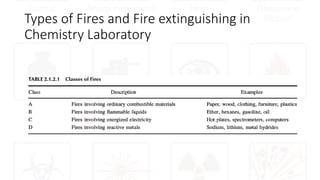
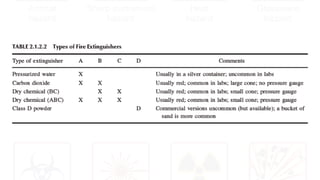
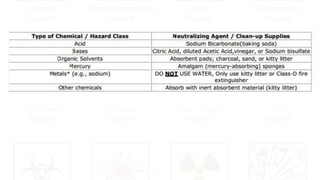
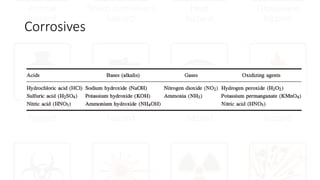
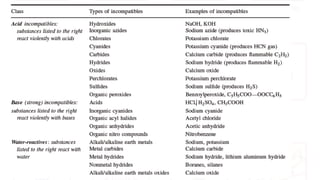
The document provides safety guidelines for chemistry laboratories. It outlines the four principles of safety - Recognize, Assess, Minimize and Prepare (RAMP). Basic safety rules are described such as wearing protective equipment, avoiding food/drink in labs, and not working alone. Material safety data sheets (MSDS) are explained. Common lab accidents like fires, chemical spills, contact with corrosives and reactions between incompatibles are discussed. For each type of accident, the RAMP approach is described to recognize the hazard, assess the risk, minimize risk and prepare for emergencies.