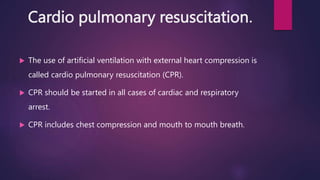
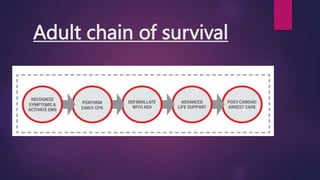
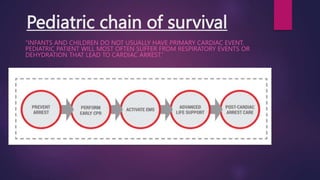
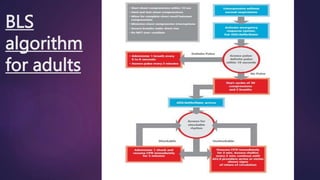
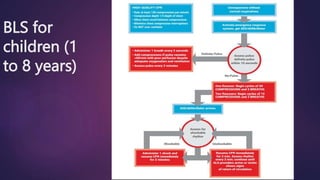
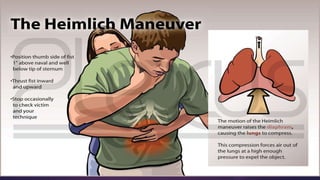
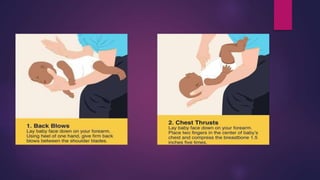
Basic life support (BLS) involves immediate assistance provided to an injured or ill person until further medical help arrives. BLS aims to provide oxygen to the heart and brain, sustain tissue function, preserve life, and make the victim comfortable. It includes chest compressions, rescue breathing, use of an AED, and treating choking. The American Heart Association provides BLS guidelines including recognition of respiratory emergencies, high-quality chest compressions for various age groups, and "Chain of Survival" protocols for cardiac arrest. BLS algorithms detail life-saving steps for one- and two-rescuer situations involving infants, children, and adults. Proper airway management, rescue breathing, and relief of choking are also essential