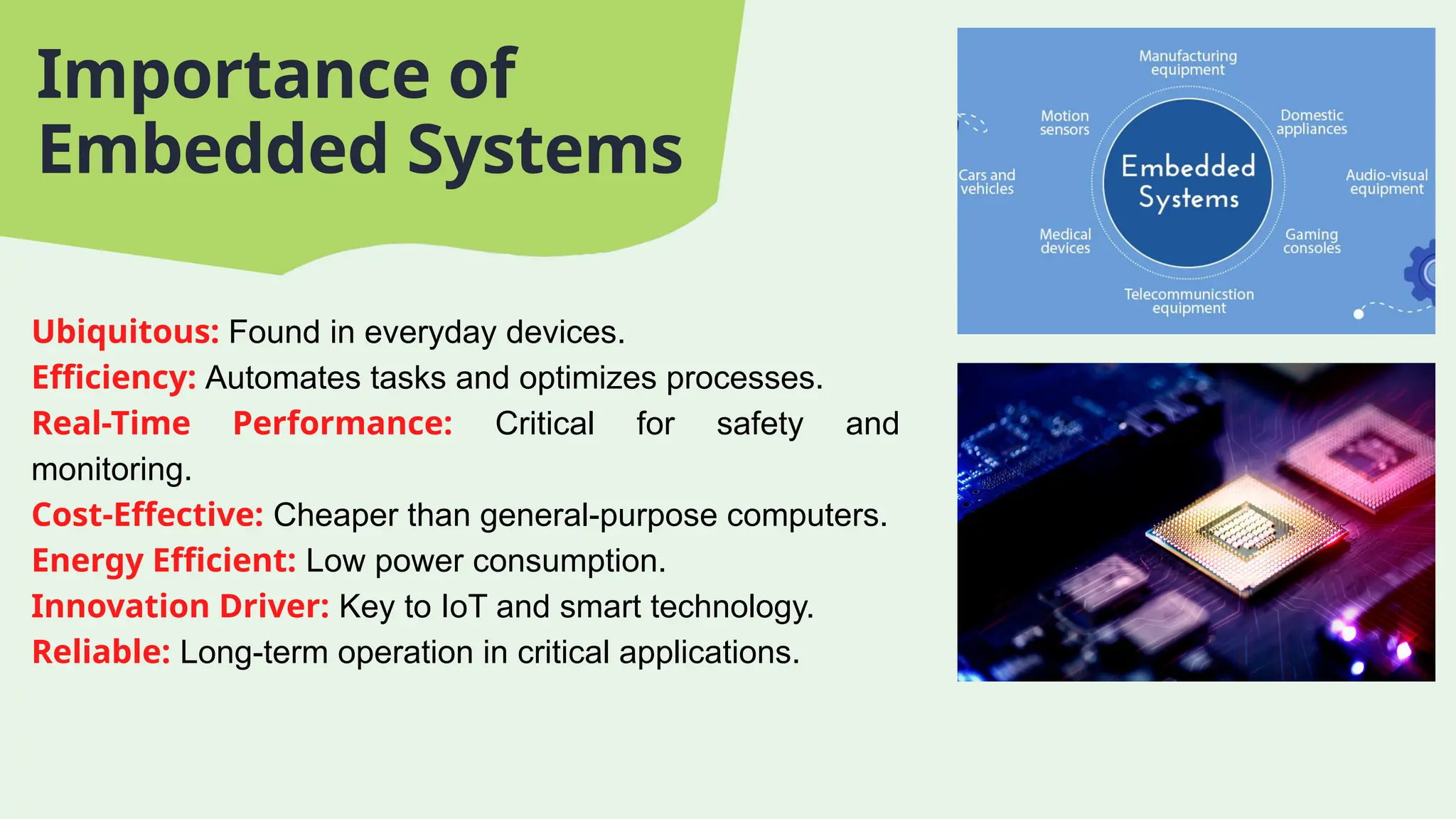
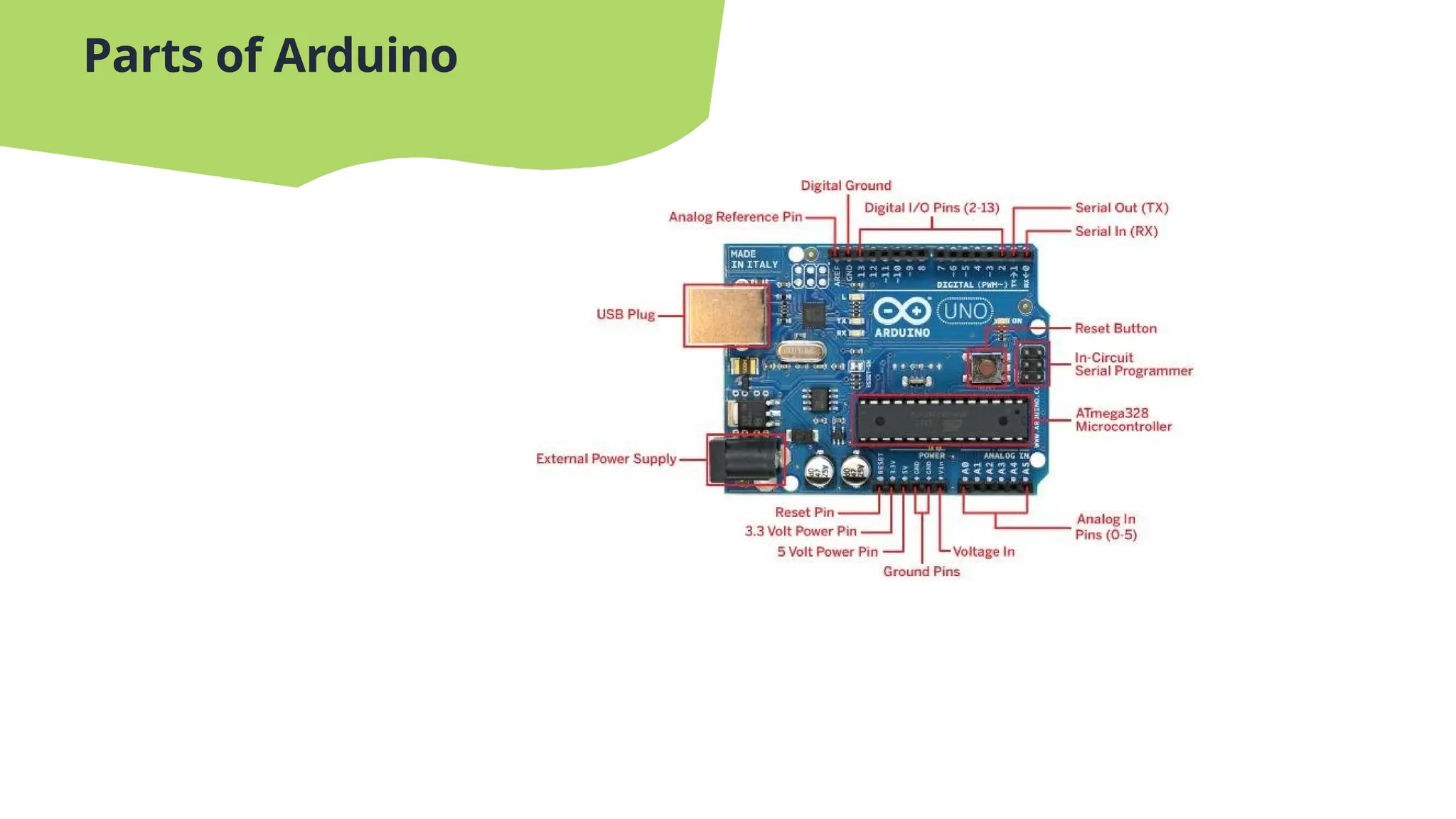
The document provides an introduction to embedded systems, highlighting their role as specialized computing systems designed for dedicated functions within larger systems. It explains the significance of microcontrollers, detailing their types and functionalities, and also introduces Arduino as an open-source platform for electronics projects. Key features of microcontrollers, such as performance, memory capacity, and energy efficiency, are discussed alongside specifications of the Atmega328P model.