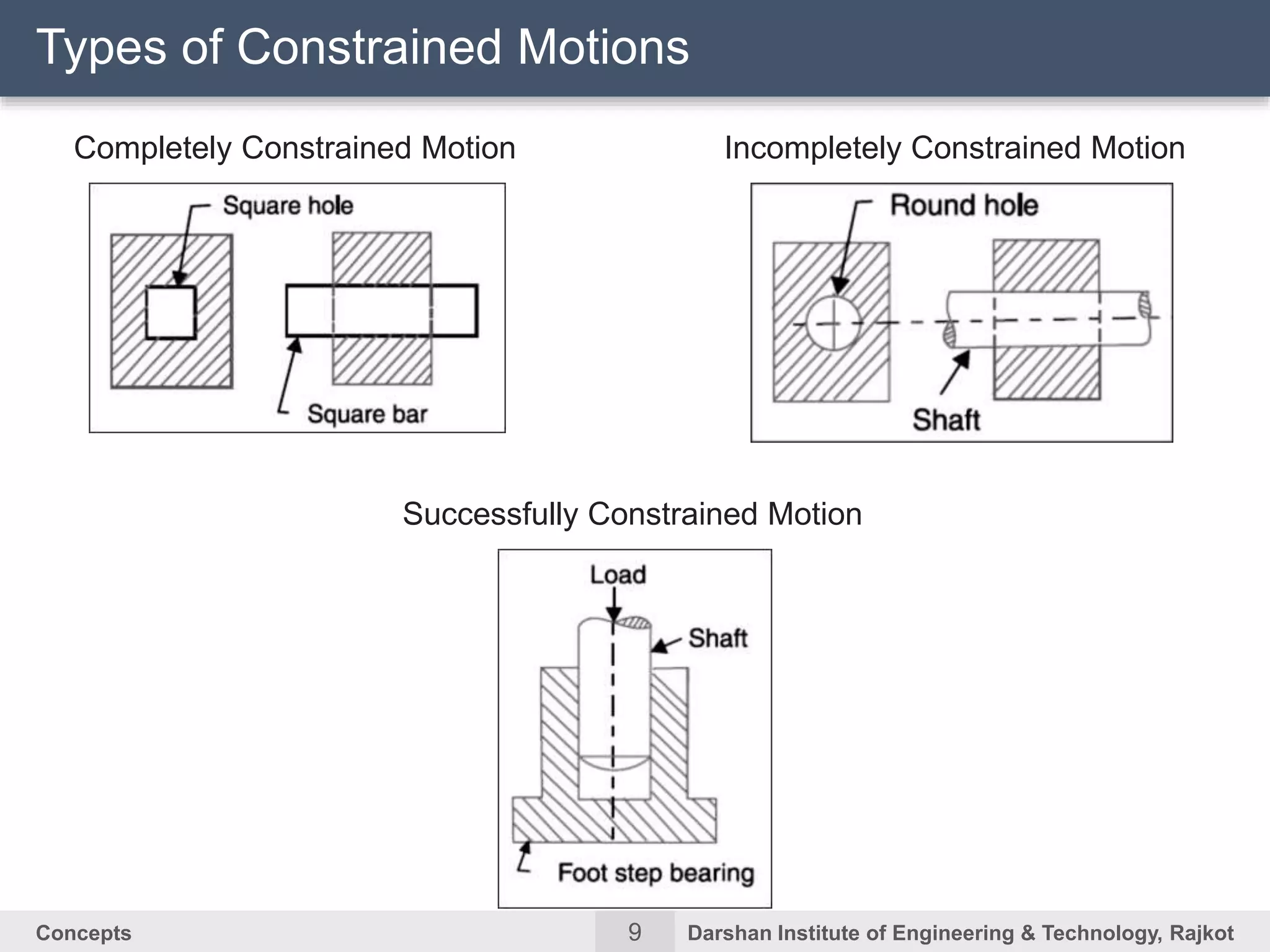
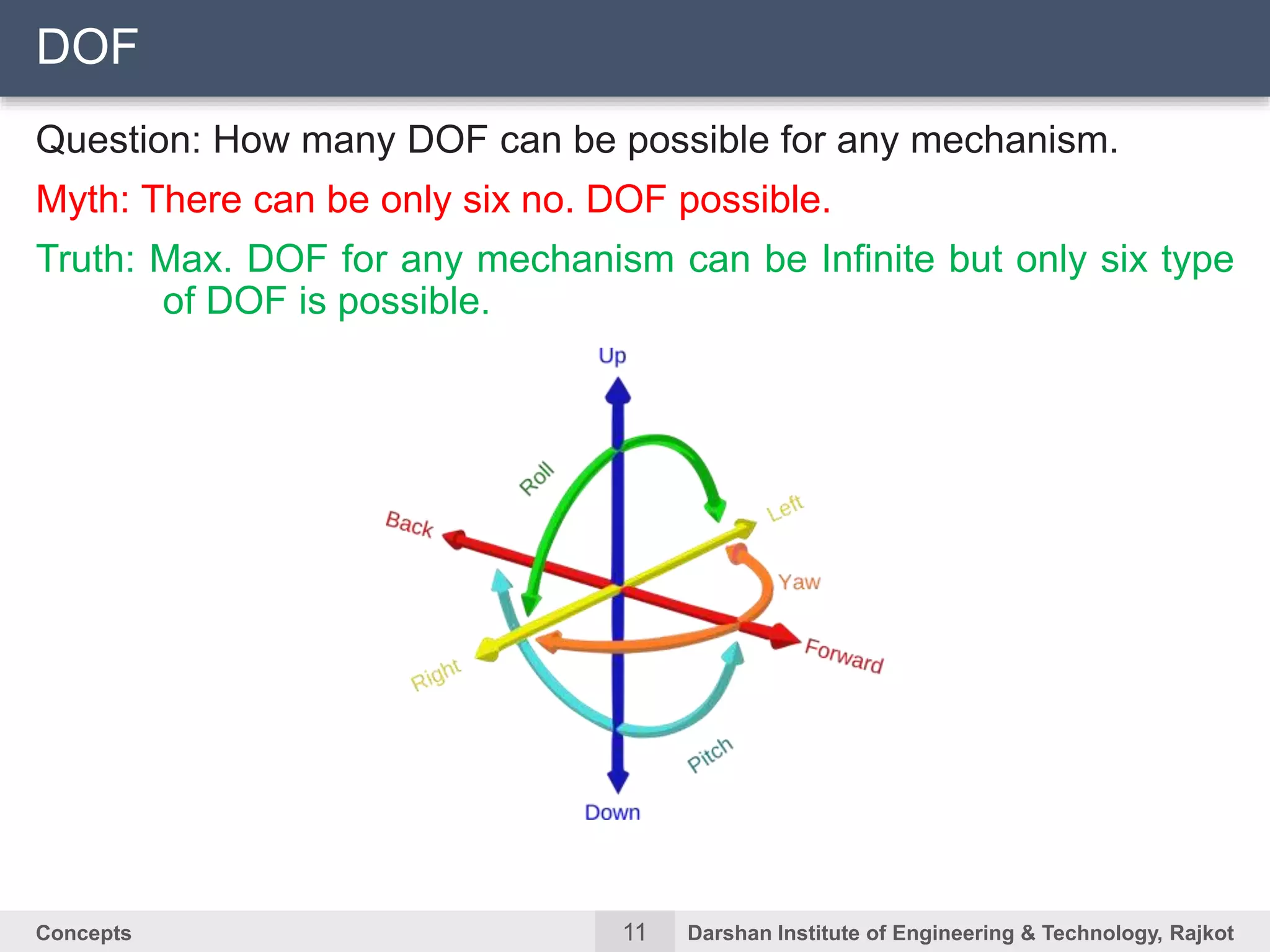
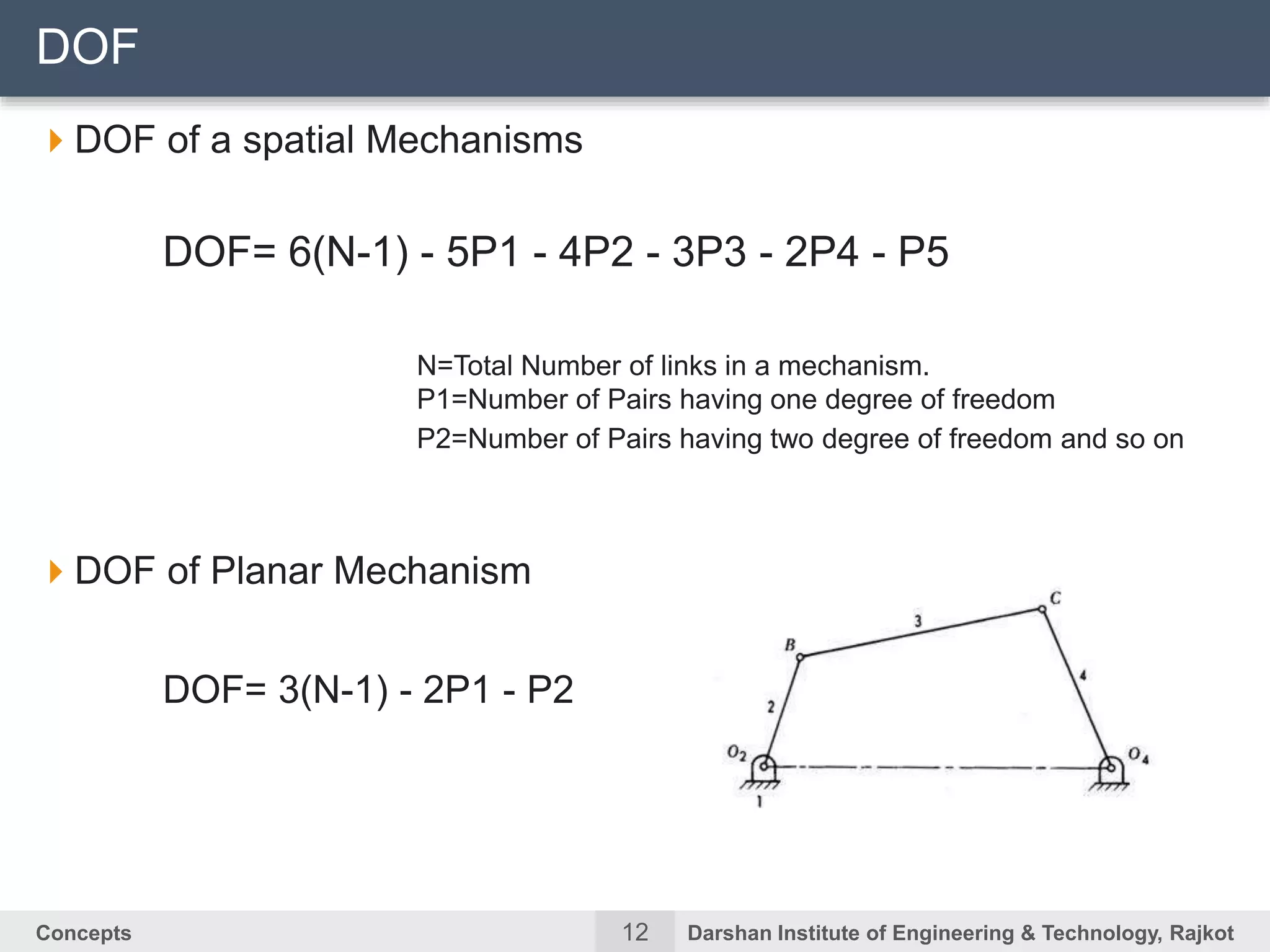
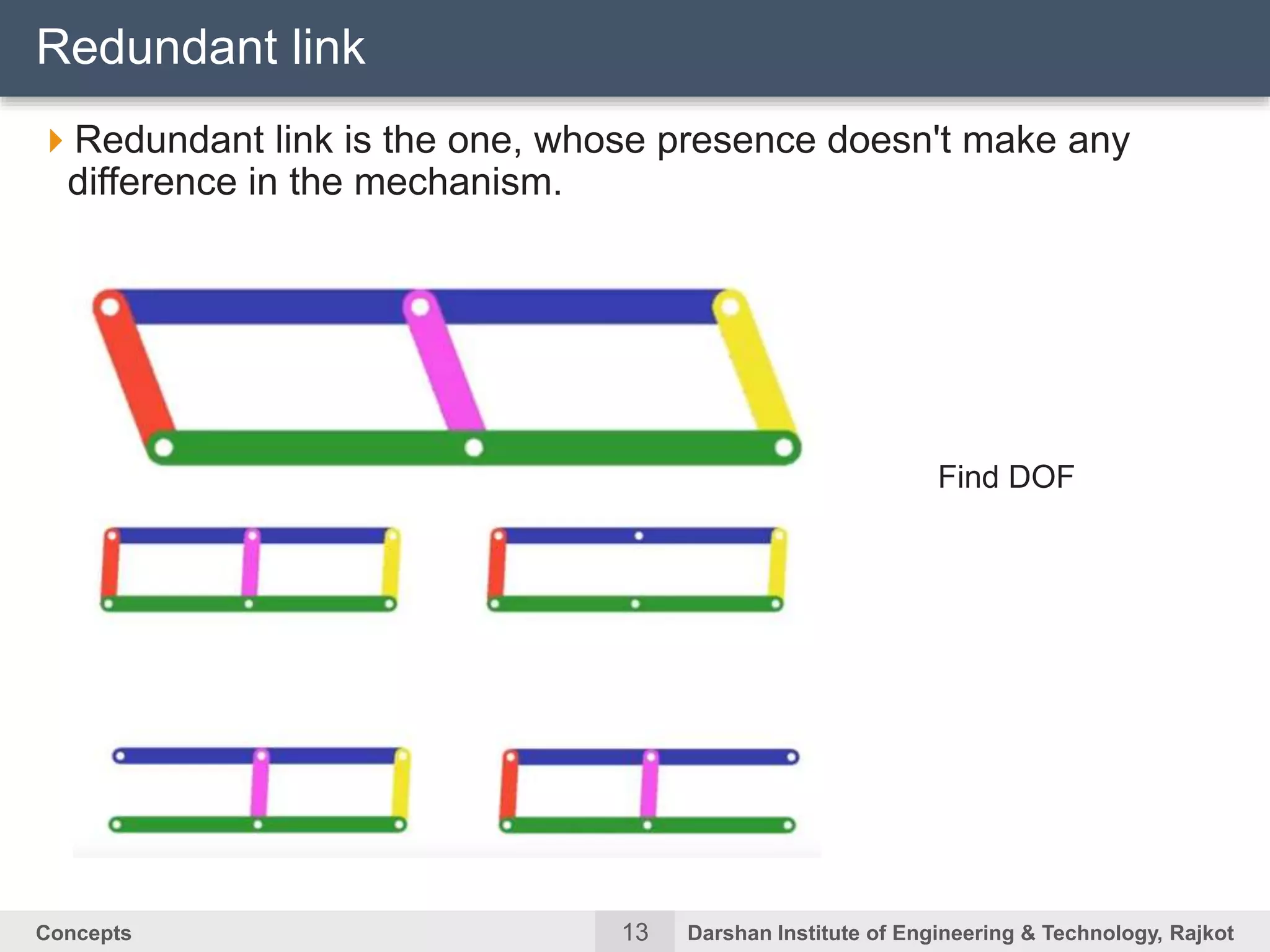
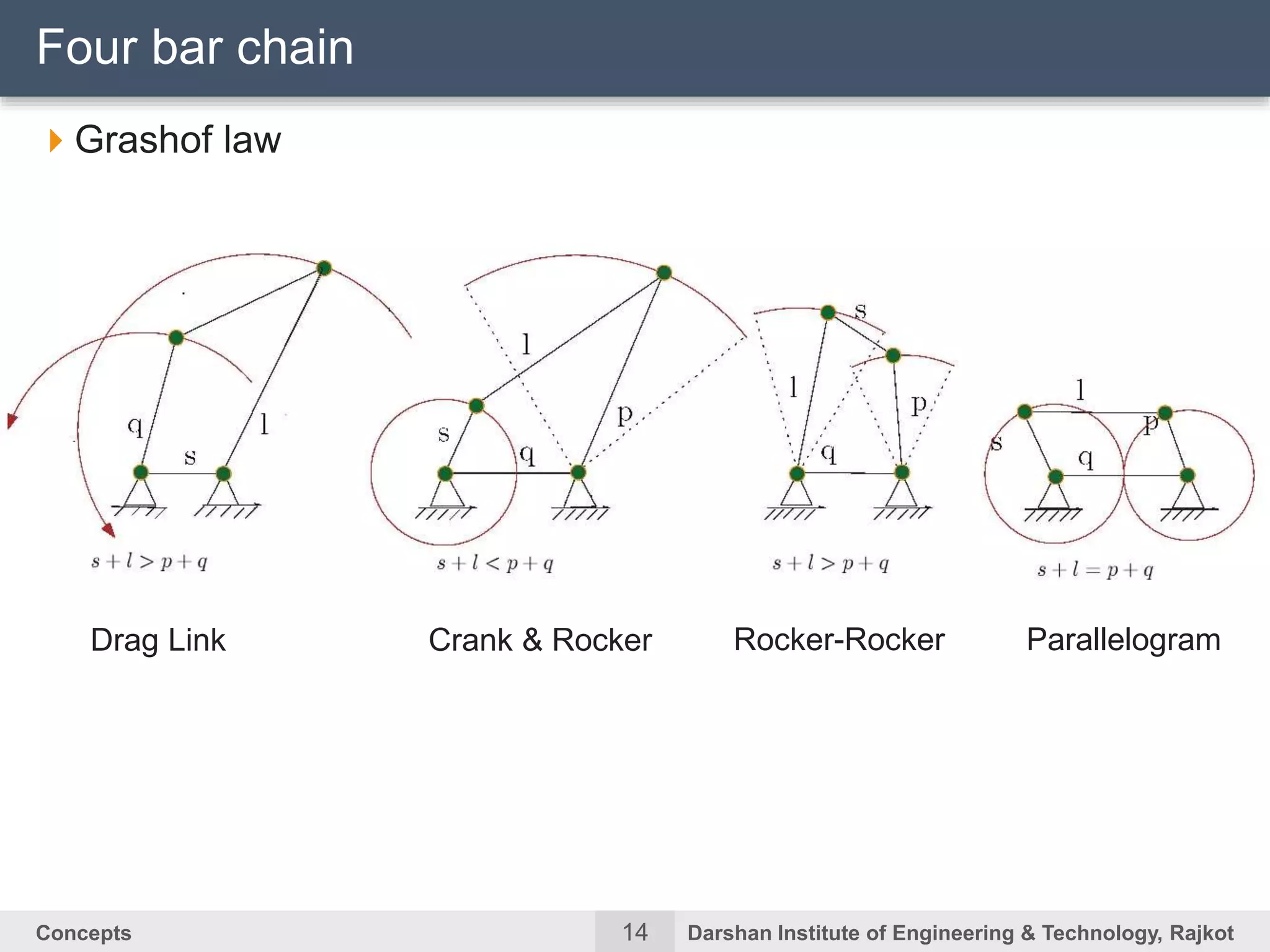
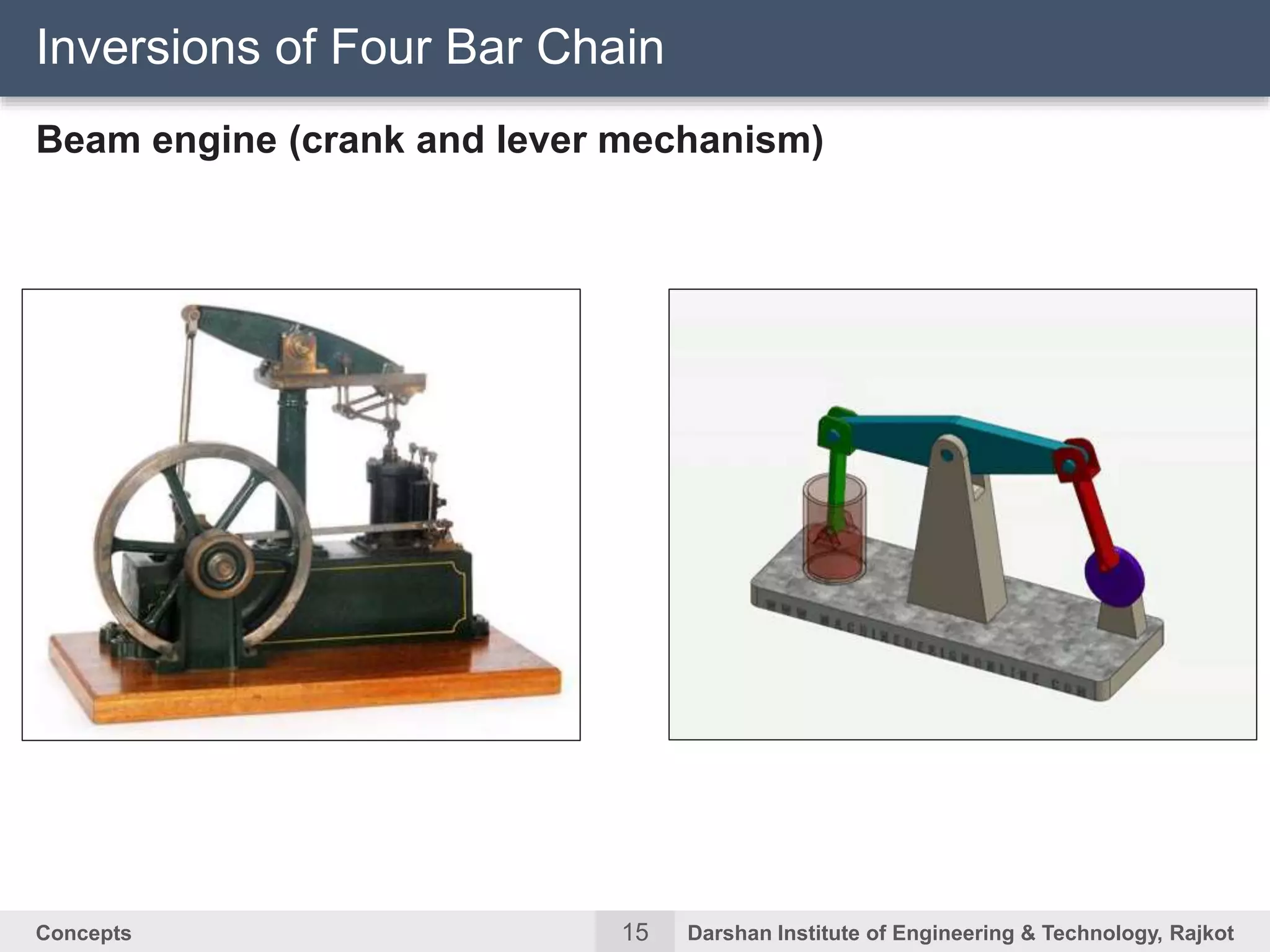
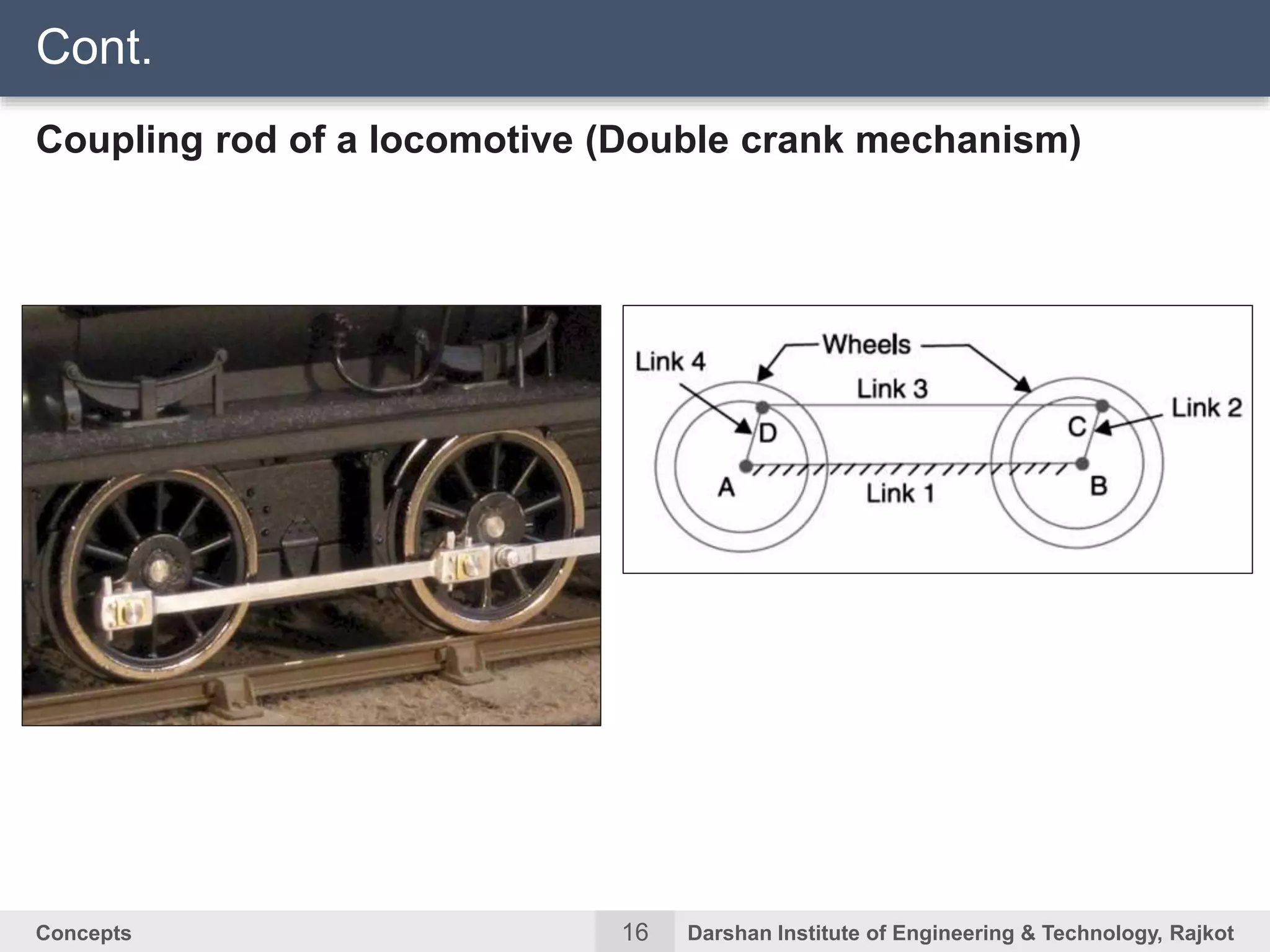
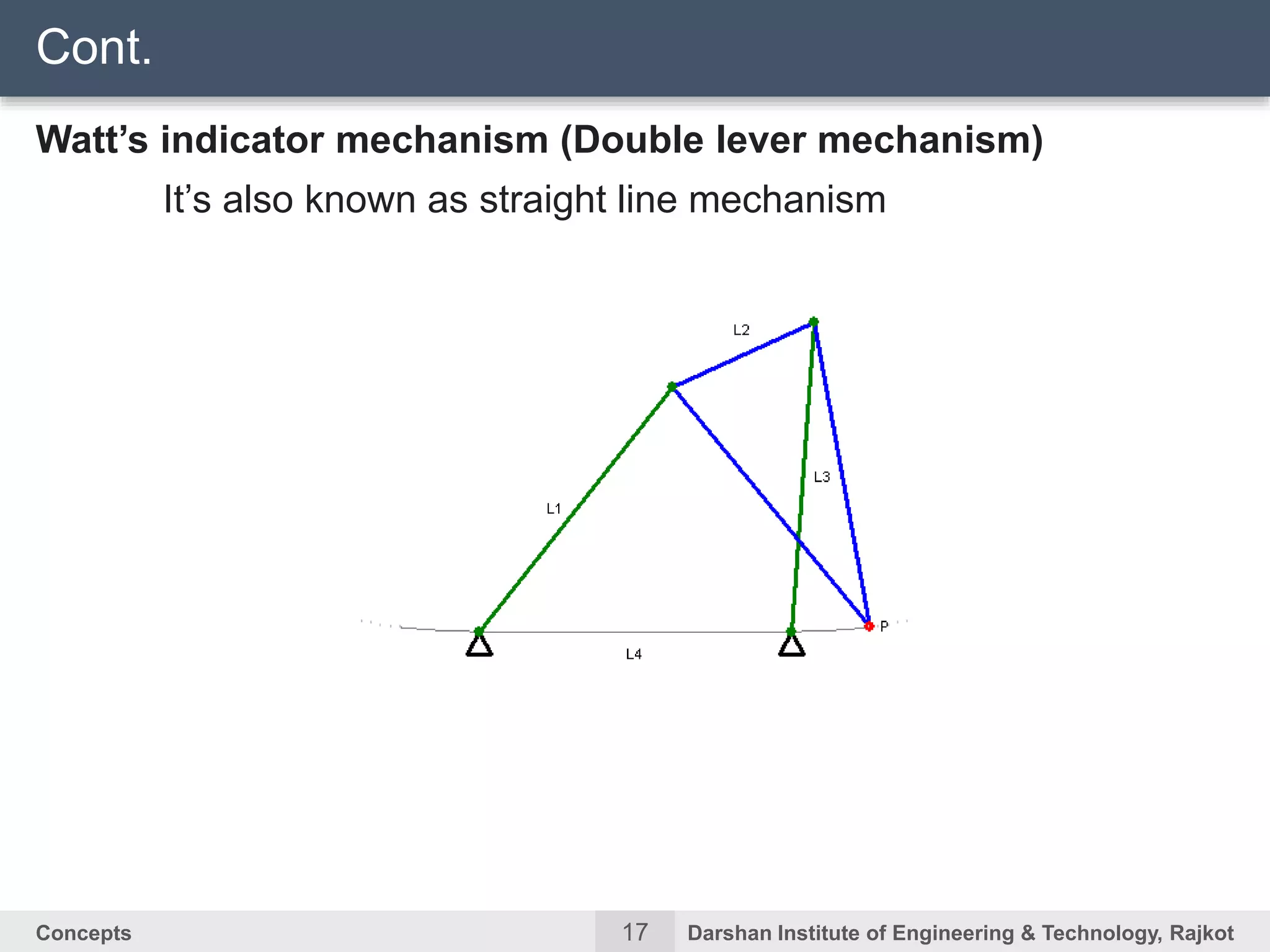
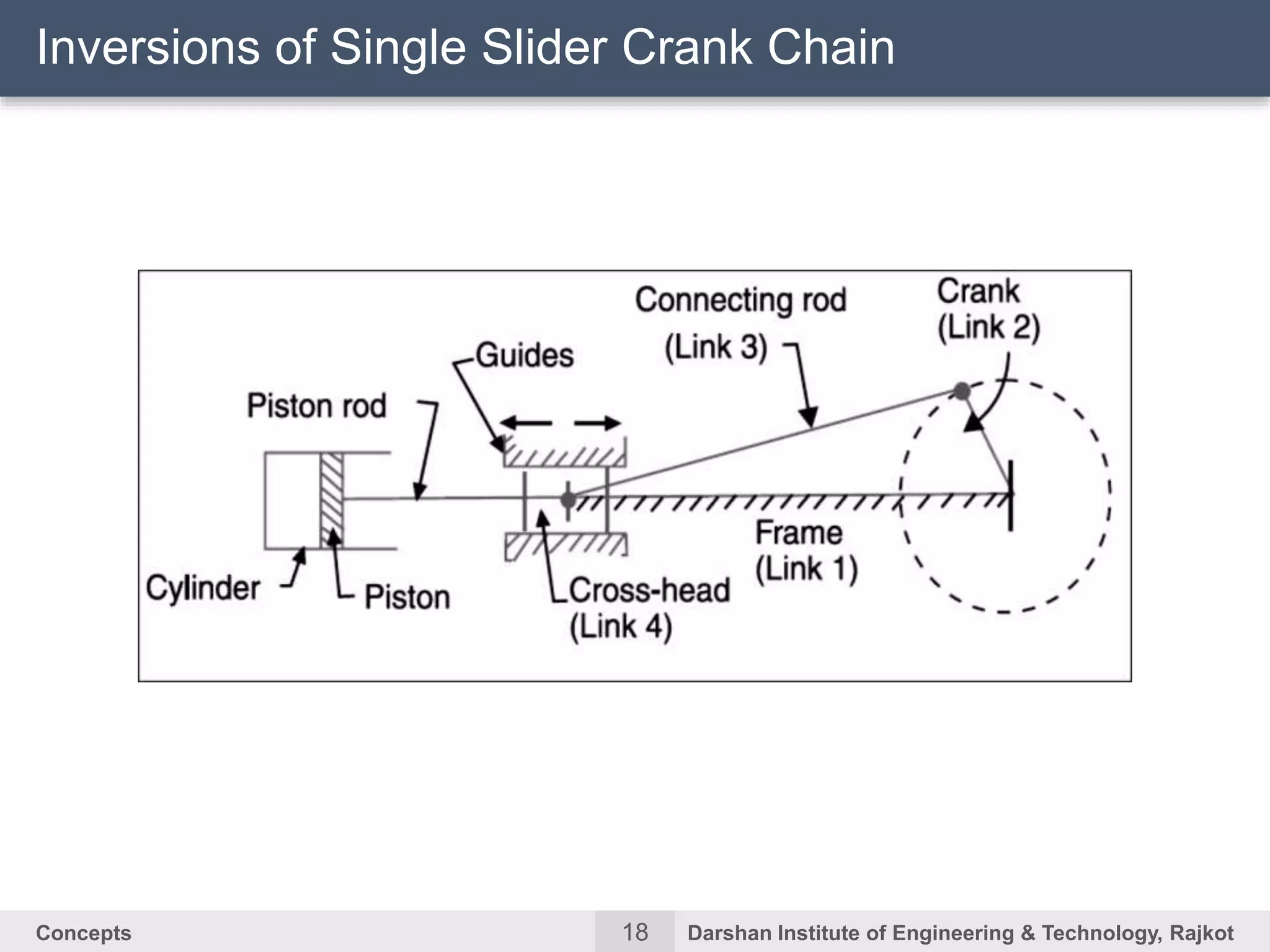
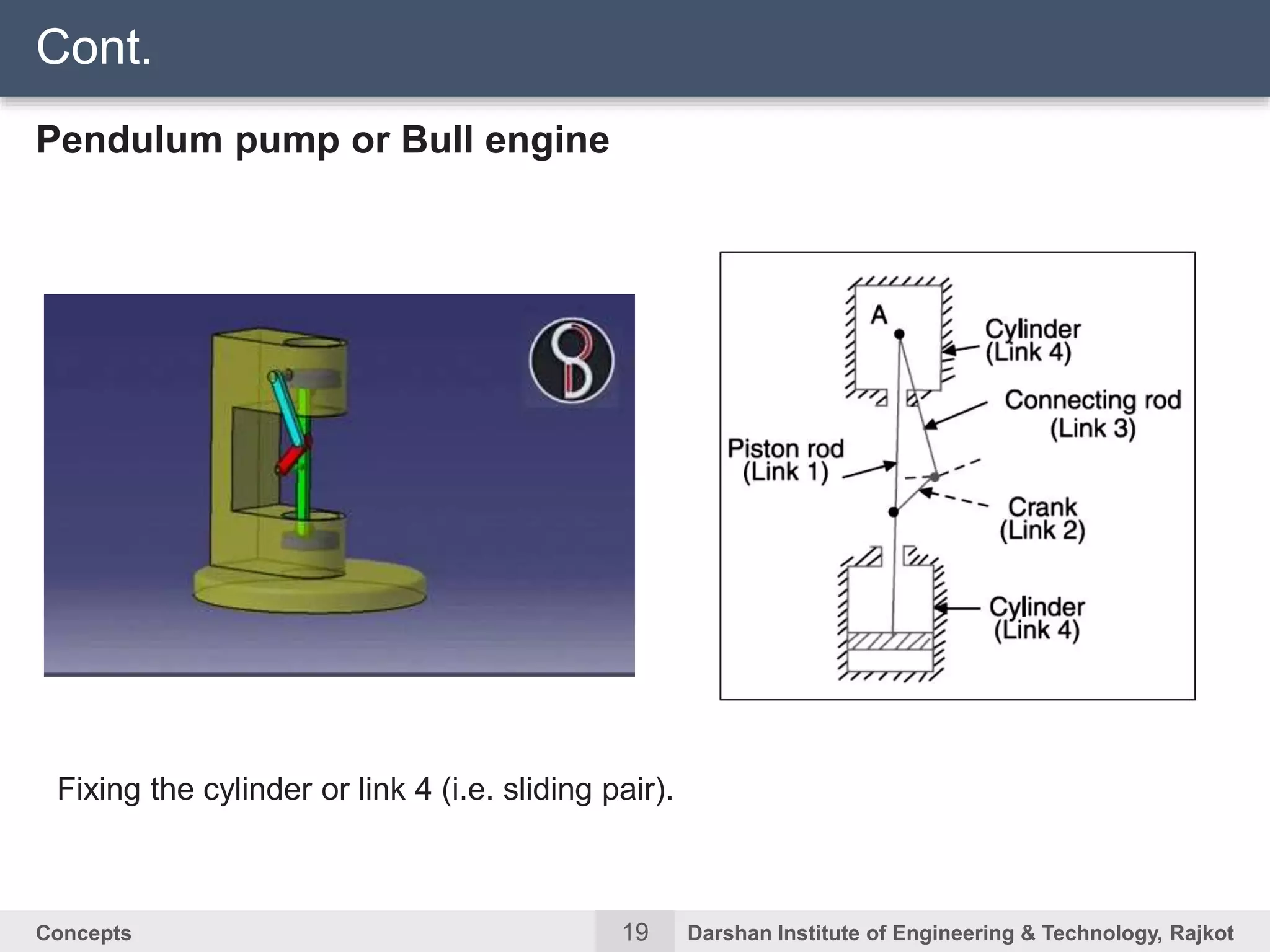
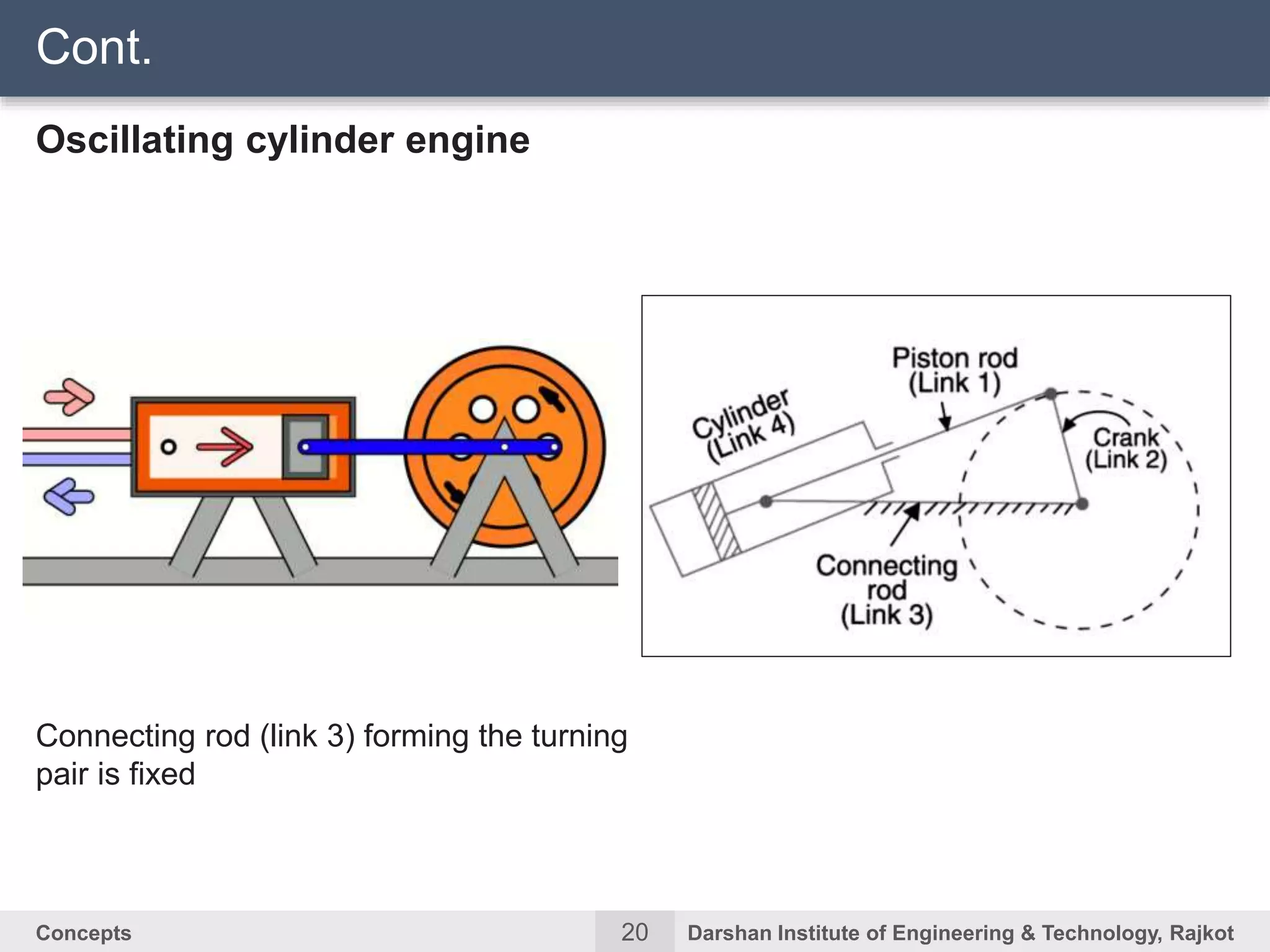
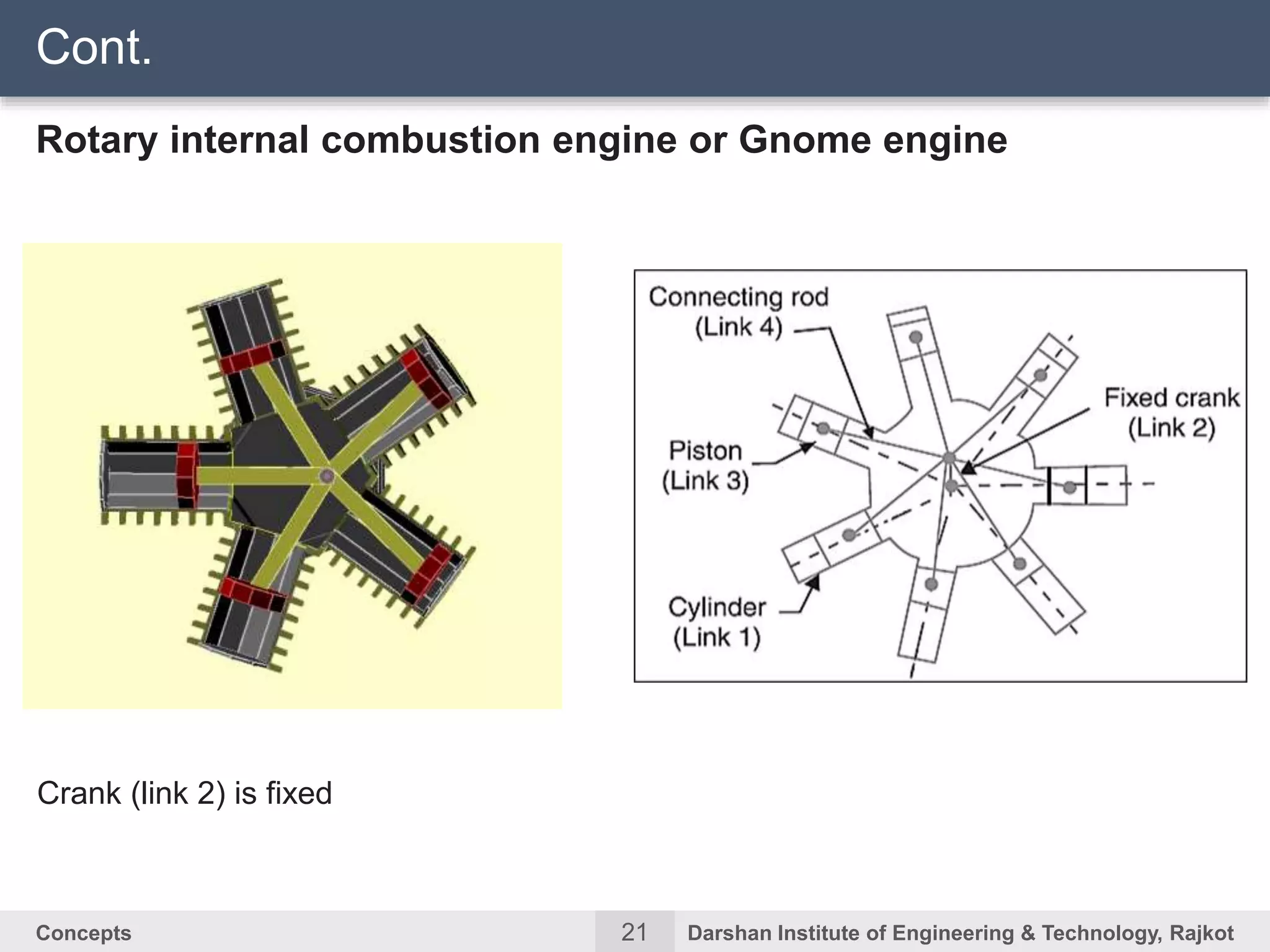
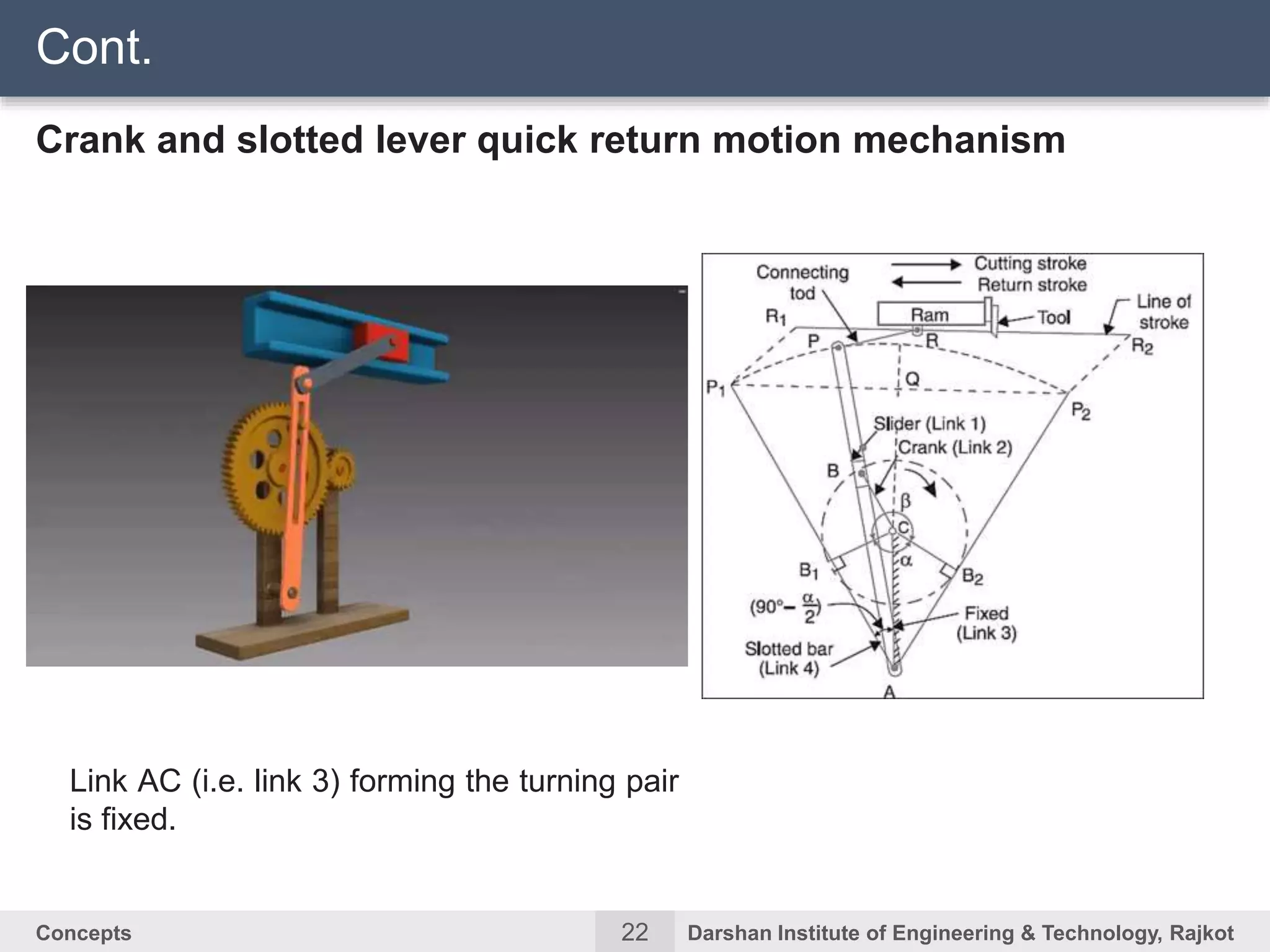
The document discusses kinematic concepts related to mechanisms and machines. It defines kinematic links, pairs, chains and their types. It describes mechanisms as kinematic chains with one fixed link and machines as mechanisms that transmit power or do work. The document discusses degrees of freedom of spatial and planar mechanisms using mobility formulas. It also covers Grashof's law for four-bar chains and examples of single slider crank inversions including the beam engine, locomotive coupling rod, and Watt's indicator mechanism.